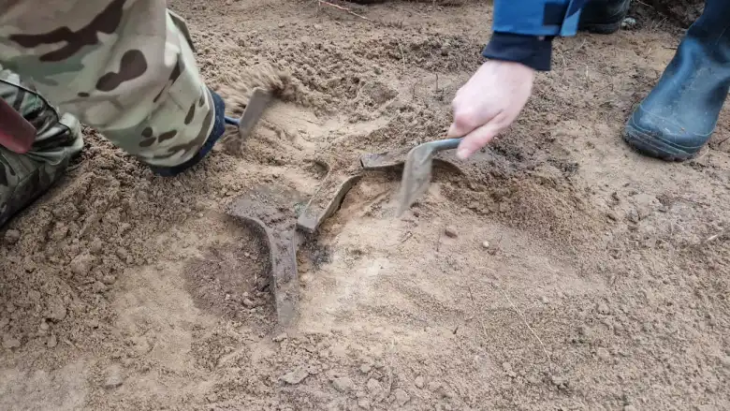
A recent study uncovered a wealth of new information regarding the production, material makeup, and cultural significance of Late Bronze Age swords found during several excavations conducted in the 20th century on Spain’s Balearic Islands in the western Mediterranean.
This cache of weapons includes artifacts that are approximately 3,000 years old, with the collection as a whole dating to the years 1000 through 800 BC, and reveal a fascinating intersection between local traditions and imported technologies, reflecting the increasing connectivity of the Western Mediterranean during this period.
The study, led by Laura Perelló Mateo of the University of the Balearic Islands, used a strategy that combines technological and archaeometric analyses with approaches that consider isotopes and typologies.
In the new study, which was just published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, a team of researchers from the University of the Balearic Islands, led by archaeologist Laura Perelló Mateo and her colleagues, analyzed both the manufacturing techniques and the chemical and isotopic compositions of these swords, offering new perspectives on cultural and technological interaction in the region.
There was a notable surge in mobility and cultural exchange in the Western Mediterranean between the 14th and 13th centuries B.C. This led to the introduction of new items and materials, like copper and tin, to the Balearic Islands, which significantly increased the number of metal artifacts. In Mallorca, Ibiza, and Formentera, the total weight of metal objects increased from 2.15 kg in the Early Bronze Age to 53 kg in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, the study found. This reflected an increase of metals obtained through trade, which had a significant impact on the eventual development of a sword-making industry.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“These swords incorporate the use of production techniques that were brought over from Iberia throughout the Middle and Late Bronze Ages,” the study authors wrote in their journal article. As examples of imported manufacturing and design innovations, they cite lost wax casting, complex bronze alloys (made from copper, tin, and lead), and the production of compound objects.
The Balearic swords analyzed by the researchers showed traces of local manufacturing traditions mixed with ideas originating elsewhere.
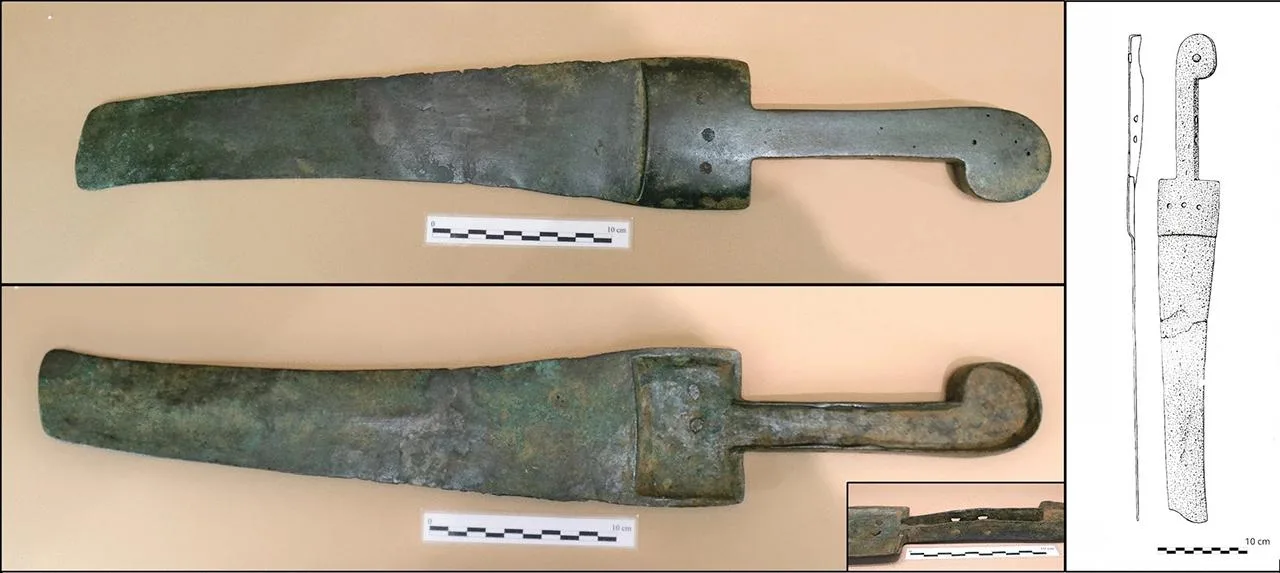
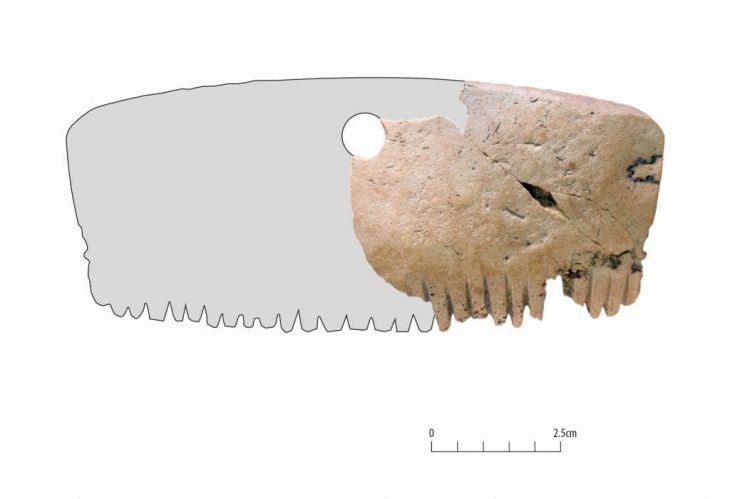
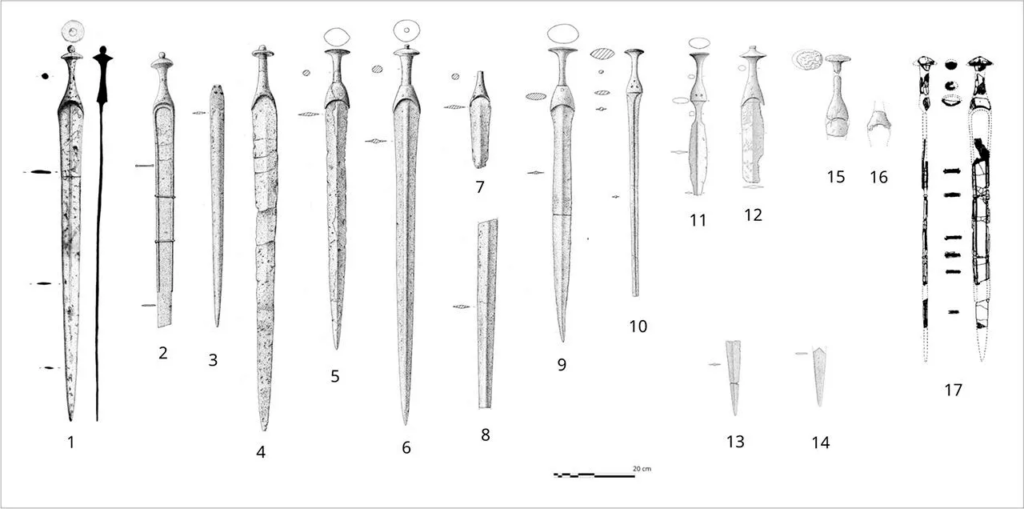
In total 18 Late Bronze Age swords were examined, most of which came from the islands of Mallorca and Menorca and classified as Son Oms type, named after the location where they were first found. The distinctive features of these weapons include solid grips, in place of the disc-or diamond-shaped pommels found on models made elsewhere, and thinner-than-usual blades that attached to the grips through direct casting techniques or via three rivets arranged in a triangular pattern.
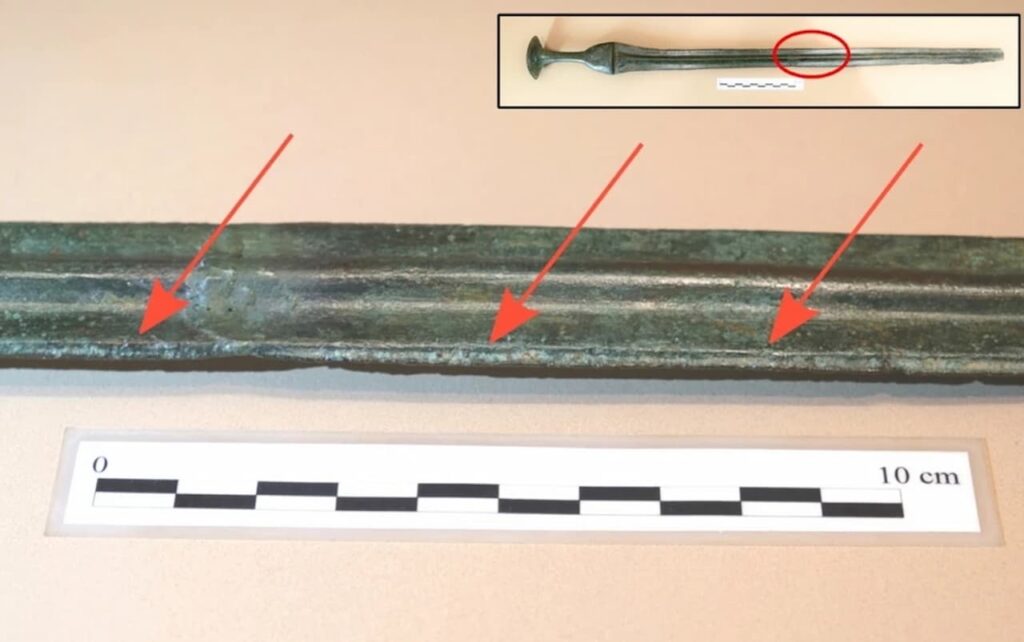

Their distinctiveness lies in regional adaptations, despite their outward resemblance to swords from the same era in Italy and Central Europe. For instance, in contrast to their continental counterparts, Balearic swords typically have a redefined function and symbolism.
“Though they [the artifacts] take on the formal concept of swords, their role and function would have been completely different to the more generalized use they received on the mainland. Documented evidence allows us to conclude that, largely, these swords were not envisaged or produced for use in combat. Rather, they were created as symbolic objects to be put on display.” the study authors wrote.
The fact that the people of the Balearic Islands weren’t using swords in battle suggests their manufacture might have been commissioned by elites who could afford to have the materials imported to make them.
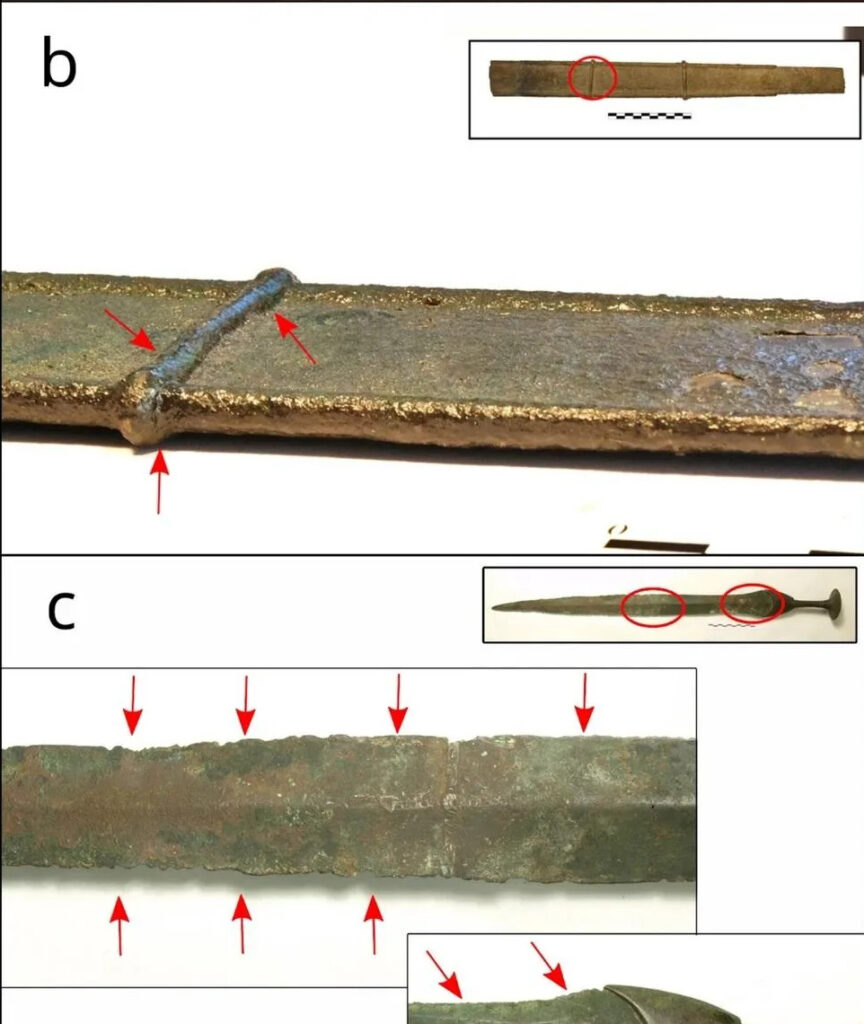
The origin of the metals used was also disclosed by isotopic analyses. Although sources in Menorca, Mallorca, and, to a lesser extent, Sardinia were also identified, deposits in Linares (mainland Spain) accounted for a significant portion of the copper. The integration of the Balearic Islands into Mediterranean trade circuits and the existence of intricate exchange networks are both confirmed by these findings.
Perelló Mateo, L., Llull Estarellas, B. & Calvo Trías, M. Almost the same, but not quite: an analysis of Late Bronze Age swords in the Balearic Islands. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 16, 194 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-024-02088-0
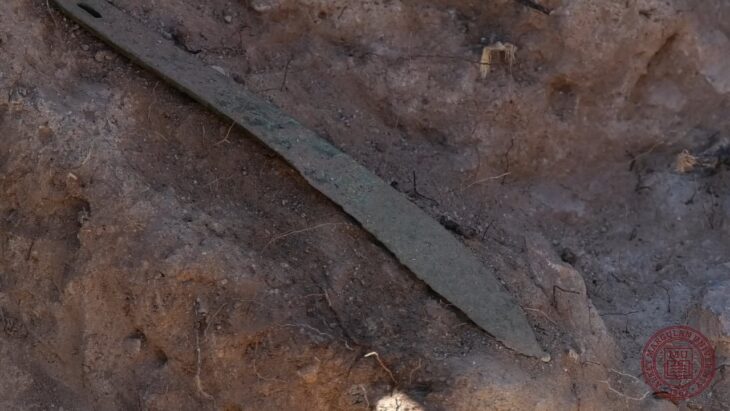
Cover Image Credit: Image of the machete from Lloseta (Archeology Museum of Catalonia). Drawing by Delibes and Fernández-Miranda 1988. Image Credit: L. Perelló Mateo et al., Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2024)