Bronze scrap uncovered in hoards in Europe was used as currency, according to researchers from the Universities of Göttingen and Rome.
Archaeologists have discovered compelling evidence that people in Late Bronze Age Europe used metal scraps or fragments as currency.
This study indicates that something like our modern-day “global economy” emerged across Western Eurasia from common people’s daily scrap-for-cash trading around 1000 years before the rise of classical civilizations. The results were published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
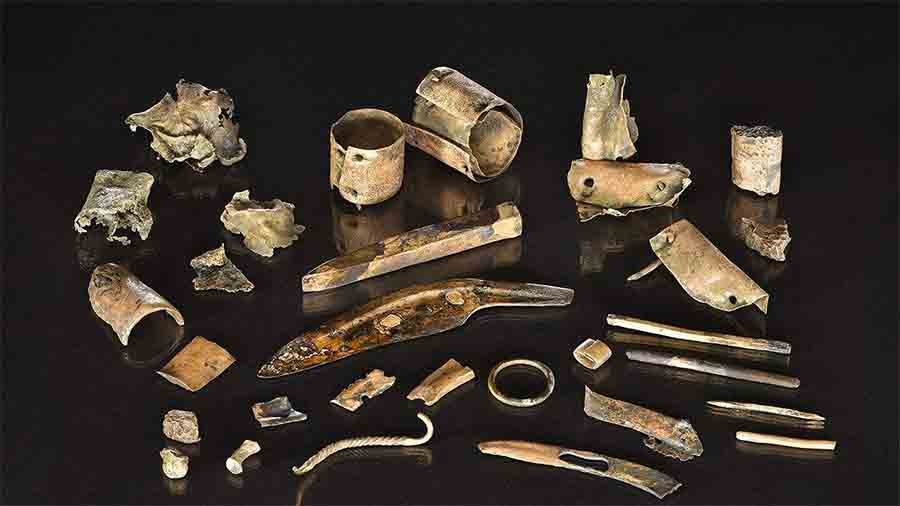
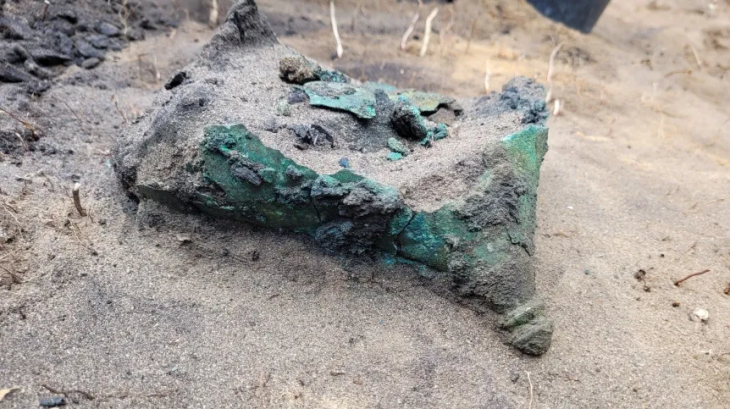
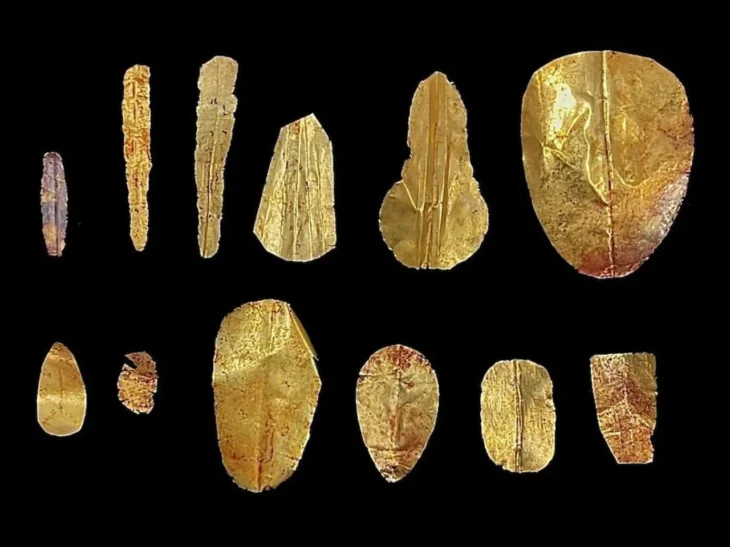
According to excavations throughout Central Europe, people started splitting metal artifacts into smaller fragments in Bronze Age Europe in the early second millennium BC. Beginning about the year 1,300 BC, the practice became noticeably more common during the Late Bronze Period. Every type of metal piece, including tools, swords, axes, clothing, small personal pieces, and metal casting waste materials, may be fragmented.
Nicola Ialongo of the University of Göttingen and Giancarlo Lago of the Sapienza University of Rome analyzed and weighed over 2,500 metal fragments recovered from Bronze Age excavation sites in Italy, Germany, and Poland to test their hypothesis that these small fragments may have been used as currency. These metal fragments were included in the heaps of objects commonly found in settlements dating to the end of the 2nd millennium BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

After weighing the metals, archaeologists used statistical models to make comparisons. The findings of this approach were significant and remarkable, showing that these objects were multiples of normal weight dimensions. It’s impossible to dismiss the fact that one thing weighs twice as much as another, or three times as much as another, or half as much as another, and so on.
Furthermore, the standard dimensions against which they were matched were not chosen at random. They corresponded precisely to the weights of balance weights in use throughout Europe throughout those ancient times.
Scales were built using these balance weights. It is now clear that such scales were used to measure bronze metal fragments retrieved from Late Bronze Age dig sites, among other things. This was required to ensure that they were sliced to the correct size and measured the correct quantity before being circulated as “coins.”
It’s worth noting that Late Bronze Age Europeans weren’t the first to use metal as currency. Beginning in the early third millennium BC, the ancient Mesopotamians used silver sticks for the same purpose.
The spread of the use of metallic scraps for cash happened against the background of the formation of a global market in Western Eurasia. “There was nothing ‘primitive’ about pre-coinage money, as money before coins performed exactly the same functions that modern money does now,” explains Dr. Nicola Ialongo at the University of Göttingen’s Institute for Prehistory and Early History.
Nicola Ialongo adds, “Using these metallic scraps was not an unexpected development, as it is likely that perishable goods were used as currency long before the discovery of metallurgy, but the real turning point was the invention of weighing technology in the Near East around 3000 BC. This provided, for the first time in human history, the objective means to quantify the economic value of things and services, or, in other words, to assign them a price.”