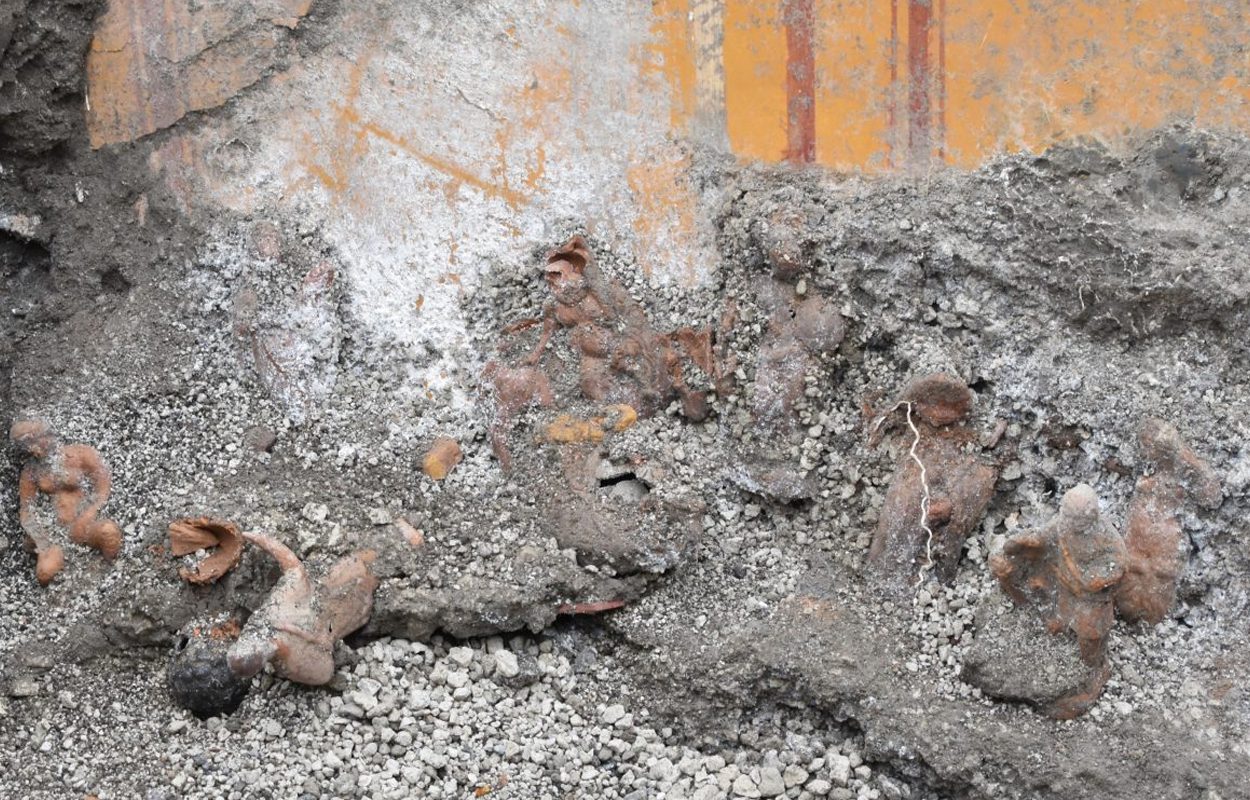
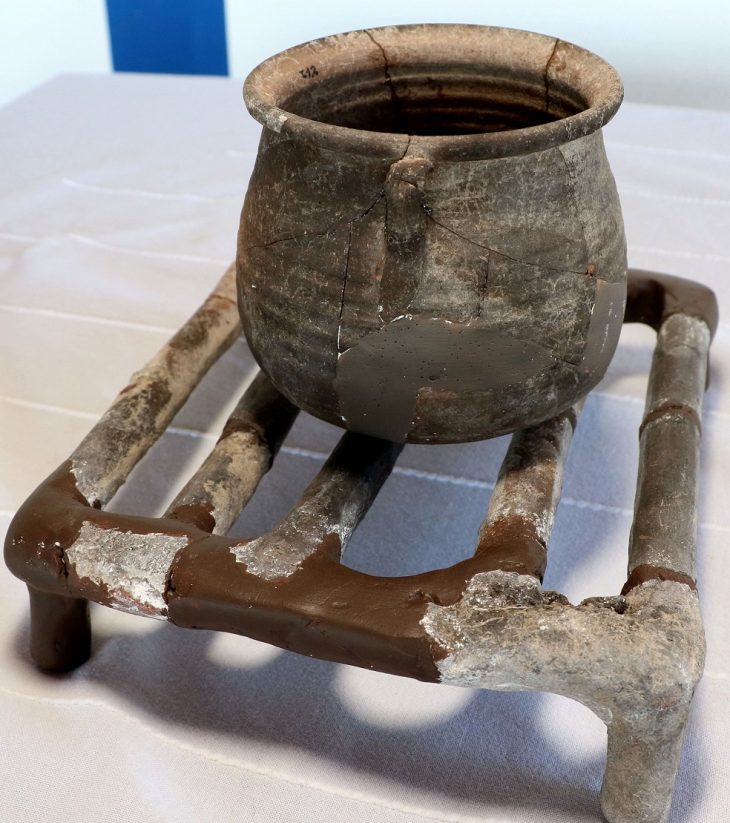
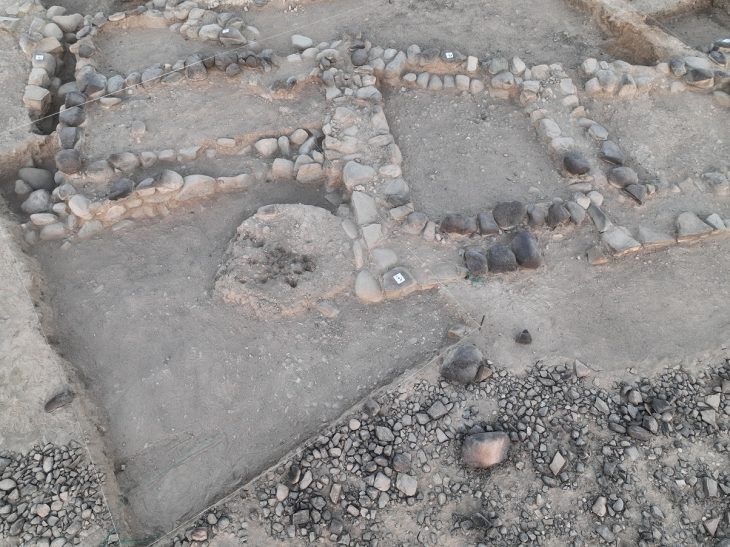
Archaeologists unearthed 13 terracotta figurines during recent excavations in the Domus adjacent to the “House of Leda and the Swan” along Via del Vesuvio in Pompeii.
The 13 clay figurines, approximately 15 centimeters high, were associated with the cult of the goddess Cybele. According to archaeologists, the figurines may be associated with Kybele and Attis, telling the story of the mother goddess’s tragic love for a mortal.
Attis was a handsome young man born in Phrygia. Cybele, also known as Kybele, was a powerful goddess associated with fertility, abundance, and nature. Attis became involved in a forbidden relationship with one of Cybele’s priestesses, which began to undermine his devotion to Cybele.
Cybele was furious at Attis’ betrayal, which drove her to a state of madness. In a fit of frenzy, Attis castrated himself in a moment of extreme anguish and eventually died. After his death, he was transformed into a pine tree.
Overwhelmed by grief, Cybele sought permission from Zeus to grant Attis immortality. Attis became revered as a symbol associated with Cybele and was celebrated as a representation of life after death, symbolizing the cycle of nature, loss, and rebirth.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
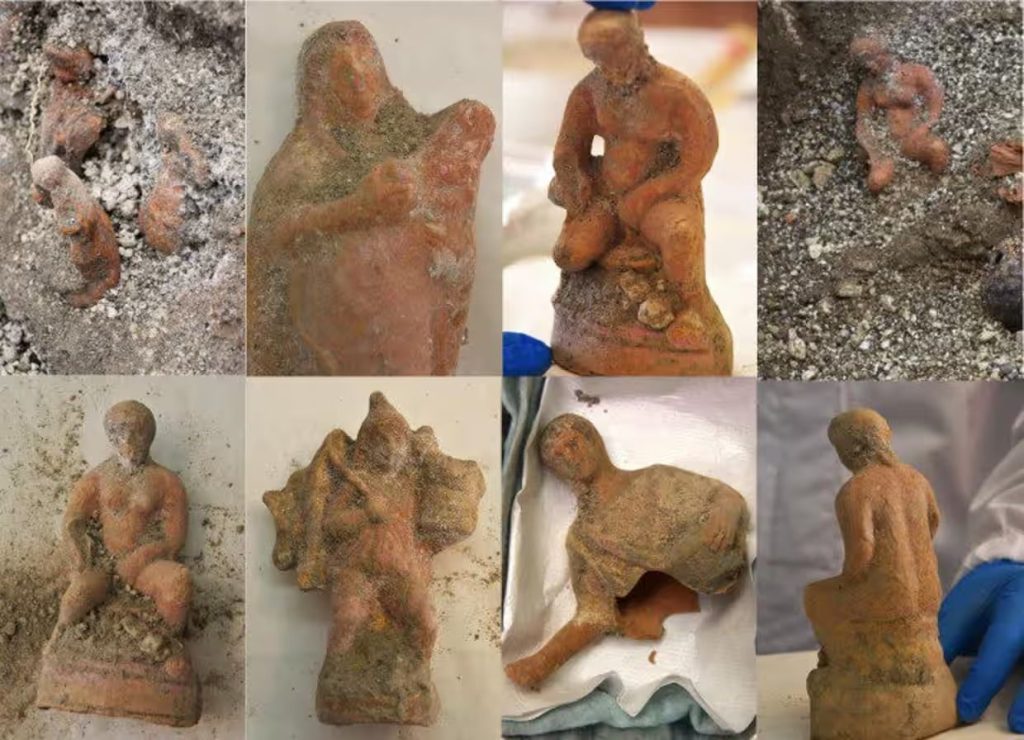

The miniature clay sculptures were found upright on a horizontal plane, probably on a shelf that once hung inside the home. Some statues were human figures, while others included a chicken head and a pine cone.
The statues found bear a striking resemblance to figures often found in Christmas nativity scenes.
‘Although the Christmas creche was obviously not a tradition in the pagan Roman city, experts believe the statues were arranged in a way that suggests they were part of an ancient ritual, ‘ archaeologists shared in the announcement.
The statues provide a glimpse at religious practices more than 2,000 years ago and ‘could potentially provide a new understanding of the influences and traditions that shaped early representations of nativity scenes,’ BNN reports.

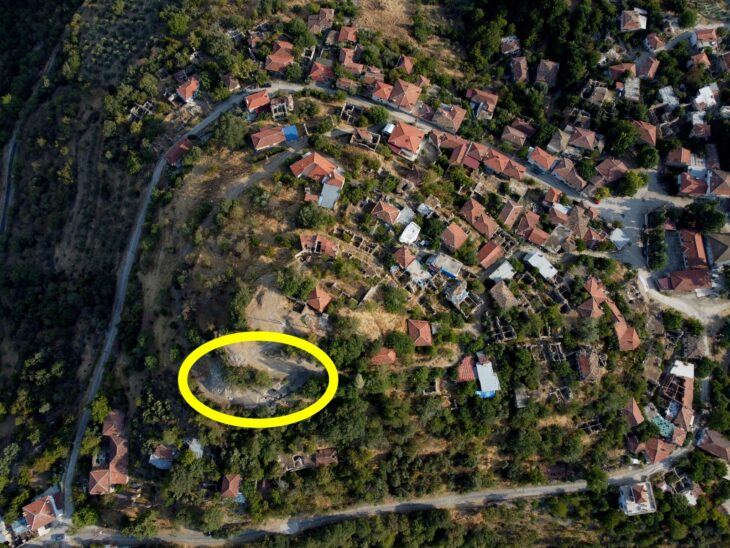
The sculptures were discovered near the House of Leda and the Swan, which gets its name from a sensual fresco depicting the Greek myth discovered in one of its rooms in 2019 and is currently undergoing excavation and restoration work. The Domus is believed to have belonged to a rich merchant who wanted to reflect his high level of culture by adorning his home with myth-inspired frescoes.
Pompeii, an ancient Roman city nestled near present-day Naples, Italy, gained monumental significance due to the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. This eruption engulfed the city in volcanic ash and preserved its remains for centuries, offering a poignant snapshot of life in antiquity.
Today, visitors wander through remarkably preserved streets, houses, temples, and theaters, providing a vivid glimpse into the daily routines and architectural grandeur of the Roman era. Pompeii’s compelling narrative of destruction and preservation continues to captivate global interest, serving as an immersive testament to both ancient history and natural calamity.
Cover Photo: Pompeiisites