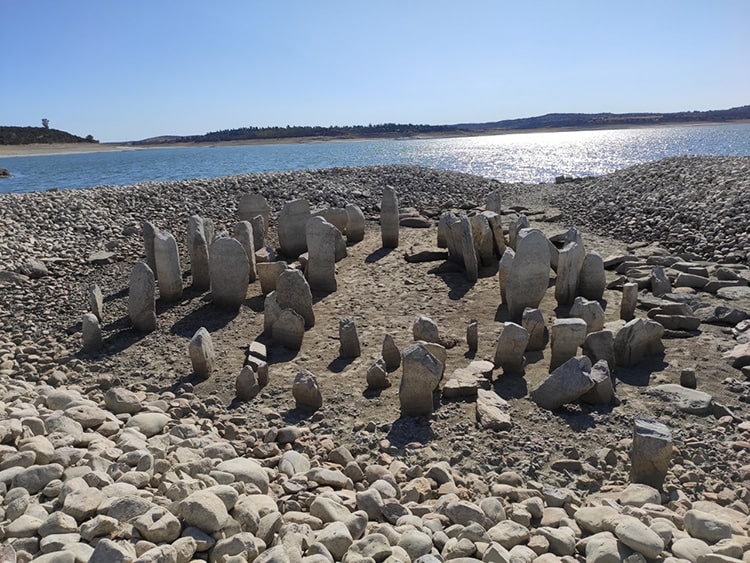
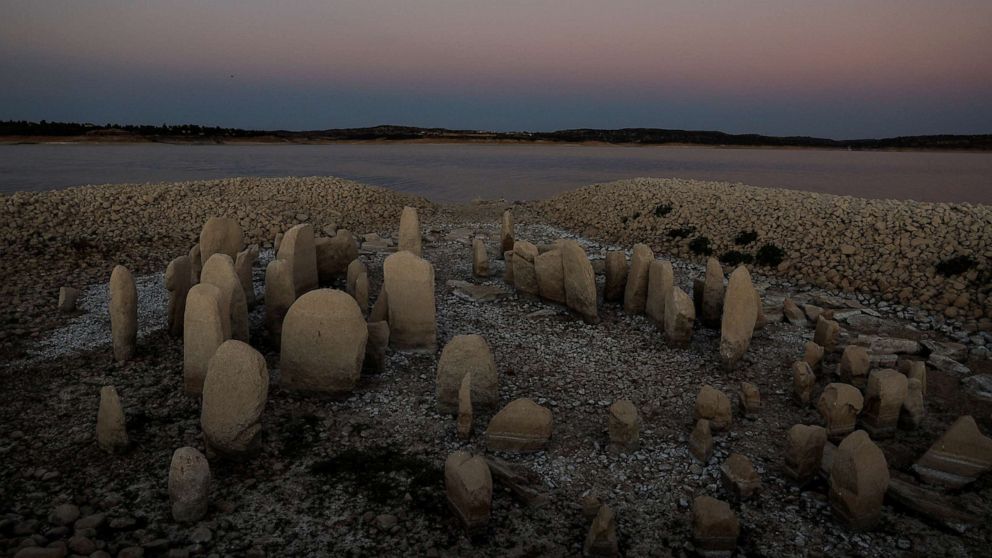
Submerged by the Valdecañas reservoir for decades, the Guadalperal dolmen has been fully exposed as it was two summers ago. The historical miracle, called the Spanish Stonehenge, has only been seen four times so far.
Experts believe that the stunning circle of dozens of megalithic stones, officially called the Guadalperal Dolmens, has existed since 5000 BC.
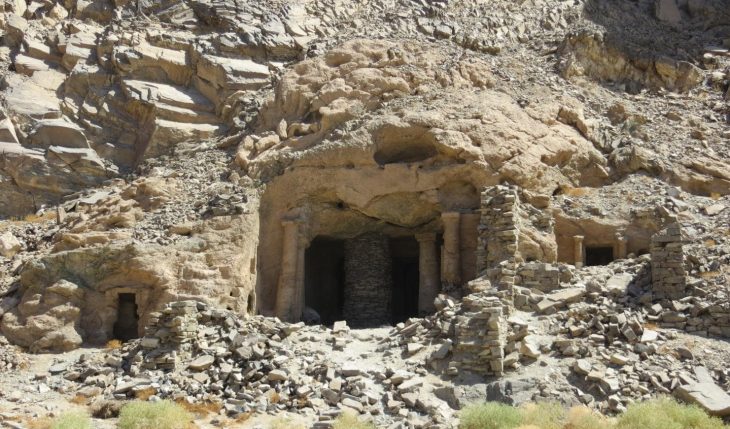
Buried for more than half a century under the waters of the Valdecañas reservoir (Cáceres), the Dolmen of Guadalperal emerged as a result of severe drought in Spain.
The water level in the reservoir has reportedly dropped to 28% capacity as Spain experiences its worst drought in 60 years, according to officials.
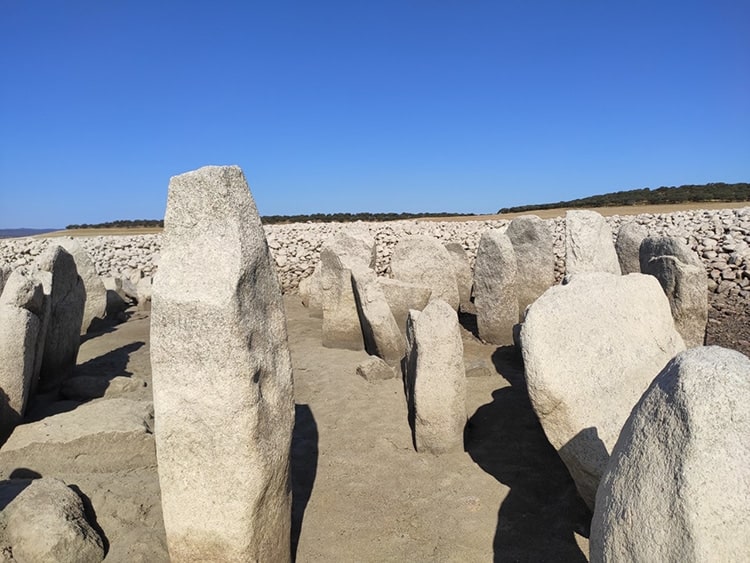
The Dolmen of Guadalperal is a collection of 150 large granite stones arranged in a circular structure guarded by a menhir (standing stone) carved with snake and cup motifs. The term “dolmen” refers to an ancient structure in which standing stones support a large capstone to form a chamber—a structure often used for early Neolithic tombs.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Dolmen of Guadalperal likely once had a mounded top, and the chamber inside may have functioned as a tomb, a religious site, or a trading post along the Tagus River in southeastern Spain.
This ancient site was first discovered by German archaeologist Hugo Obermaier in 1926 before it became flooded in 1963 due to a rural development project under Francisco Franco’s dictatorship.
This ancient site was first discovered by German archaeologist Hugo Obermaier in 1926. In 1963, under the rule of Francisco Franco, the government flooded the area containing the Dolmen to create the Valdecañas Reservoir.
Until the last drought that hit Europe in the summer of 2019, only the tips of the largest megaliths were visible above the waterline, and this year we were able to see them again. With record low water levels, the Dolmen emerged in full.

According to a study published in the journal Nature Geoscience, the Iberian peninsula where the dolman lives is at its driest point in 1,200 years, and winter rains are predicted to become even less frequent.
More than 45,000 signatures were collected in 2019 for the relocation of the structure.
Cover Photo: The Dolmen of Guadalperal, known as the “Spanish Stonehenge.” (Photo: Pleonr via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0)