An archaeological dig at Kopilo, a hill settlement founded around 1300 BC about 70 miles west of Sarajevo, has discovered new forms of jewelry in several Bronze Age graves.
The Kopilo cemetery in central Bosnia is one of the most significant finds in the Balkans in recent decades.
Archaeologists from the Austrian Academy of Sciences and Bosnia and Herzegovina researching at Kopilo also found evidence that burials continued in the Kopilo cemetery in central Bosnia, in addition to cremation, although European burial customs varied during the Bronze and Iron Ages.
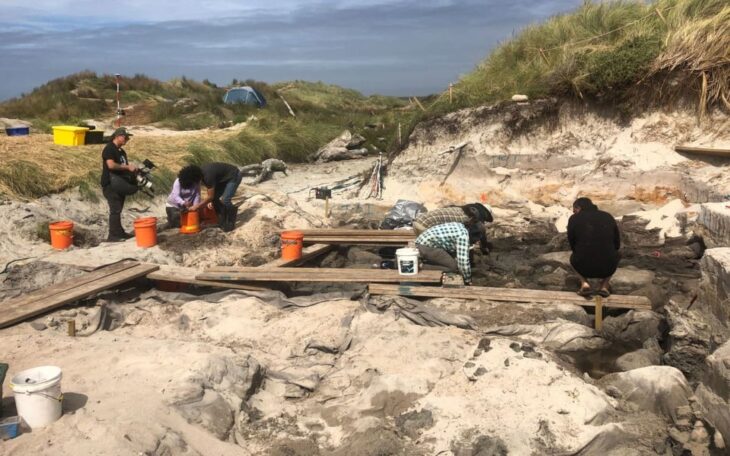
With a team from the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, excavation director Mario Gavranovic has been investigating Kopilo’s settlement on the hill since 2019.
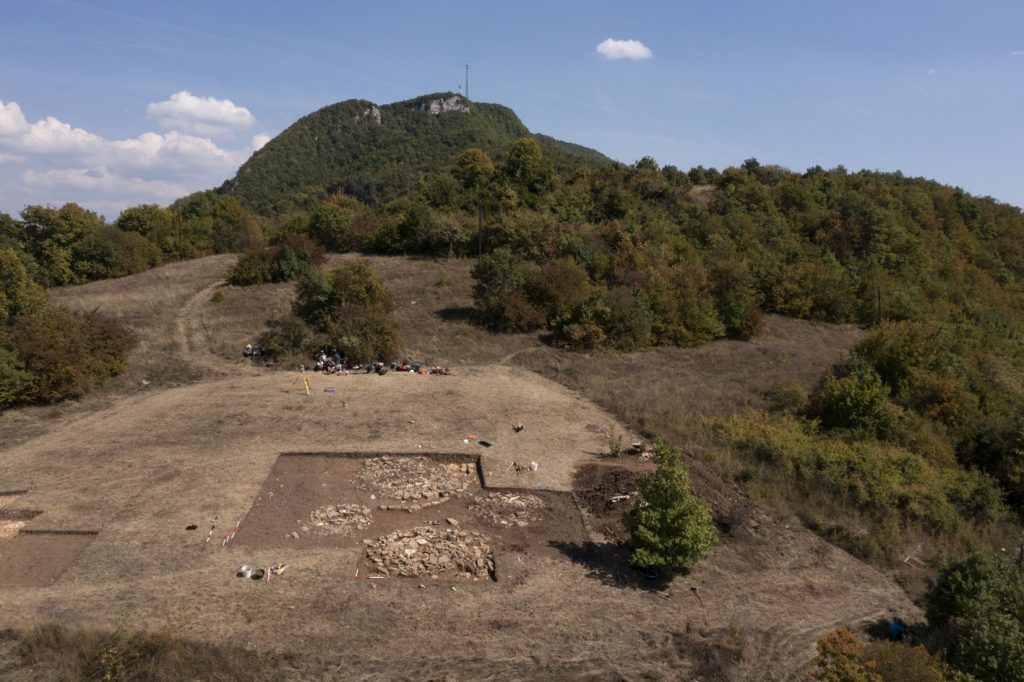

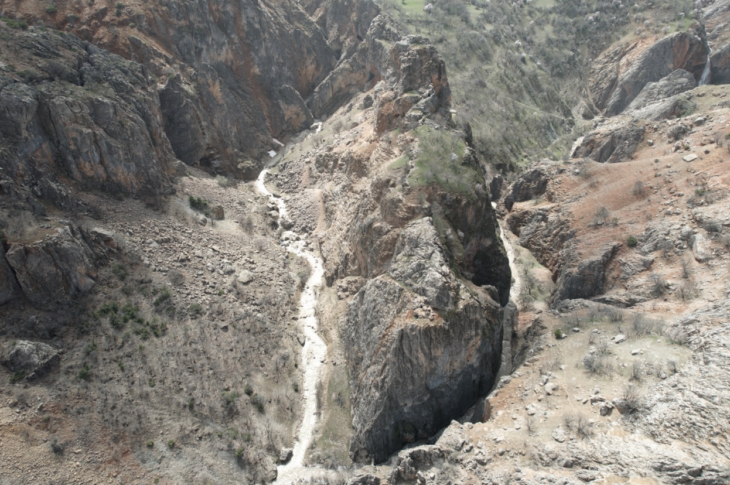
Kopilo was a farming community that had been occupied continuously for a thousand years on a plateau 2000 feet above sea level. Pig, cattle, and goat skeletons have been discovered, indicating livestock breeding. The pre-Illyrian Bronze and Iron Age culture that settled the site was known for its network of fortified hilltop settlements and metallurgical skills, but little was known about its funerary practices. The Kopilo site has been excavated since 2019, but only two tombs were discovered until 2021.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
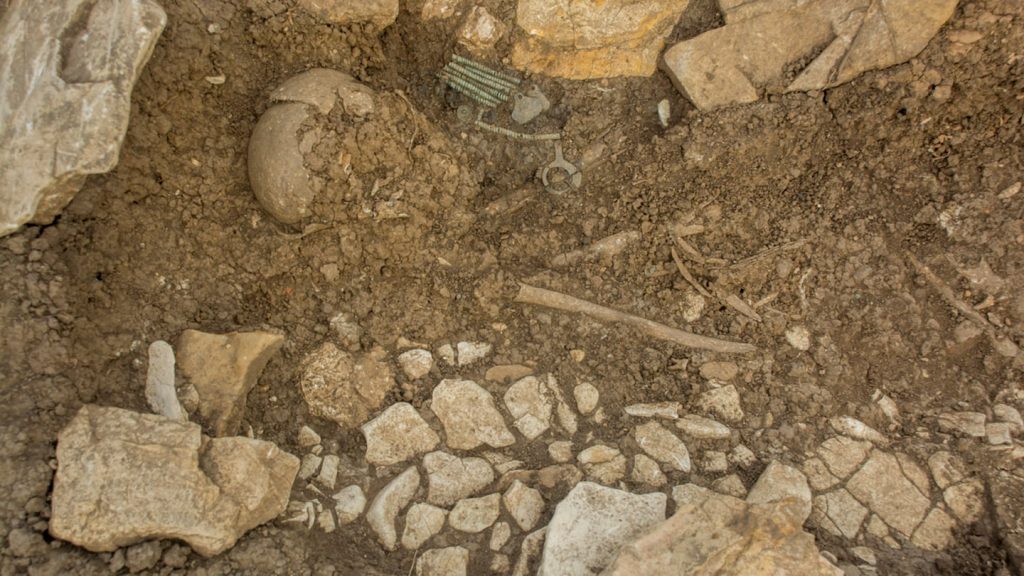

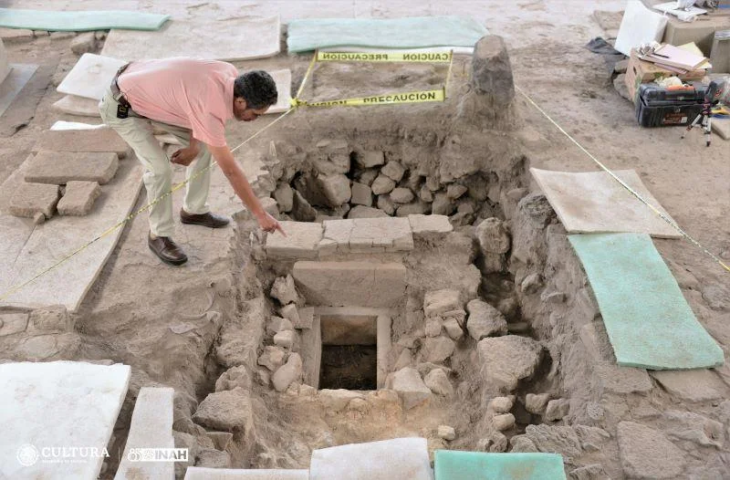
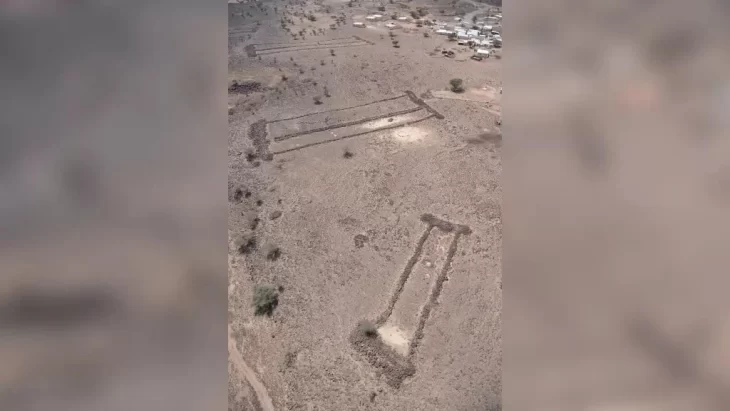
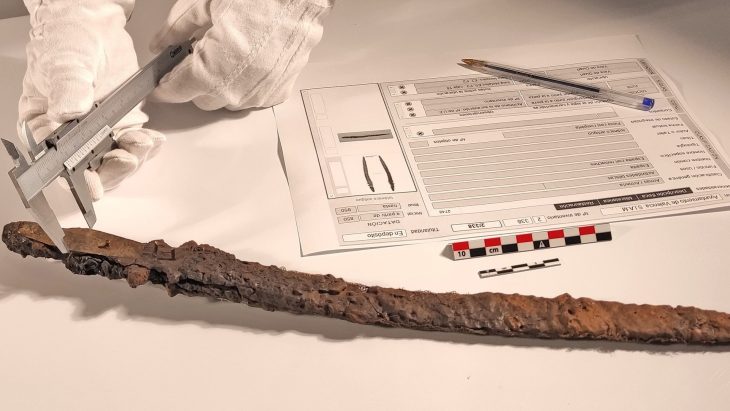
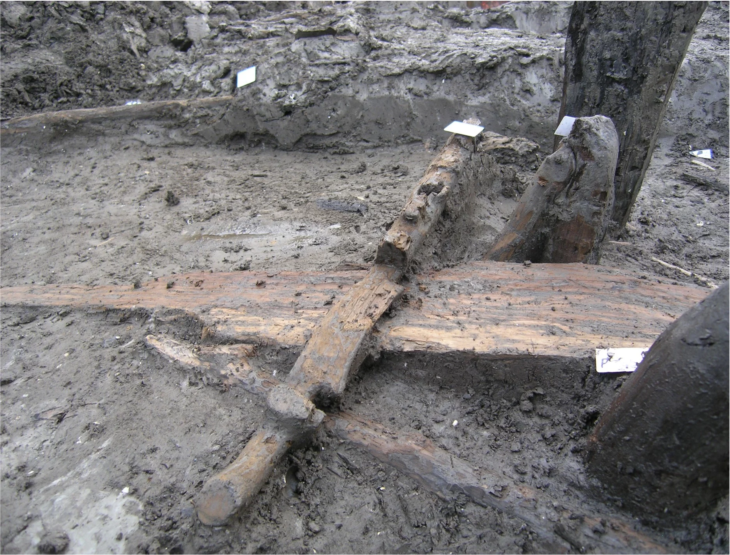
In 2021, the necropolis of the settlement was discovered. This year, the entire burial ground was excavated and documented in detail. Usually, two to five tombs were found within a round stone structure. From the 11th to the 5th century B.C., the necropolis was in continuous use. Archaeologists discovered 46 graves containing the remains of 53 people. They were buried in the crouch burial position, on their sides, with their legs and arms slightly bent. A small vessel was frequently buried at the deceased’s head. Early osteological examinations reveal a disproportionate number of young children, indicating a high child mortality rate. Pottery, bronze jewelry, glass beads, and iron weapons are among the grave goods.
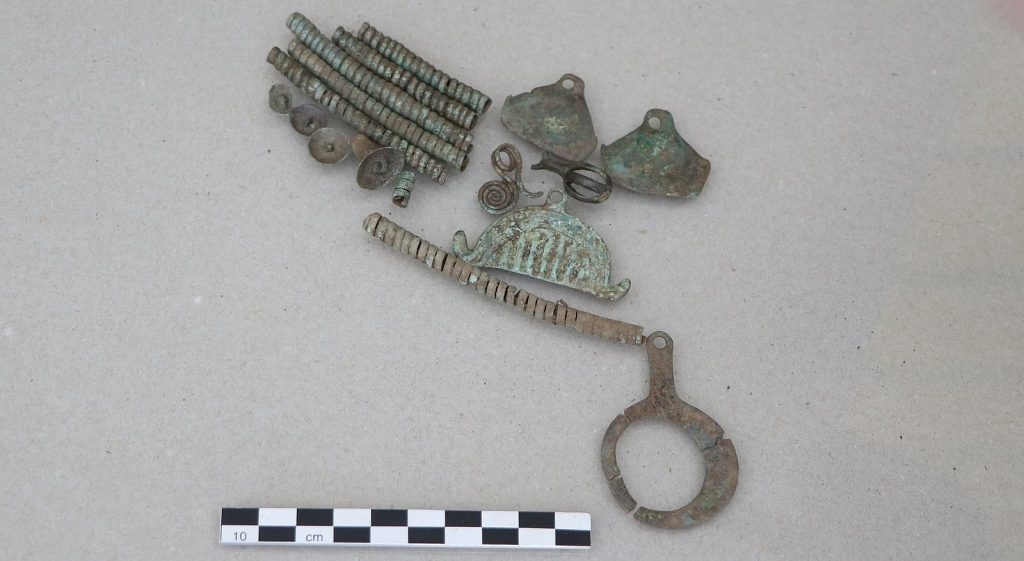

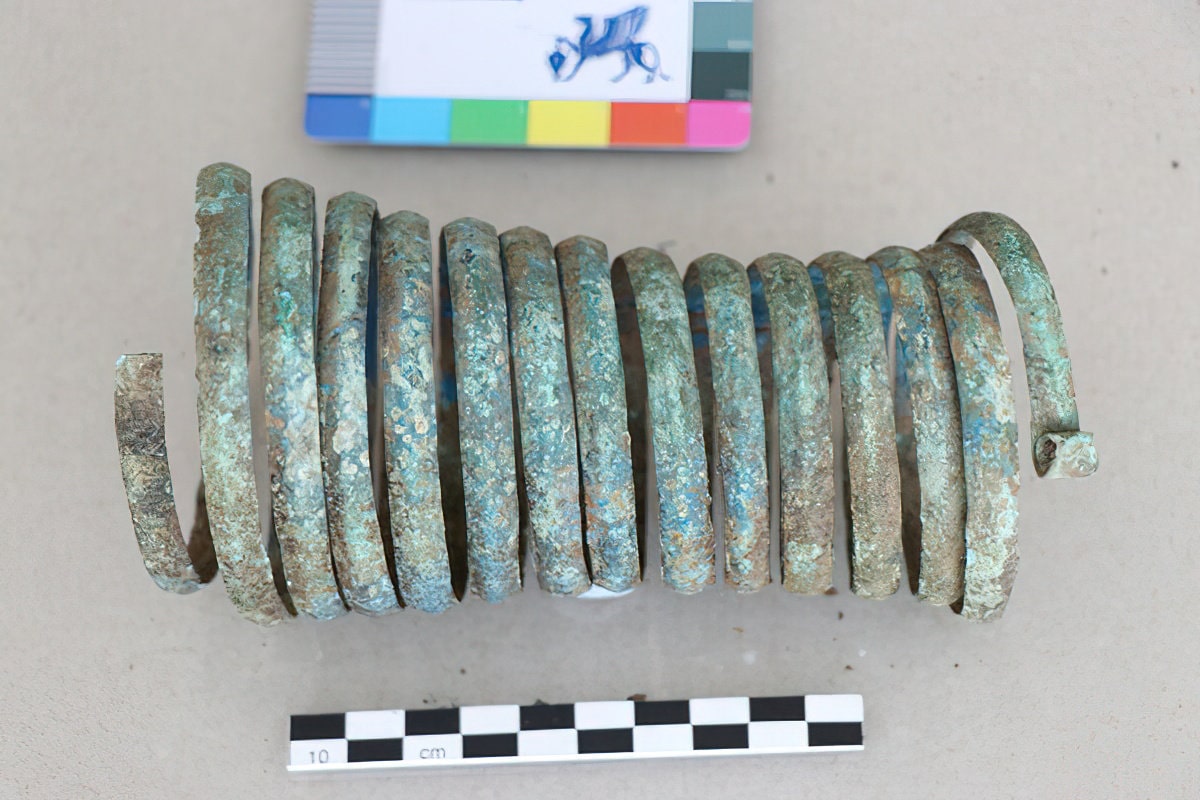
Bronze fibulae in previously unseen shapes are featured in the jewelry. Archaeologists discovered some of the earliest worked iron objects in Bosnia in addition to the new types of jewelry that are now being revealed for the first time, demonstrating that iron metallurgy was active at the location as early as the 9th–8th century B.C.
What is the fibula?
A fibula is a brooch or pin used to fasten clothing, typically at the right shoulder. The fibula evolved in a variety of shapes, but they all followed the safety-pin principle. Unlike most modern brooches, fibulae originally served a practical purpose: they were used to fasten clothing for both sexes, such as dresses and cloaks.