Chinese archaeologists announced on Saturday that some new major discoveries have been made at the legendary Sanxingdui site in southwestern China, which will help shed light on the cultural origins of the Chinese nation.
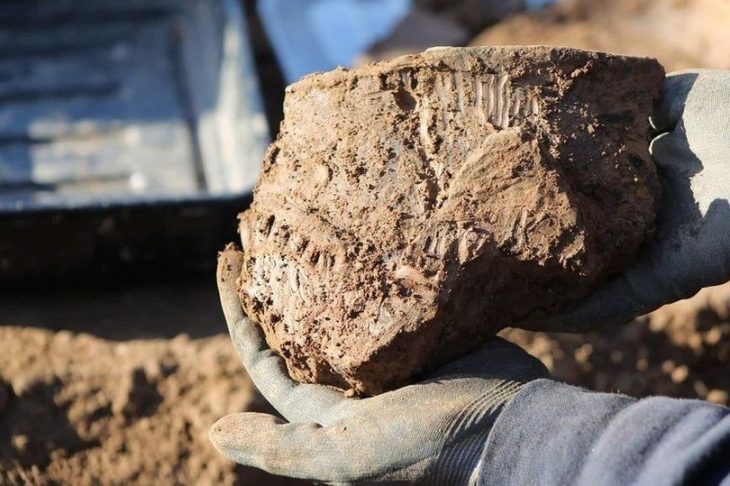
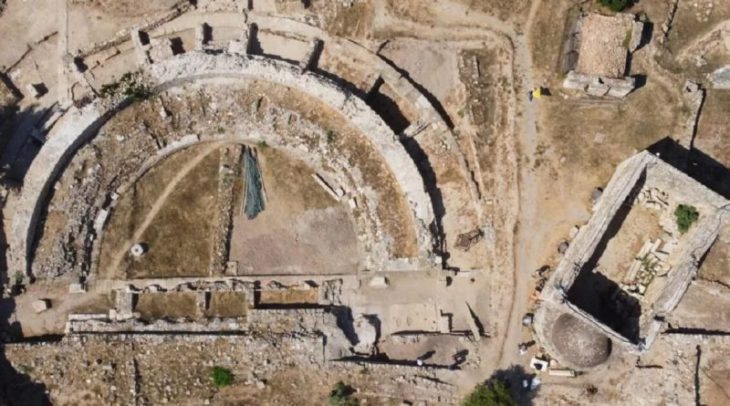
The National Cultural Heritage Administration (NCHA) announced in the provincial capital Chengdu that at the Sanxingdui site in Sichuan Province, archaeologists have discovered six new sacrificial pits and unearthed about 500 objects dating back 3,000 years.
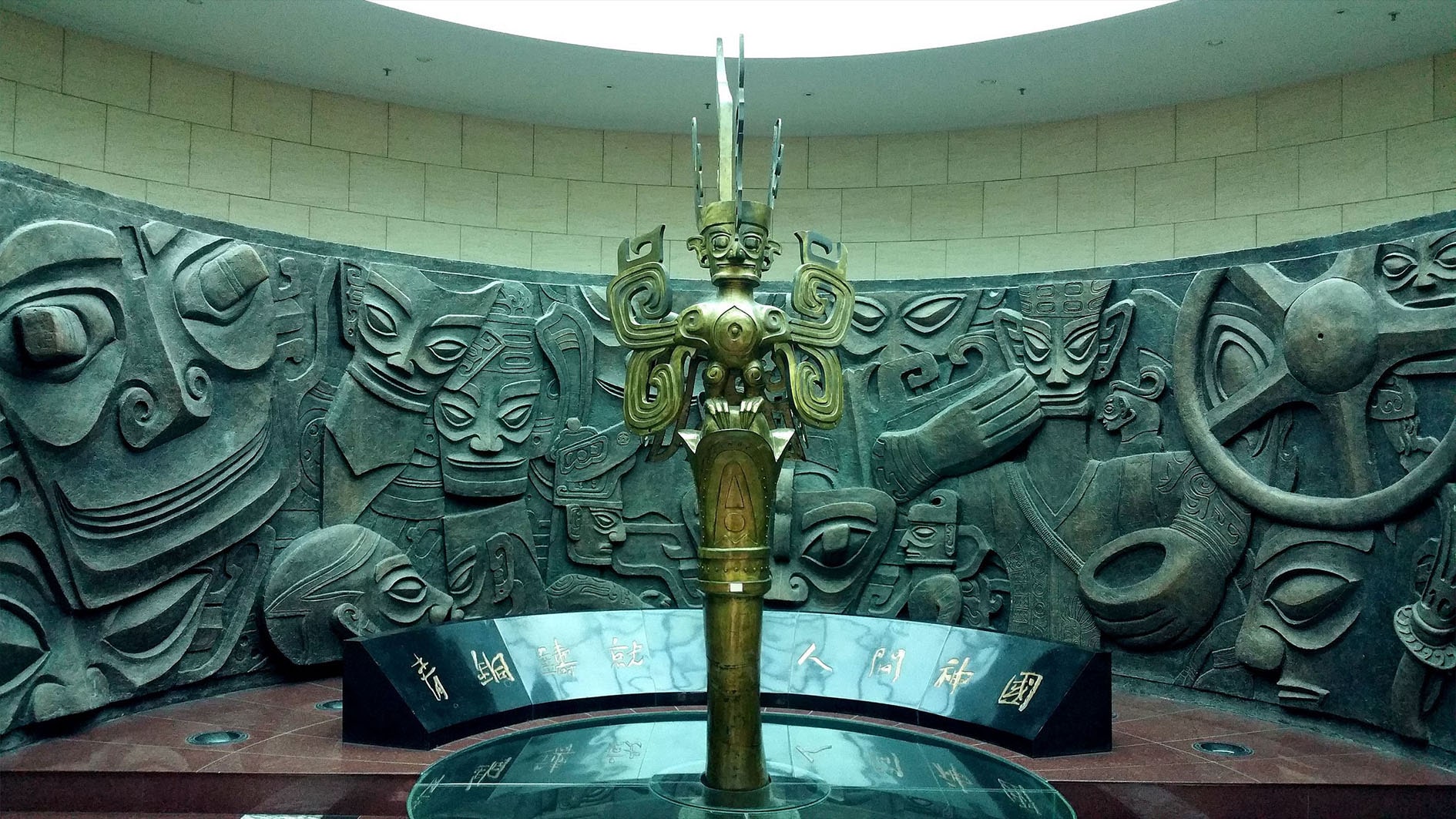
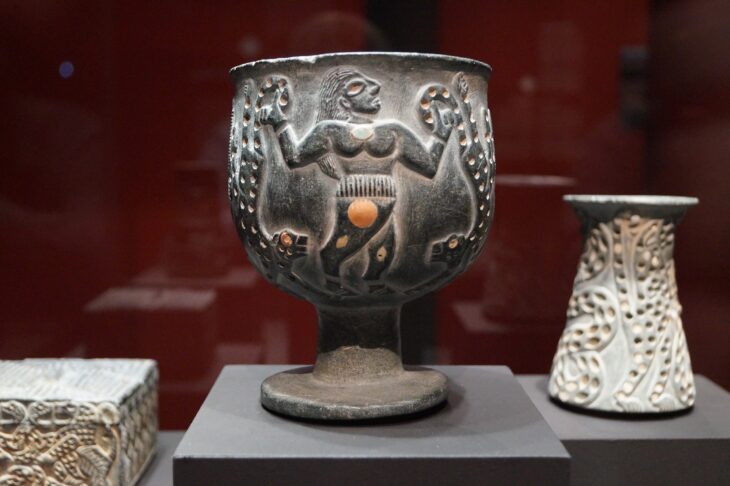
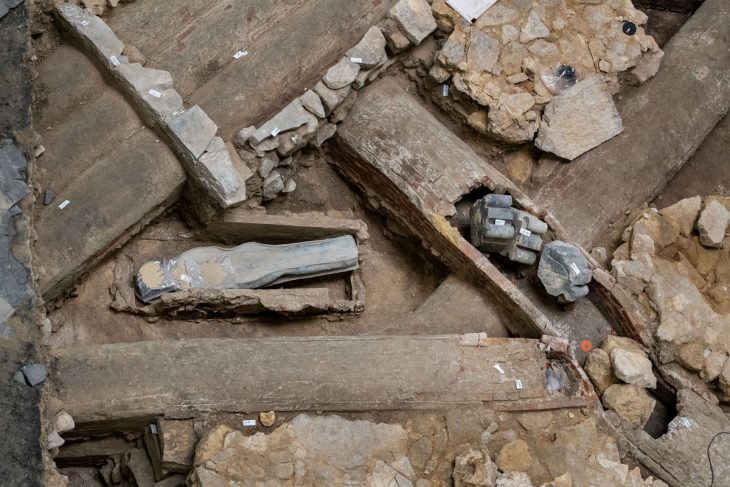
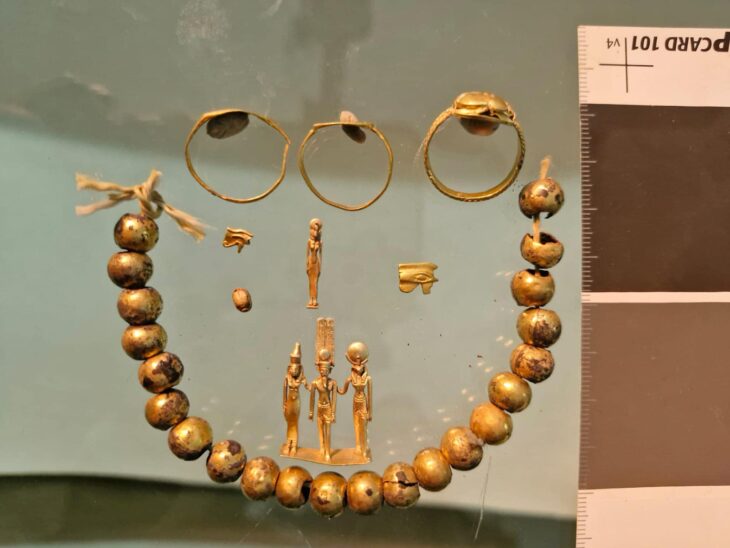
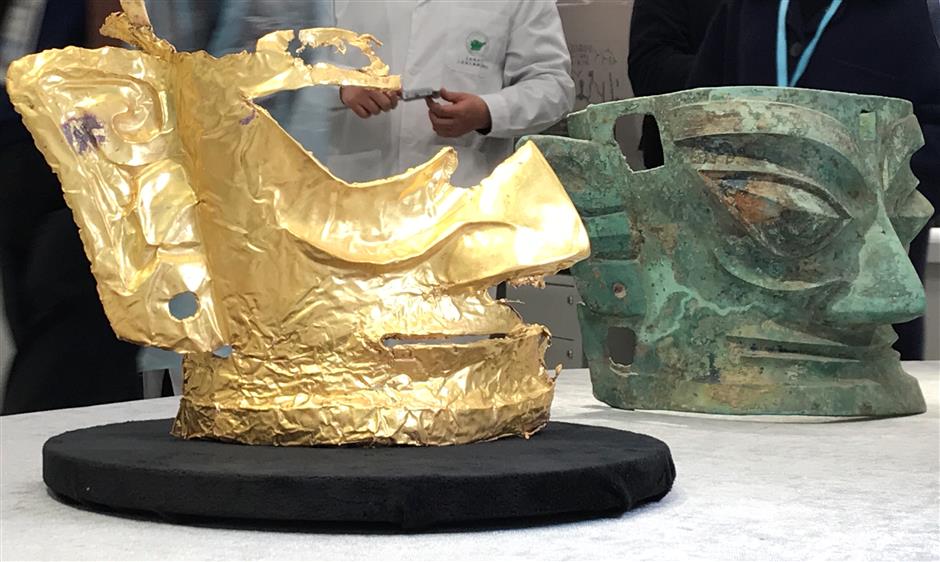
So far, archaeologists have unearthed various important cultural objects from the four mines, including gold masks, gold leaf, bronze masks, bronze trees, and large amounts of ivory. It also discovered miniature ivory sculptures, carbonized rice, and tree seeds. The remaining newly discovered pits are still being excavated.
In another major discovery, residues of silk and textile products were unearthed for the first time at Sanxingdui, indicating “the ancient Shu Kingdom was one of the important origins of silk in ancient China,” according to Tang Fei, head of the excavation team and chief of the institute.
In this process, archaeologists made full use of modern science and technology to build an archaeological excavation room, a comprehensive excavation platform, and a multi-functional excavation operation system.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
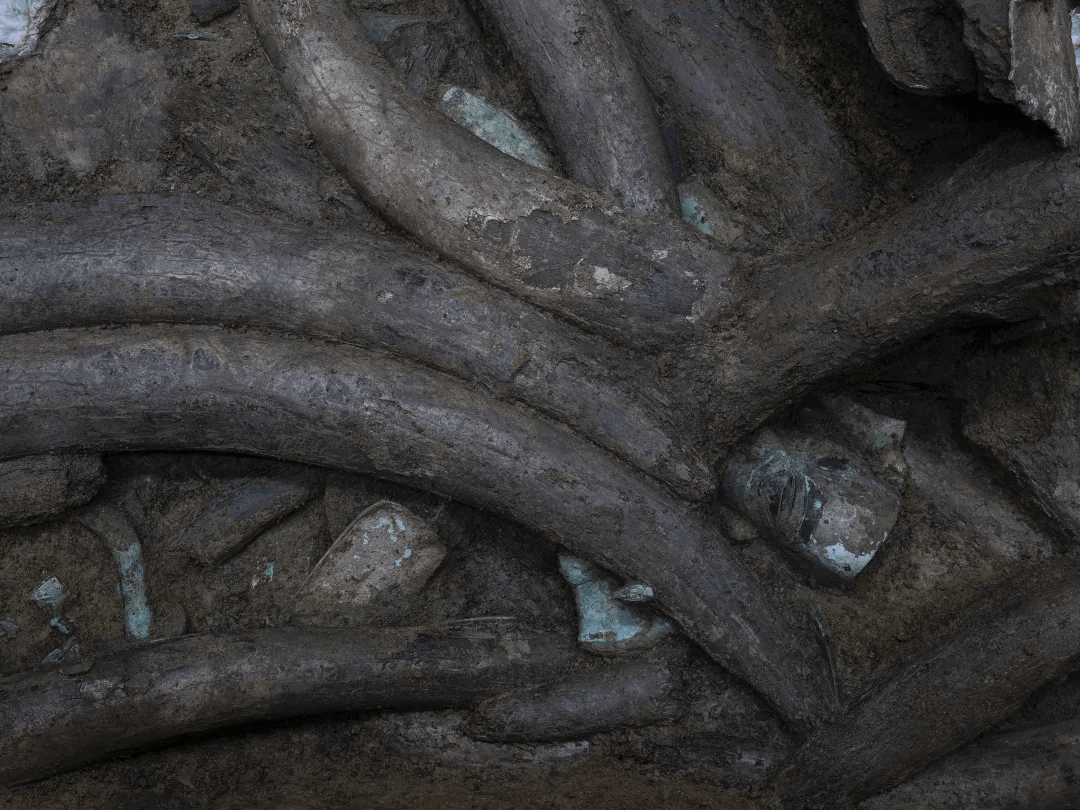
With the support of professional teams from multiple disciplines and institutions, they formed a comprehensive working model that combines traditional archaeology, laboratory archaeology, technical archaeology, and cultural relic protection. NCHA said at the meeting that this combination will ensure high-quality and high-level archaeological work.
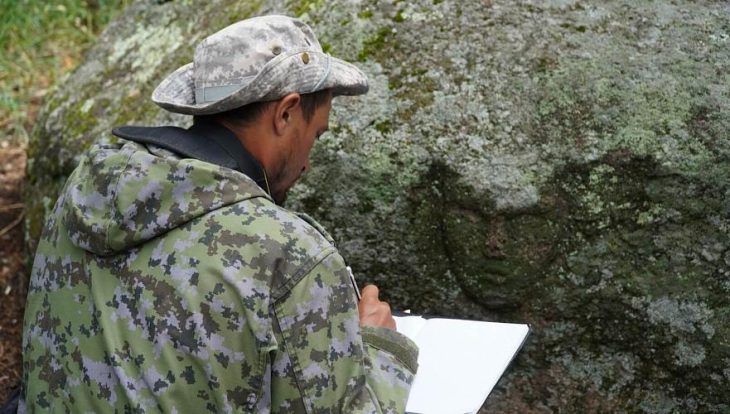
In Xinkeng, archaeologists are using hand shovels, scalpels, and bamboo sticks to carefully retrieve ancient artifacts.
“We have to be extra careful in retrieving these relics,” said Jiang Luman, with the Chengdu Cultural Relics and Archaeology Research Institute. Jiang is one of the workers at the No. 5 pit.
Jiang said a lot of the ivory pieces at the pit are in poor condition and require special care during excavation.
“The ivory needs to remain humid and at a stable temperature, so we take various measures to ensure it is kept under such conditions,” she said. “So far, we have retrieved more than 100 cultural items from the pit.

Chinese researchers say that the ancestral types of some bronzes unearthed in Sanxingdui can be found in the Central Plains or other areas along the Yangtze River, which is strong evidence of frequent exchanges.
“The new discoveries will enrich and deepen our understanding of the Sanxingdui culture,” said Song Xinchao, deputy director of the National Cultural Heritage Administration.
According to archaeologists, the newly discovered golden masks, copper masks, and figures all reflect the uniqueness and creativity of the ancient Shu civilization.
Jay Xu, head of the Asian Art Museum of San Francisco, told Xinhua that the highly developed bronze ware art at Sanxingdui “made it outstanding among many regional civilizations in China and unique among ancient civilizations,” adding that the new discoveries will be of enormous interest internationally.