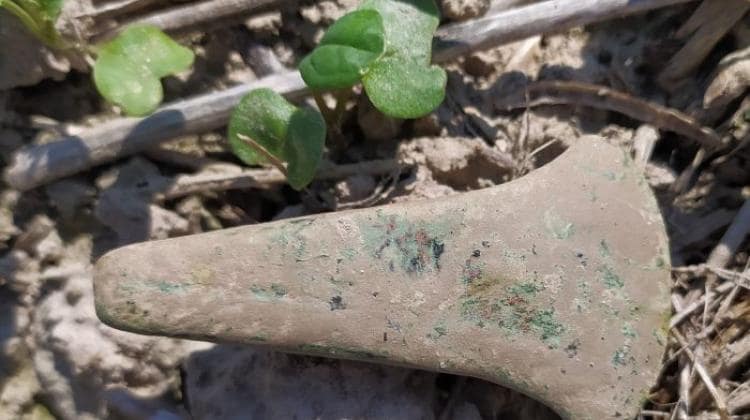
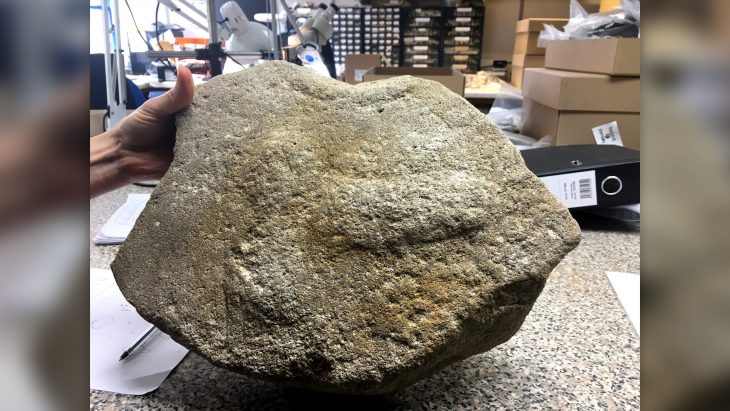
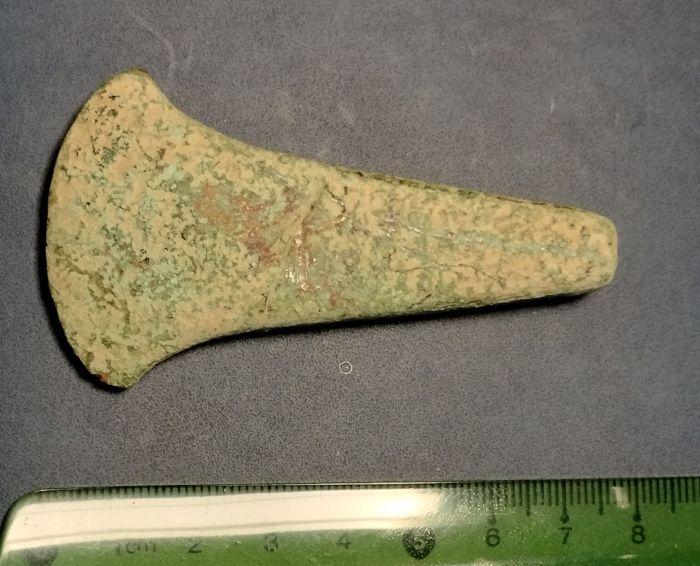
A copper axe from the 4th to 3rd millennium BC identified with the Trypillia culture was found in the Horodło municipality in the Hrubieszów district.
An axe discovered in the Hrubieszów district, identified with the Trypillia culture, is most likely the oldest find of a copper product in Poland informed the Lublin Provincial Conservator of Monuments.
The Lublin Provincial Conservator of Monuments has described the valuable relic as being 7.4 cm in length, with a wide fan-shaped blade 4.1 cm wide, and a rectangular convex head measuring 0.9 cm x 0.6 cm.
The Cucuteni-Trypillia culture was one of the most important in South-Eastern Europe. It originated as a result of interactions between different Neolithic groups in the Carpathian-Balkan region during the second half of the sixth millennium BCE.
The fact that the ax appeared in eastern Poland is surprising because the territorial scope of the Trypillian culture covered the areas of today’s Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, and western Ukraine.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Analyzing the find in terms of its chronological and cultural affiliation, the archaeologist from the Zamość delegation of the Voivodeship Office for the Protection of Historical Monuments, Wiesław Koman, sought the assistance of Professor Elżbieta Kłosińska from the Institute of Archaeology of the Maria Curie-Skłodowska University in Lublin. The specialist ruled out that the presented axe belonged to Bronze Age cultures, as the artifact in no way corresponded to the known and already fairly well-recognized typologies of axes from that period.
“In addition, our ax was made in a quite simple ‘primitive’ casting method, in a flat-convex form, no longer used in the developed metallurgy of the Bronze Age. Therefore, it was necessary to pay attention to the earlier Neolithic era. Unfortunately, in the inventories of Neolithic cultures from Poland there is no such equivalent,” the Lublin Conservator reported on social media.
The puzzle was solved by turning to archaeological finds from within Ukraine. “Wiesław Koman came across the publication of an identical find of a copper axe discovered in the village of Shcherbanivka in the Kyiv region, where the accompanying fragments of vascular pottery made it possible to attribute it to the Trypillia culture and date it to the late period of development of this culture, estimated at the 4th to 3rd millennium BC,” – reported the conservator.
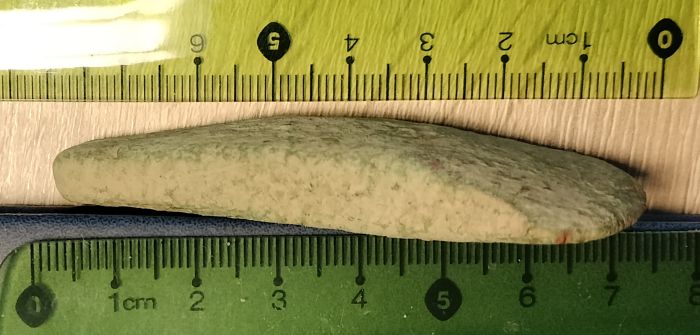
The Lublin conservator says: “It is true that we have recorded finds of Trypillian culture pottery from Gródek, Hrubieszów commune, and the presence of this ax in nearby Matcz can be considered as confirmation of the settlement of people of this culture also in eastern Poland.”
The axe will soon be transferred to the collection of the Hrubieszów Museum, where it will undergo further research, reports the conservator.
Cover Photo: Lublin Provincial Conservator of Monuments
















