Due to their interactions and conflicts with the major contemporaries of Eurasia, the Scythians enjoyed legendary status in history and popular culture.
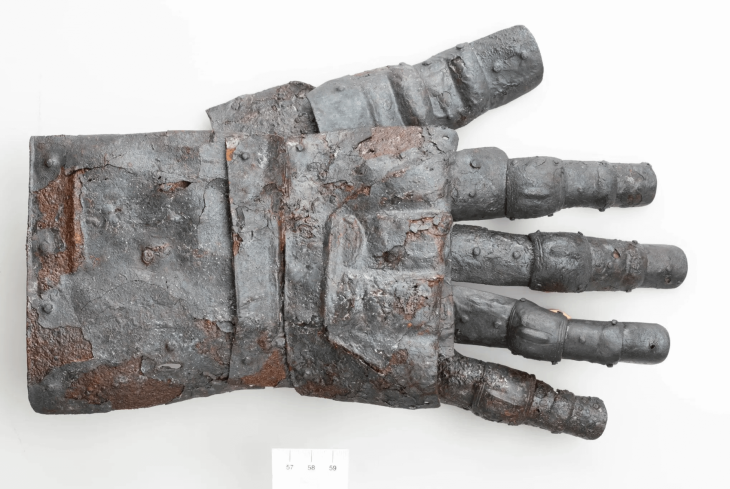
The Scythians were the Iron Age cultures that ruled the Eurasian steppes, playing an important role in Eurasian history. Despite evidence from external sources, little is known about the history of the Scythians. Without written language or direct sources, the language or languages they used, where they came from, and the extent to which the different cultures spreading over such a vast area were actually related to each other remain unclear.
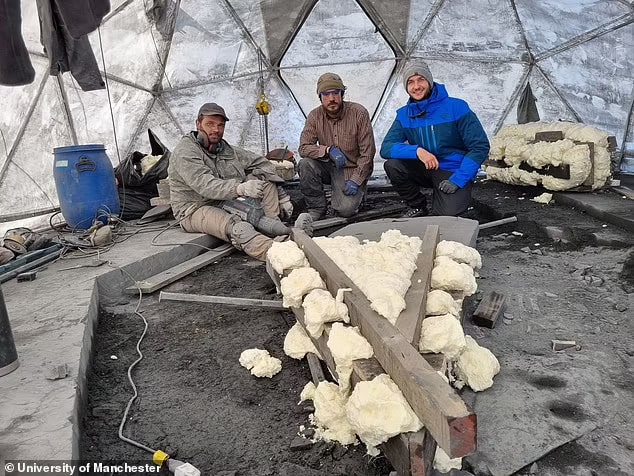
A new study published in Science Advances by an international team of geneticists, anthropologists and archaeologists led by scientists from the Department of Archaeogenetics of the Institute of Human History Max Planck in Jena, Germany helps illuminate the history of the Scythians with 111 ancient genomes from key Scythian and non-Scythian archaeological cultures of the Central Asian steppe.
The results of this study reveal that significant genetic changes were associated with the disappearance of long-term sedentary Bronze Age groups and the rise of Scythian nomadic cultures during the Iron Age. The findings show that, in keeping with the relatively homogeneous origin of the Late Bronze Age shepherds, at the turn of the first millennium BC, flows from the east, west, and south to the steppe created new mixed gene pools.
The diverse peoples of the Central Asian Steppe
The research went even further, identifying at least two main sources for nomadic Iron Age groups. The source in the east may come from the population of the Altai Mountains. During the Iron Age, the Altai Mountains spread west and south and mixed together as they moved.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
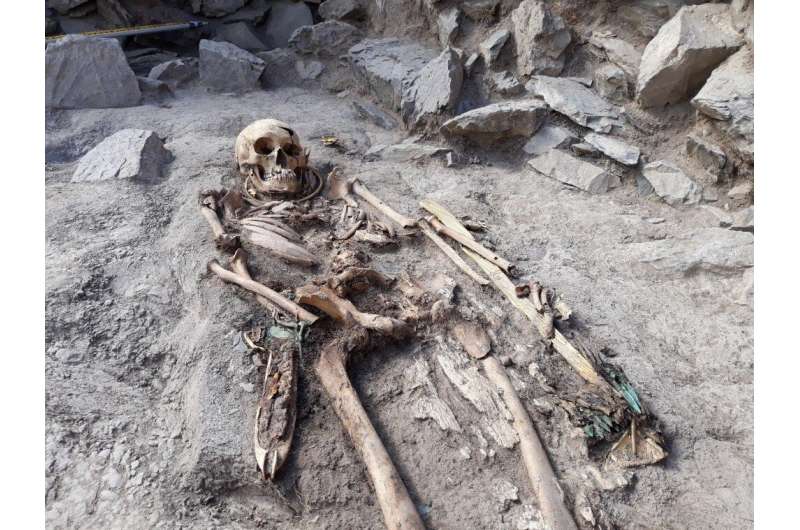

These genetic results coincide with the time and locations found in the archaeological record and suggest an expansion of the populations of the Altai area, where the first Scythian burials are found, connecting different renowned cultures such as Saka, Tasmola, and Pazyryk that are found in the south. , Central and eastern Kazakhstan respectively.
Surprisingly, the groups located in the western Urals come from a second separate but simultaneous source. Contrary to the Eastern case, this Western gene pool, characteristic of the early Sauroman-Sarmatian cultures, remained largely consistent thanks to the spread of Sarmatian cultures westward from the Urals to the Pontic-Caspian steppe.
The decline of the Scythian cultures associated with new genetic turnovers
The study also covers the transition period after the Iron Age, revealing new genetic renewal and mixed events. These events intensified at the beginning of the first millennium AD, while at the same time, the Scythian cultures on the central grassland declined and then disappeared.
In this case, the new influx of Eurasia from the Far East is plausibly associated with the expansion of the nomadic empires of the eastern steppe in the early centuries CE, such as the Xiongnu and Xianbei confederations, as well as minor influxes from Iranian sources probably linked to the expansion of civilization related to the Persians from the south.
Although ancient DNA alone cannot solve many unanswered questions about the history of the Scythians people, this study shows how much change and integration of the population of Eurasia have occurred over time.