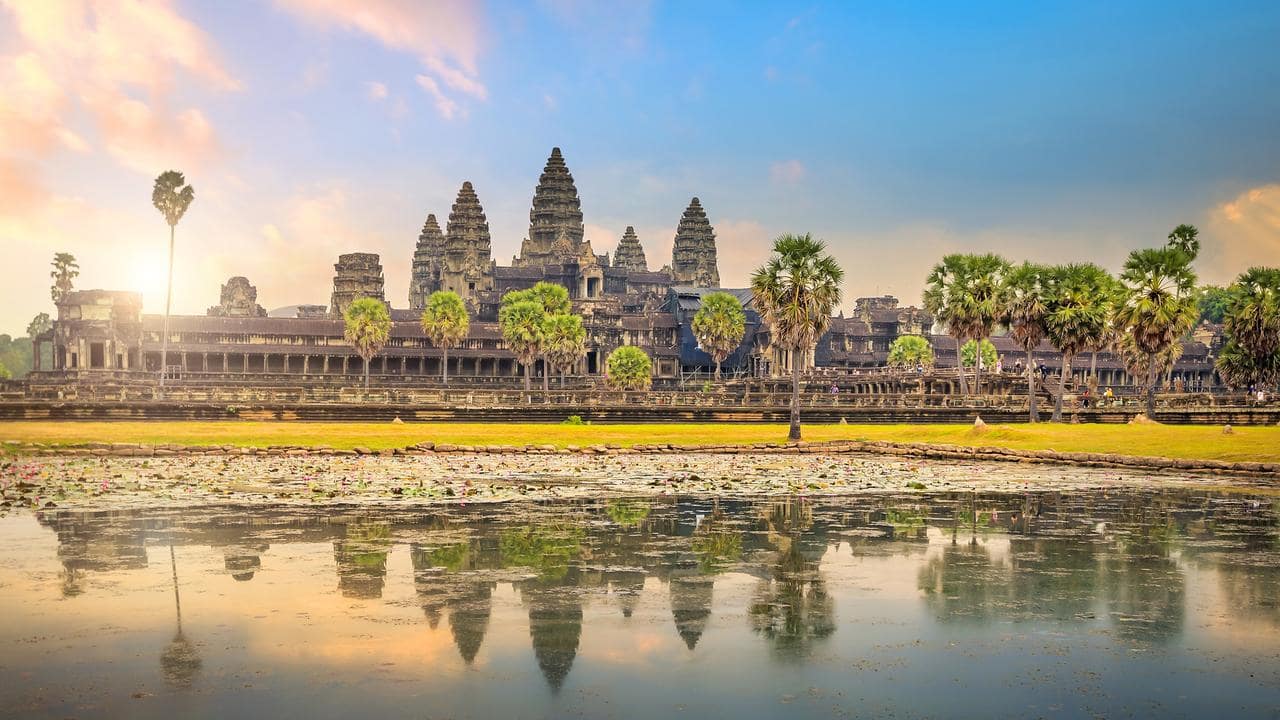
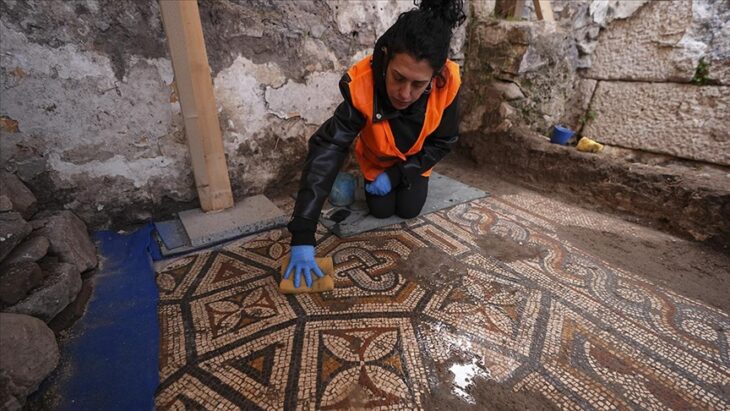
Angkor Wat was the grand capital of ancient Cambodia. The population of Angkor Wat, one of the most magnificent cities of the time, was between 750,000 and 900,000. This meant quite a large population density.
For the city, which seemed to be abandoned suddenly in 1431 after AD, researchers say the city was abandoned gradually, not suddenly.
An international team, led by the University of British Columbia, examined three decades of data to create a demographic model of the Medieval city.
This method for modeling urban center development, according to Sarah Klassen and colleagues, could be applied to other premodern cities.
Dr. Sarah Klassen, the lead author of the new paper, said the capital of the Khmer Empire represented “one of the largest pre-modern cities in the world, built up over several centuries of growth at different rates.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This new form of data provides insights not only into the dynamics of rising and fall in ancient settlements but also into the complexities of Khmer social complexity. The report claims that Angkor, the ancient capital of the Khmer Empire, “suffered a slow decline,” and one of the most intriguing features of this study is that it shows how long Angkor Wat was abandoned.
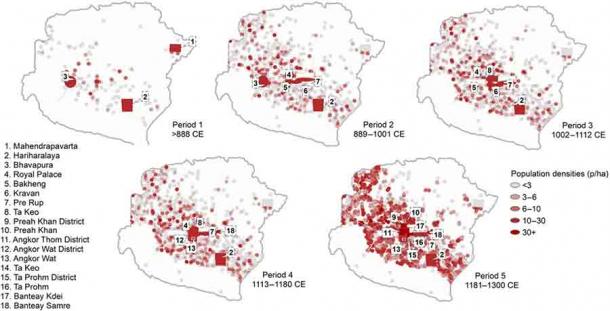
The new model shows “a gradual and protracted migration of its inhabitants dating back to the start of the 14th century.” Archaeologists and scholars have long questioned whether the kingdom collapsed after the 1431 AD conquest by Thai forces, but the new model reveals “a slow and prolonged exodus of its inhabitants dating back to the start of the 14th century.”
Since the city’s nonreligious architectural structures were made of organic materials that had long since decayed, no systematic demographic analysis of Angkor had ever been completed. According to Klassen and colleagues that this made traditional population size and density measurement techniques impractical.
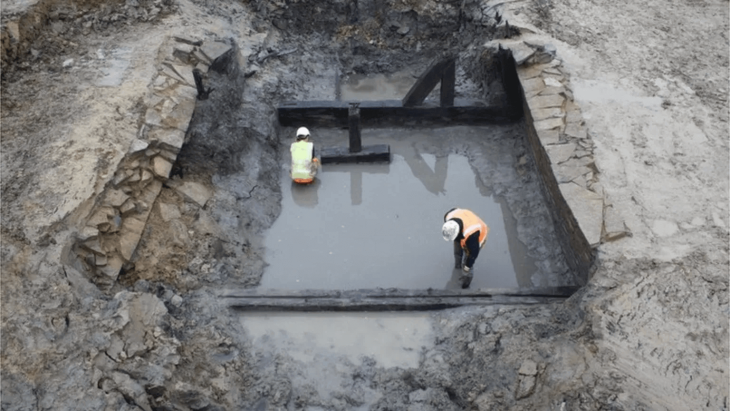
To solve this obstacle, they created maps that model the city’s development over time using decades of archaeological excavation results, historical archives and maps, recent lidar surveys, and multiple machine learning algorithms.
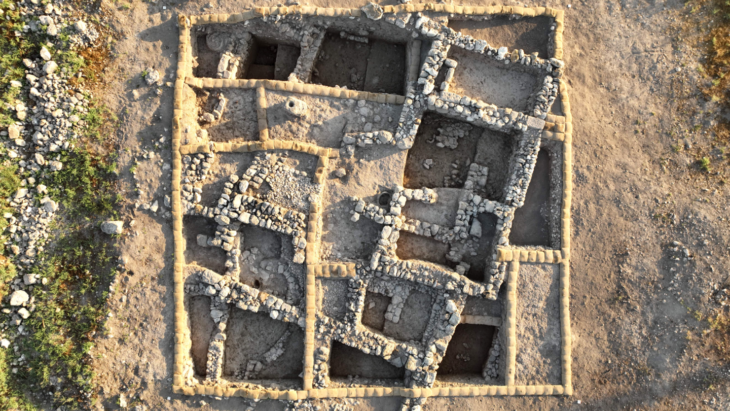
The researchers discovered that it may have taken generations for Angkor’s population to hit its height, with development happening at varying rates in each of the temple’s three occupation zones. The civic-ceremonial center, which housed the royal residence and huge stone temples, the metropolitan district, and the embankments were among them.
When the researchers compared Angkor’s development to that of other preindustrial tropical and subtropical urban centers, they discovered that its range of metropolitan urban area densities was much smaller than that of the Mayan city of Caracol. Nonetheless, the density of its civic-ceremonial centers was equivalent to that of Teotihuacan in modern-day Mexico or Anyang in China.
The team also shows the abandonment of Angkor Wat as a gradual abandonment rather than a mass Khmer migration.
The findings have been published in the journal Science Advances.
Source: Daily Mail