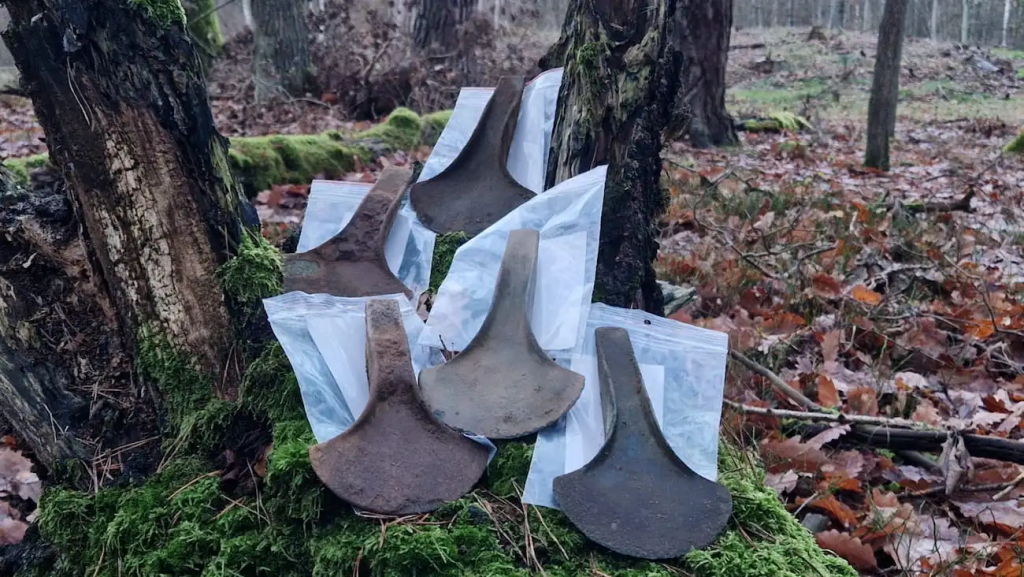
Archaeologists in Poland have discovered five Bronze Age axes in Starogard Forest District, located in Kociewie.
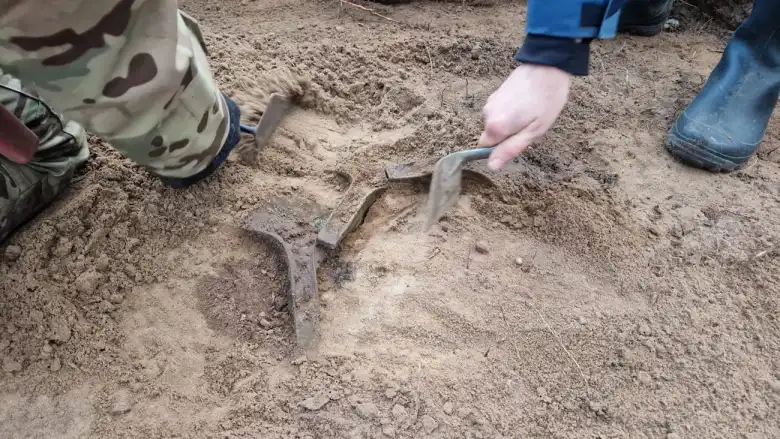
A metal detectorist named Denis Konkol was exploring the forests of Kociewie when he came across five bronze axes buried just below the surface of the soil.
The discovery date from between 1700 and 1300 BC according to Igor Strzok, the Pomeranian Provincial Conservator of Monuments.
In Poland, it is illegal to conduct an amateur search for artifacts using a metal detector, whether for commercial or personal purposes, unless licensed by local authorities, and all finds must be reported.
Kociewie is a region of forests and farmland in northern Poland. Denis Konkol had obtained the proper permits to conduct a metal detecting survey in the area. When he discovered the axes, he promptly reported his find to the local officials in charge of protecting archaeological sites.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Igor Strzok, Pomeranian provincial conservator of monuments, said: “The extraction of these finds took place under the archaeological supervision of our colleagues from the Provincial Office for the Protection of Monuments. This means that we prevented possible destruction of the site.”
Under a layer of dirt and grass, they discovered the five axes buried together in a shallow pit 20 to 30 centimeters below ground. Strzok said artifacts from this time period are rarely uncovered in this region, making this an especially unique find.
Igor Strzok suggested a potential connection to a Baltic culture originating from contemporary Lithuania or northeastern Poland, specifically categorizing the axes as the tautušiai type.
Characterized by their substantial size, the axes comprised a slender handle with elevated edges and a broad blade.
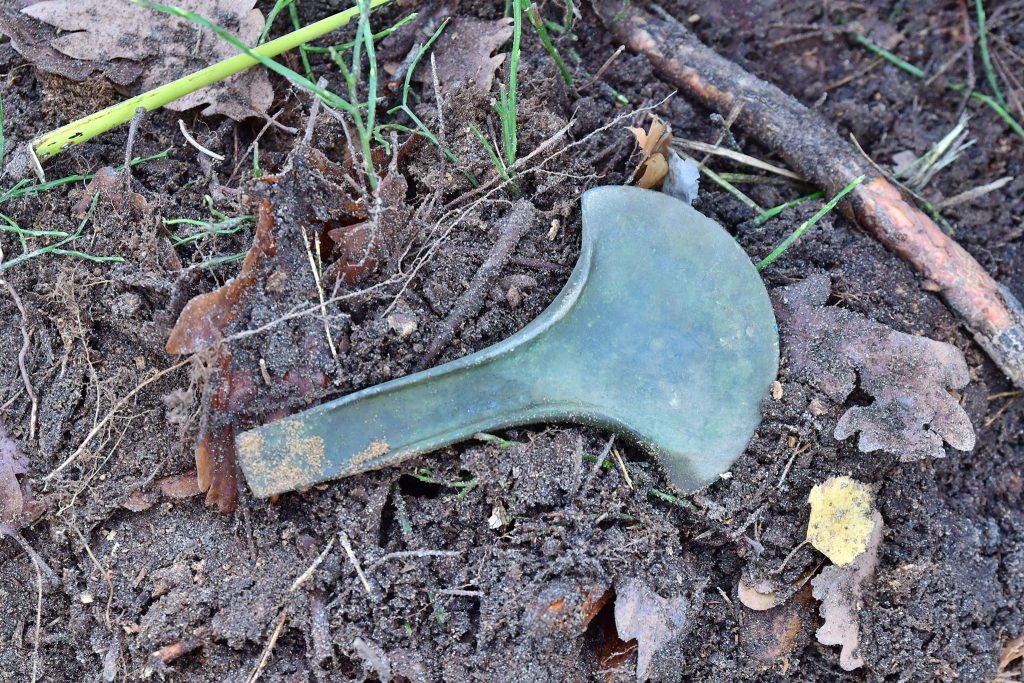

The axes were examined by Piotr Klimaszewski, the head of the Archaeological Monuments Department, and he believes they were part of a ritual deposit or offering, possibly related to trade or the religion practiced by Bronze Age peoples in this area.
The discovery sheds new light on the cultures that flourished in Poland over 3,000 years ago. Similar lone bronze axes from this period have been found before, but never a group of five artifacts buried together.
Strzok said the last comparable find was about 20 years ago in the Lublin area. Traditionally, Bronze Age deposits in the region yielded predominantly bracelets or breastplates, making the discovery of these axe heads a distinctive archaeological marvel, according to Strzok.
The five Bronze Age axes will be transported to the Archaeological Museum in Gdańsk for further study and preservation in the coming days.
Cover Photo: Nadleśnictwo Starogard