A Roman road network spanning across Devon and Cornwall has been discovered by the University of Exeter archaeologists.
A Roman road network that spanned Devon and Cornwall and connected significant settlements with military forts across the two counties as well as wider Britannia has been discovered for the first time.
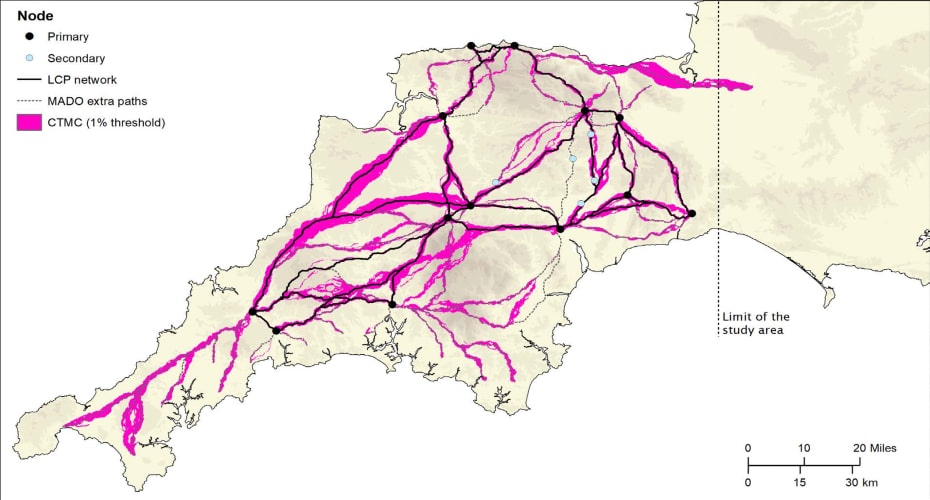
Archaeologists have used laser scans to identify new sections of road west of the previously understood boundary. Using sophisticated geographical modelling techniques, which incorporate information around gradients and flood risk, the researchers have then been able to map out the full extent of the network and begin to understand the rationale for its existence.
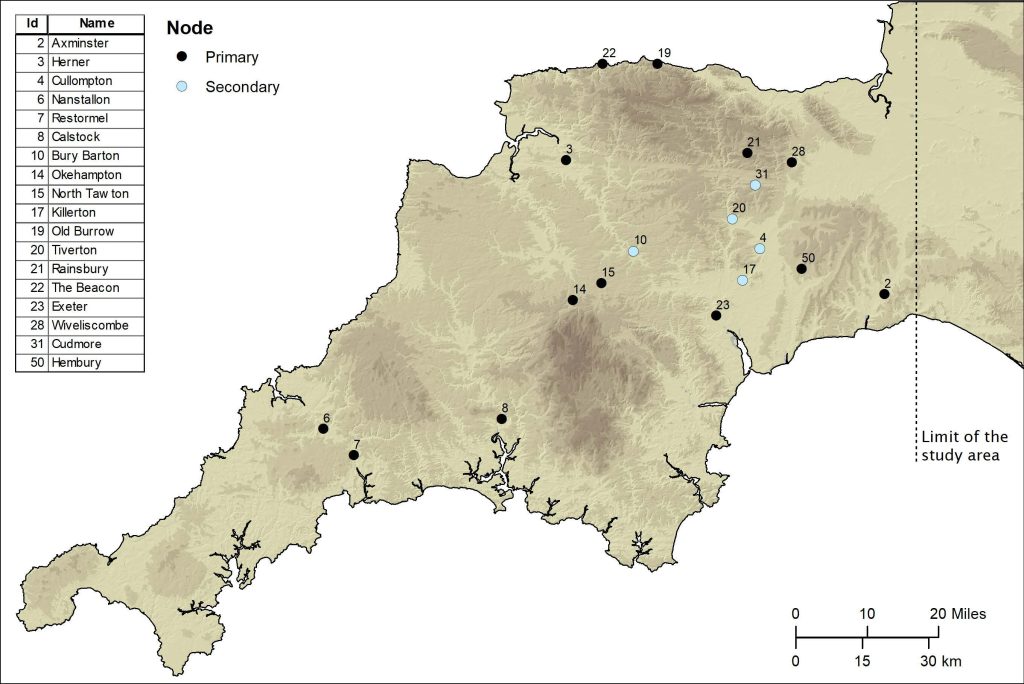
Among the things it reveals is that far from Exeter being the main nerve centre of the network, it was North Tawton that supported strategically vital connections with tidal estuaries north and south of Bodmin and Dartmoor.
These findings are explored in Remote Sensing and GIS Modelling of Roman Roads in South West Britain, which has been published in the Journal of Computer Applications in Archaeology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research was led by Dr Christopher Smart and Dr Joao Fonte, specialists in landscape archaeology and the heritage of the Roman Empire, in Exeter’s Department of Archaeology and History.
“Despite more than 70 years of scholarship, published maps of the Roman road network in southern Britain have remained largely unchanged and all are consistent in showing that west of Exeter, Roman Isca, there was little solid evidence for a system of long-distance roads,” said Dr Smart.
“But the recent availability of seamless LiDAR coverage for Britain has provided the means to transform our understanding of the Roman road network that developed within the province, and nowhere more so than in the far south western counties, in the territory of the Dumnonii.”
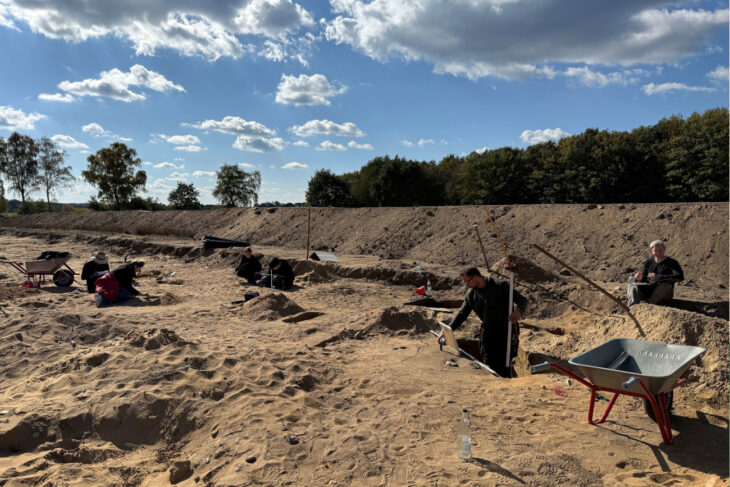
The National LiDAR Programme was conducted between 2016 and 2022 by the Environment Agency covering the whole of England. It transformed the amount of terrain mapped of Devon and Cornwall, which had previously stood at just 11%. The Exeter team studied the scans and together they were able to map around 100km of additional roads.
Although this represented a significant advancement, the overall picture remained fragmented and patchy, with large portions of the map showing no evidence of Roman roads. The team developed a geographic information system predictive model, which could intelligently fill in the gaps as to the likely layout of the network.
They plotted primary and secondary “nodes” across the two counties, which included permanent military fortifications, including the known forts of Old Burrow and The Beacon at Martinhoe, as well as the settlements at Exeter and North Tawton. They then calculated the easiest routes between these points.
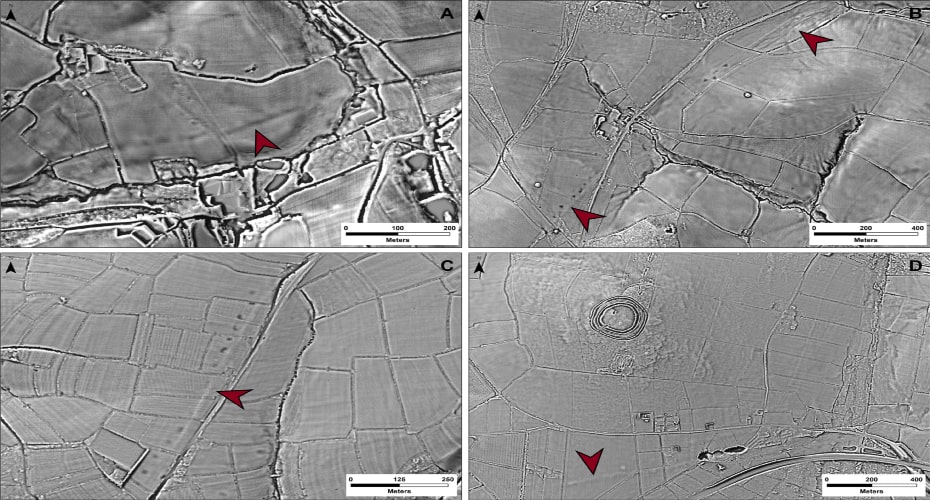

And when the team returned to the LiDAR scans, they were able to identify a further 13km of Roman road within a short distance predicted by the model.
The final stage saw the researchers use focal mobility networks and transit corridors to extend the road network to areas that lay beyond the main Roman sites known in the region.
“In terms of chronology, it is likely that the proposed network is an amalgam of pre-existing Prehistoric routeways, Roman military campaign roads or ‘tactical roads’ formally adopted into the provincial communications system, and of those constructed during peacetime in a wholly civilian context,” said Dr Fonte.
“This evolutionary model is supported by the fact that the network does not solely connect Roman forts and their hinterlands directly, which are often connected by branch roads, but instead appears to serve a broader purpose than required by military supply.”
The research concludes that the main rationale for the network was to facilitate animal-drawn vehicles and circumvent those areas where flooding was possible. It could also influence, say the authors, future archaeological research in the region.