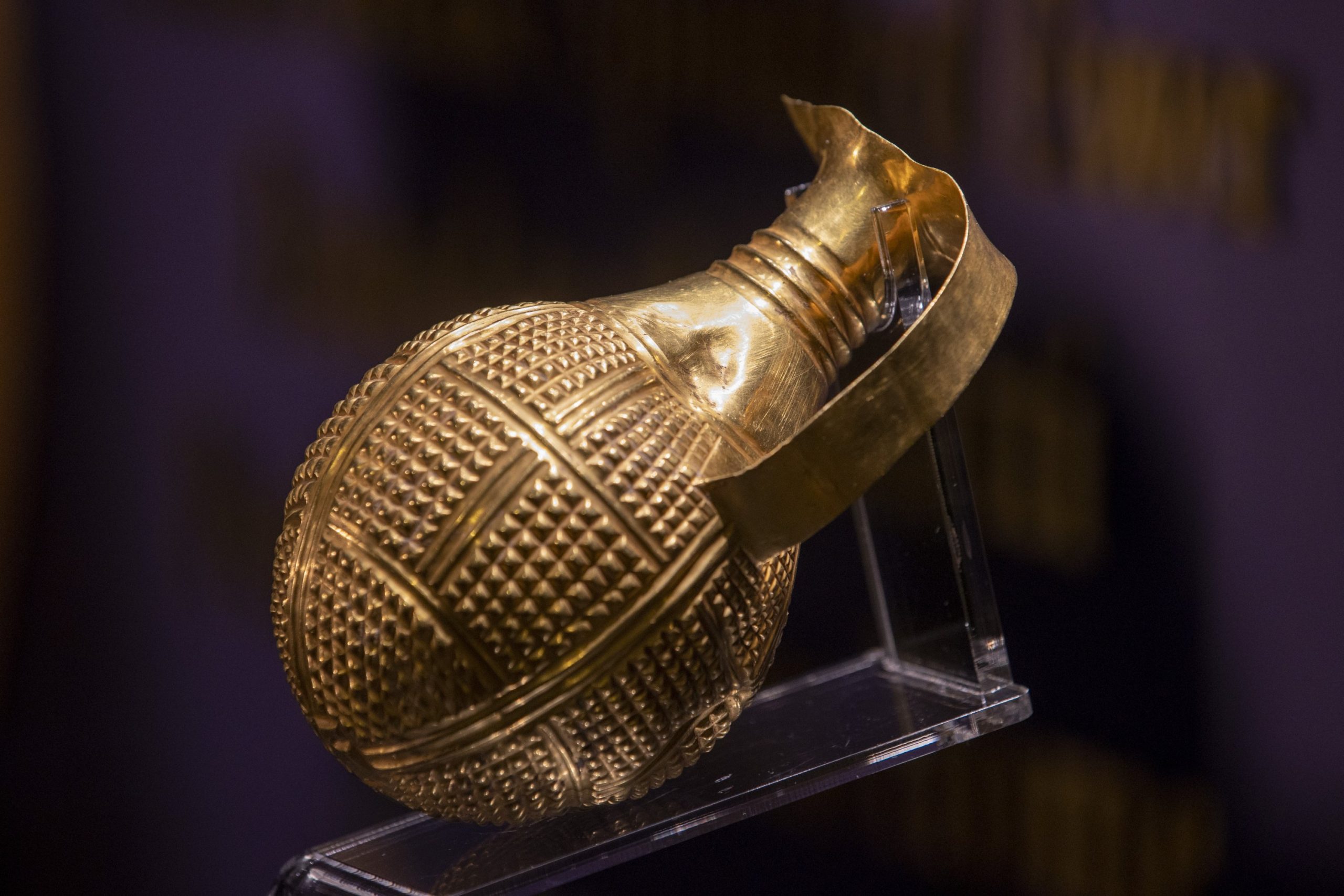
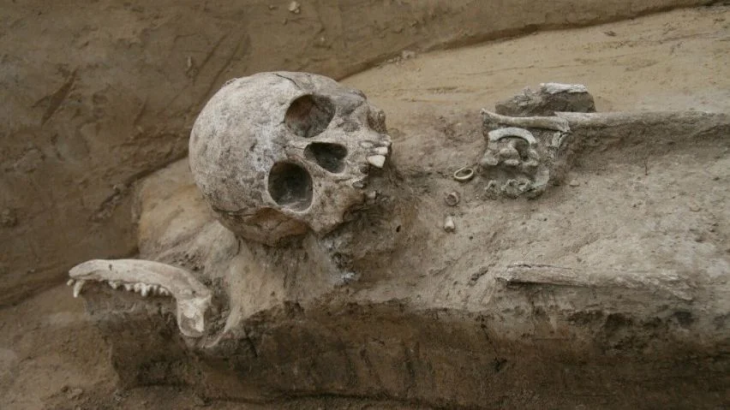
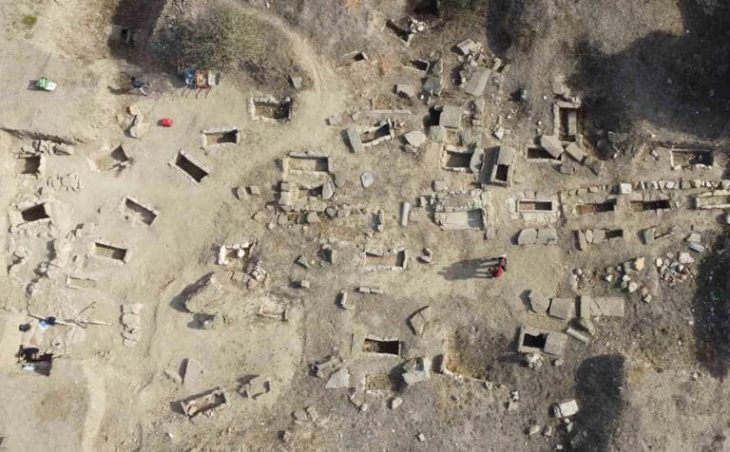
The 4,250-year-old golden beak-spouted ewer was returned to the Anatolian Civilizations Museum by the Gilbert Art Foundation.
Culture and Tourism Minister Mehmet Nuri Ersoy attended the ceremony held at the Ankara Anatolian Civilizations Museum on the return of the golden beak-spouted ewer from England to Turkey.
Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy said in a statement, “This cultural heritage returned to the land it belongs to.”
The identification came from the General Directorate of Museums and Cultural Heritage’s department of anti-smuggling. It was found that the ewer was purchased by art collector Arthur Gilbert from Los Angeles in 1989 to add to his collection of gold and silver artifacts and was loaned to the Victoria-Albert Museum in London. The Gilbert Art Foundation, founded by Arthur Gilbert, was contacted for the return of the artifact, which was found to have been illegally obtained from excavations and smuggled out of Anatolia.
Gilbert Art Foundation officials reported having no knowledge of illegal ties when the artifact was received.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
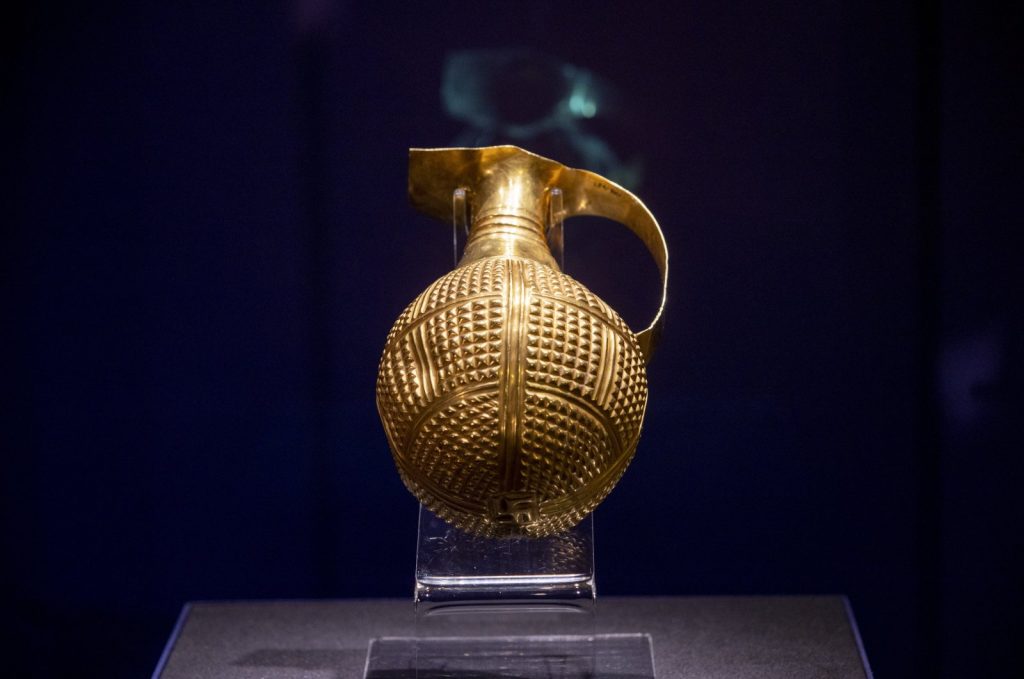

In cooperation with the foundation, ministry experts were able to compare it with similar artifacts, confirmed that the piece was dated to the Hatti period, and notified the foundation. The foundation shared the results of the chemical analysis of the metal components of the work with the ministry. It was determined that the beak-spouted ewer was closely related to other artifacts found in the archaeological excavations in Alacahöyük and Mahmatlar, and similar examples were found during the archaeological excavations of the Hatti settlement in Çorum and Amasya. Finally, the ewer, which is thought to have been used for drinking during holy ceremonies by distinguished rulers, was returned to its homeland.
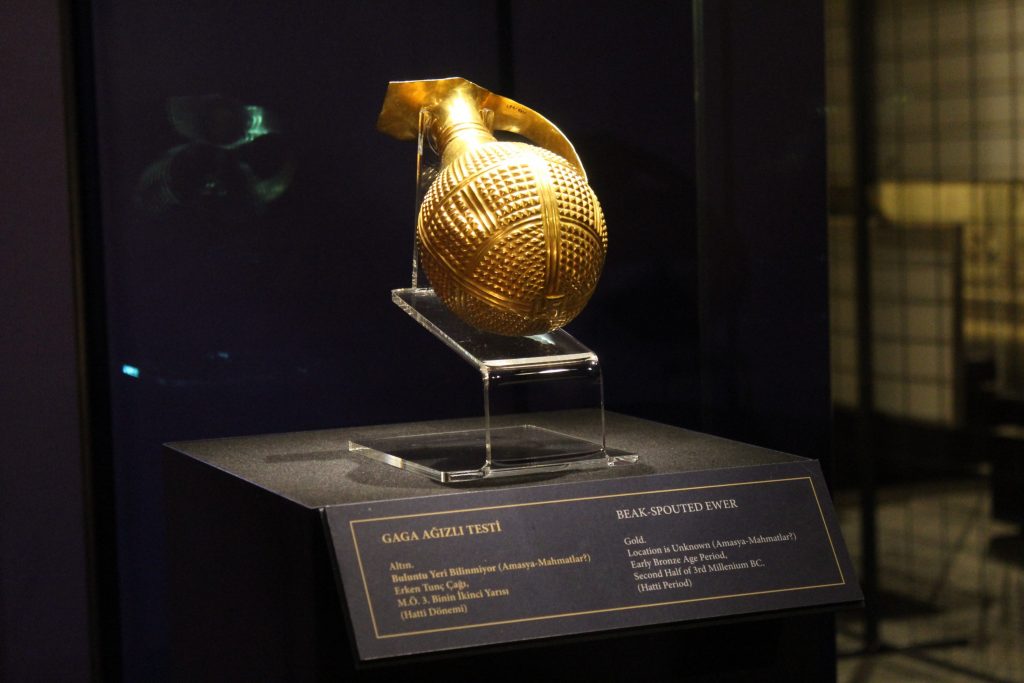

Providing additional information on the return process of the artifact, Minister Ersoy said: “Comparisons of the metal component data related to the artifact were made by the experts of Ankara Restoration and Conservation Regional Laboratory affiliated to our ministry. The results were also confirmed by mining expert Professor Ünsal Yalçın, an academician of Bochum University.”
“After our correspondence, we found the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations to be the right address for the exhibition and preservation of this piece, due to its magnificent Hatti collection,” said Minister Ersoy.
Also explaining that the ceremonial nature of the beak-spouted ewer can be understood from the craftsmanship of the work, he added, “This artifact, which was presumably placed on the ground as a grave gift, was taken out of its context by unidentified people.”
Minister Ersoy concluded by saying: “I believe that our people have made the greatest contribution to the protection of cultural assets. We should all protect these efforts from damage. It is important to retrieve our cultural assets that are abroad; however, the end of these incidents will only come with the protection of our cultural assets in the country. Let’s not forget that this protection is also a service to our country, science and humanity.”