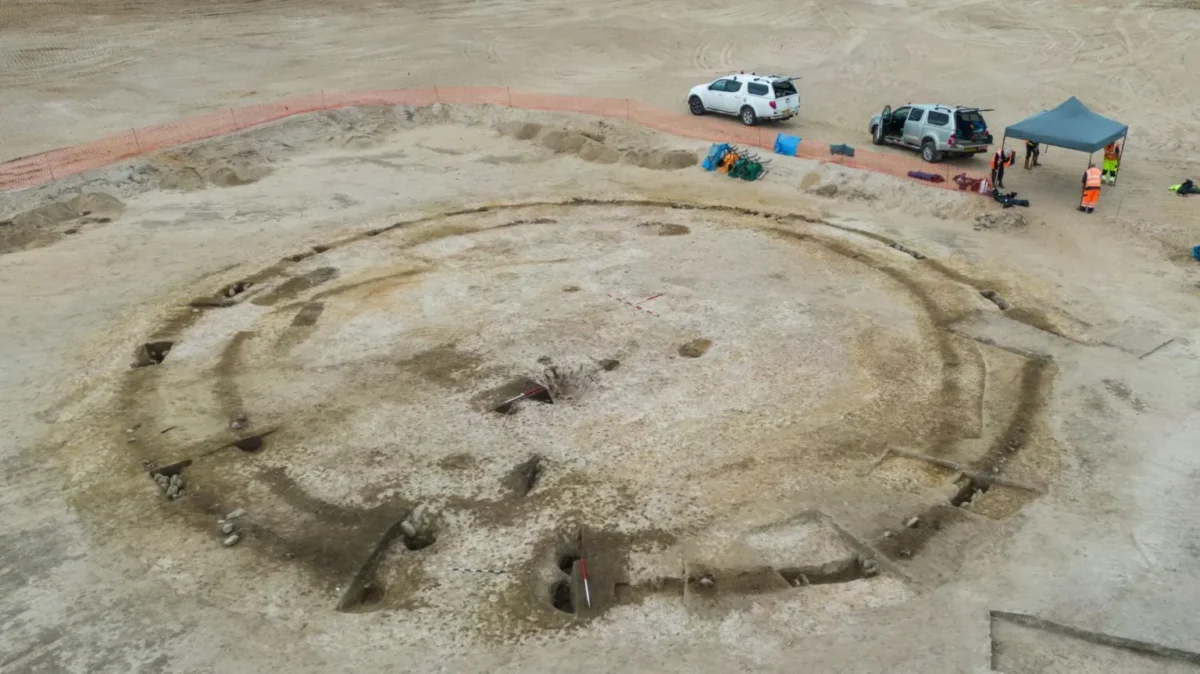
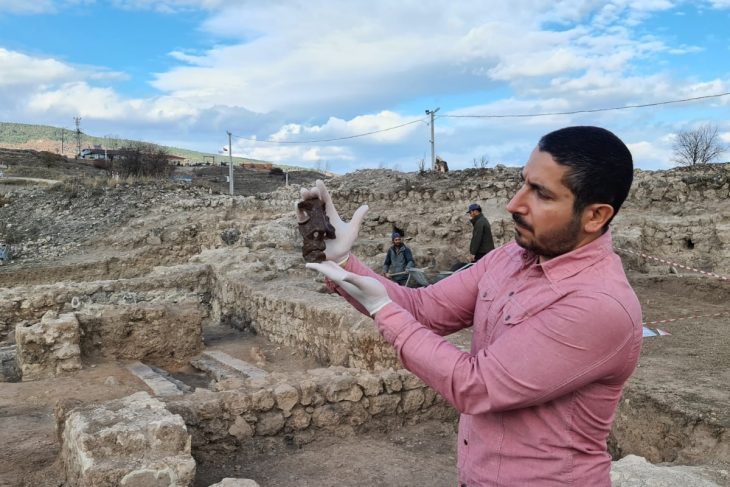
Archaeologists have discovered a rare prehistoric chariot wheel at the site of a future golf course near Inverness. The discovery sheds light on ancient ceremonial practices and the lives of those who inhabited the Highlands thousands of years ago.
This extraordinary discovery, unearthed during the excavations for the Old Petty Championship Golf Course, underscores the profound historical significance of the region and beautifully intertwines the threads of modern development with the echoes of its ancient past.
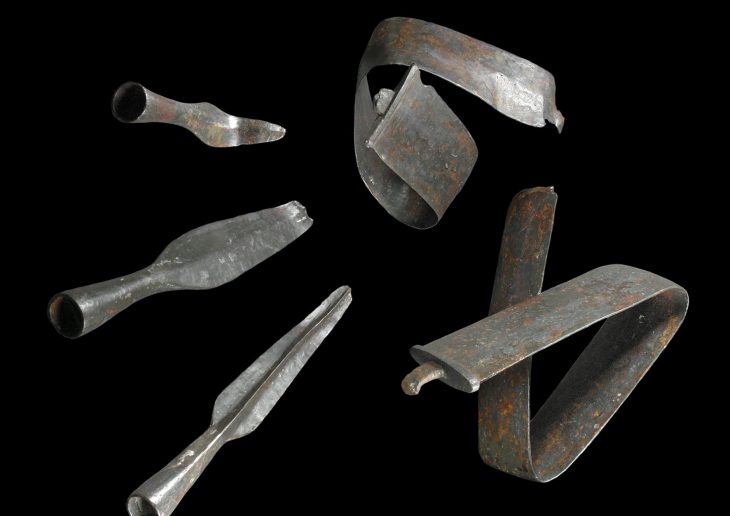
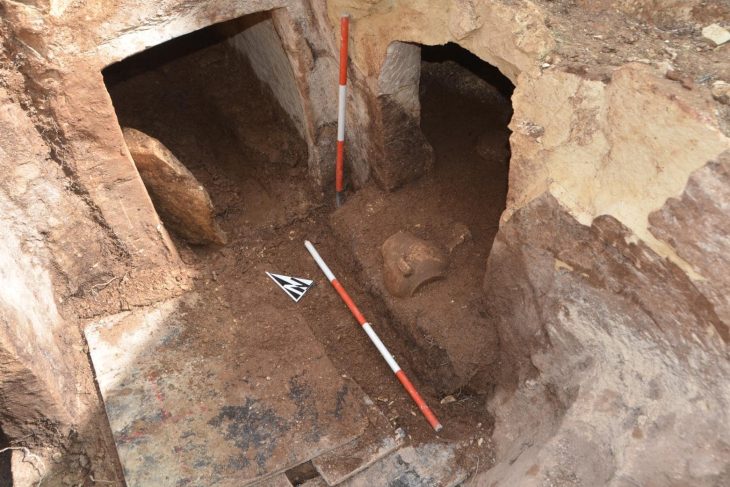
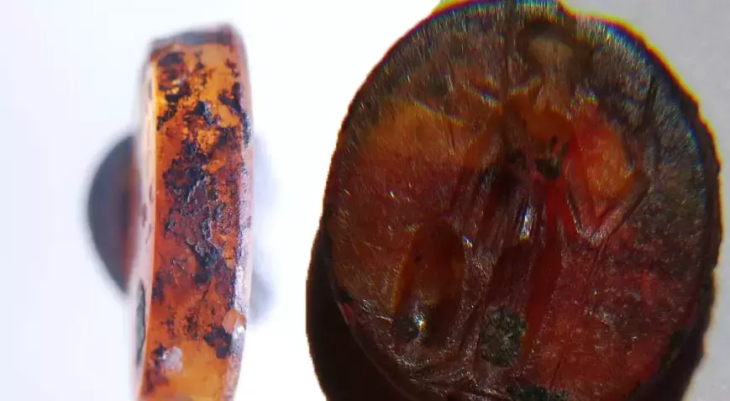
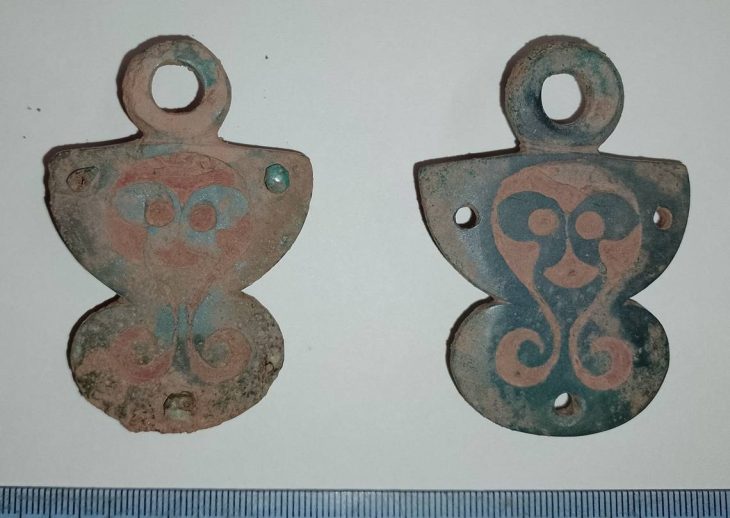
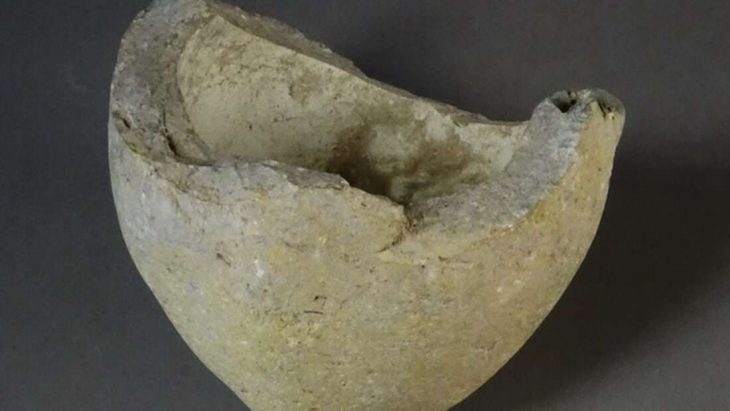
The chariot wheel was discovered in a cremation burial pit, believed to date back thousands of years. Alongside this significant find, archaeologists also unearthed a 3,500-year-old Bronze Age cremation urn, flint tools, quern stones, and evidence of at least 25 Neolithic wooden buildings. These artifacts collectively paint a vivid picture of life in the Highlands from approximately 6,000 years ago through to the Middle Ages.
Andy Young, Principal Archaeologist at Avon Archaeology Highland, emphasized the importance of the chariot wheel, stating, “They are such a rare thing. None of us had really seen one before in terms of physically excavating one.” Initially, Young was skeptical about the find, mistaking it for a more modern piece of equipment. However, further investigation revealed its historical significance, marking it as potentially the first chariot component discovered in the Highlands and one of only five known in Scotland.

The excavation site, which is being developed into a championship golf course by Cabot, has been a treasure trove of historical artifacts. The discoveries not only highlight the ceremonial practices of ancient peoples but also their agricultural innovations. Stuart McColm, Vice-President of Golf Development at Cabot, expressed pride in the project, stating, “It’s humbling to think that our new championship course, Old Petty, will rest on such historically rich ground.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
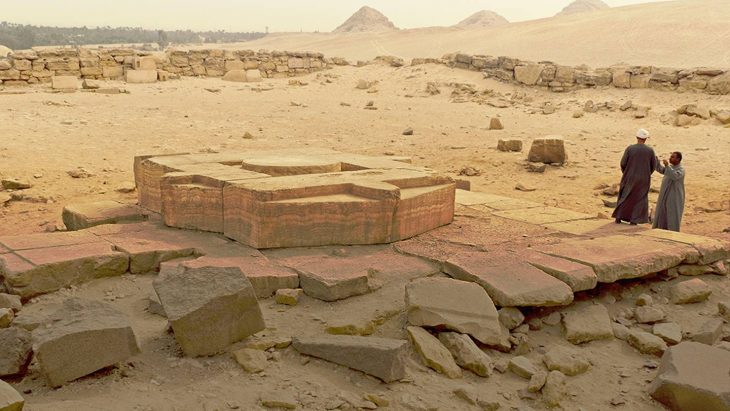
In accordance with Scottish archaeological best practices, efforts are being made to preserve key features of the site, including a prehistoric ceremonial circle, which has been carefully reburied in its original location. The collaboration between Cabot and Avon Archaeology Highland has been praised as a model for responsible development, balancing the preservation of heritage with modern construction.
The findings from the excavation will be meticulously documented and radiocarbon dated, with final reports expected to coincide with the official opening of the golf course in 2025. The artifacts will eventually be handed over to museums in Inverness and Edinburgh, ensuring that this glimpse into the past is preserved for future generations.
As the Old Petty Championship Golf Course takes shape, it stands as a testament to the rich history of the Highlands, inviting both golf enthusiasts and history buffs to appreciate the ancient stories that lie beneath the surface.
Cover Image Credit: Area PS5 Prehistoric palisade enclosure. Credit: Avon Archaeology Highland / SWNS