Researchers have proven that breeding small brachycephalic (shorter-nosed) dogs took place already in ancient Rome. Research on a 2,000 years old dog skull indicates that the dog resembled a French bulldog.
Analyzing the remains of a canine skull at a Roman-era site in Türkiye, researchers have determined that the ancient pooch had a brachycephalic skull similar to that of a French Bulldog.
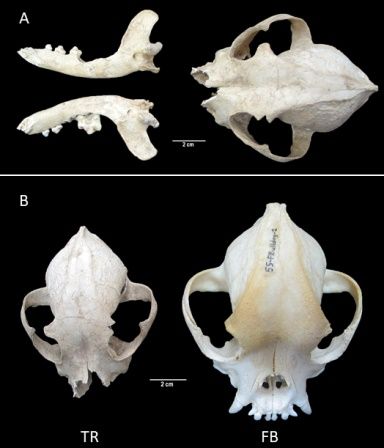
In 2007, dog bones were found in the ruins of the ancient Tralleis, near the Turkish city of Aydın. The find was incomplete, and due to the poor condition of the remains no one paid much attention to it for many years. In 2021, the bones caught the attention of Professor Aleksander Chrószcz and Dr. Dominik Poradowski from the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences and a team of researchers from Istanbul University led by Professor Vedat Onar.
‘Fortunately, the skull was not so damaged or fragmented to prevent its measurements, and this research is an important part of our investigation because taking measurements allows to compare it with other results of archaeozoological research, and with bone material from modern animals. We conducted craniometry, or in the simplest terms, we determined measurement points on the bones of the skull and based on these points, we not only managed to determine the value of individual measurements, but also compare them with contemporary, testable dog skull craniometry results’, says Professor Aleksander Chrószcz.
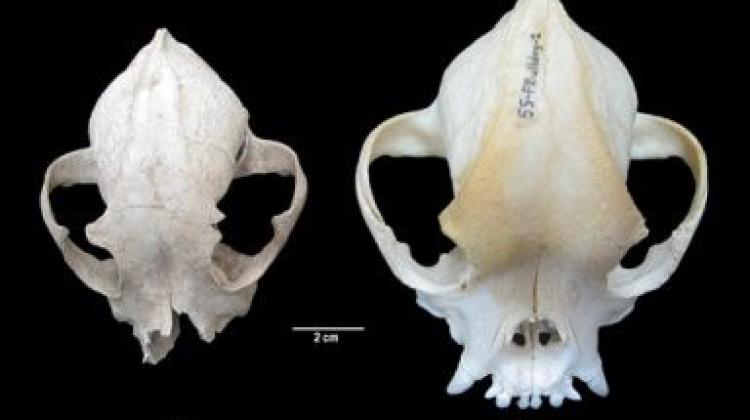
He adds that due to the state of preservation of the remains (measuring the length of the skull was not possible), the researchers relied on other measurements, including the area of the base of the skull, the tympanic cavity, the teeth and palate.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
‘In this case, there was no doubt that it was the skull of a brachycephalic (short-nosed) dog, and a relatively small one. The analysis of the preserved and measurable parts of the animal’s skeleton and the skeletons of dogs of modern breeds shows that it was most likely an animal that was lower at the withers than the well-known, also short-nosed Molossian hounds, whose pedigree originating from ancient Hellas is beyond doubt’, says Professor Aleksander Chrószcz.
He emphasizes that in order to make sure that scientists were dealing with such an ancient find, a radiocarbon dating procedure was carried out at a reputable, reference laboratory in the United States.

‘The discovery of the remains of a dog with this anatomy brings us valuable information. Scientists have been able to prove that in Ancient Rome, Molossian hounds were not the only known brachycephalic dogs. It would not be new information if not for the fact that this animal was much smaller, and its morphology more similar to that of a French bulldog, a modern companion dog. It was supposed to accompany its guardian, sharing a fairly comfortable life, instead of being a working dog often mentioned in the available Roman literature, we read in the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences press release.
According to the release, the animal was probably cared for not only during its life, but also after death. Skeletal examinations showed that the quadruped was treated exceptionally well, which distinguishes it from other discovered remains of working dogs.
‘Someone must have loved this dog, because most they likely they ordered to be buried with it. This means that the love between humans and animals is not a modern invention’, concludes the scientist from the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences.