Contrary to what was thought, Maya farmers may have planned for population growth, says a new study.
According to a Brown University press release, Andrew Scherer of Brown University and Charles Golden of Brandeis University, together with their colleagues, undertook a lidar survey of a stretch of the Western Maya Lowlands on the border between Mexico and Guatemala.
“It’s exciting to talk about the really large populations that the Maya maintained in some places; to survive for so long with such density was a testament to their technological accomplishments,” Scherer said. “But it’s important to understand that that narrative doesn’t translate across the whole of the Maya region. People weren’t always living cheek to jowl. Some areas that had the potential for agricultural development were never even occupied.”
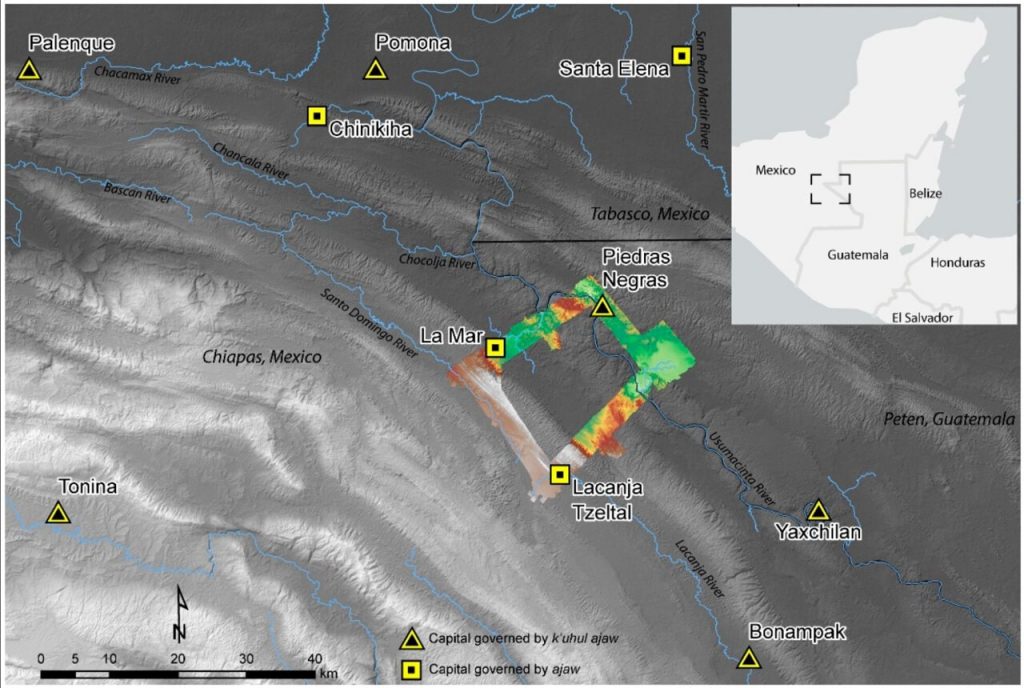
The Maya urban centers of Piedras Negras, La Mar, and Lacanja Tzeltal, the capital of the kingdom of Sak Tz’i’, are located in this region.
Scherer explained that all three kingdoms were governed by an ajaw, or a lord — positioning them as equals, in theory. But Piedras Negras, the largest kingdom, was led by a k’uhul ajaw, a “holy lord,” a special honorific not claimed by the lords of La Mar and Sak Tz’i’. La Mar and Sak Tz’i’ weren’t exactly equal peers, either: While La Mar was much more populous than the Sak T’zi’ capital Lacanjá Tzeltal, the latter was more independent, often switching alliances and never appearing to be subordinate to other kingdoms, suggesting it had greater political autonomy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
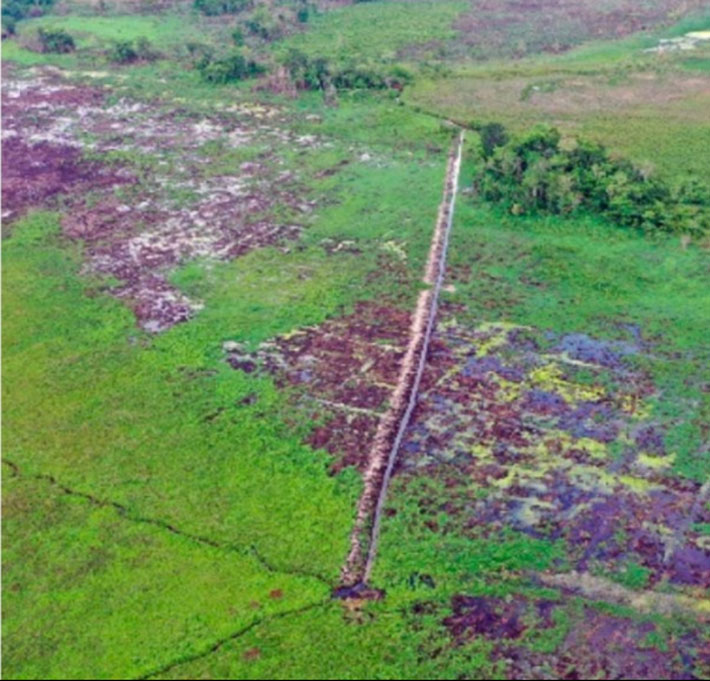

The lidar survey showed that, despite their differences, these three kingdoms boasted one major similarity: agriculture that yielded a food surplus.
“What we found in the lidar survey points to strategic thinking on the Maya’s part in this area,” Scherer said. “We saw evidence of long-term agricultural infrastructure in an area with relatively low population density — suggesting that they didn’t create some crop fields late in the game as a last-ditch attempt to increase yields, but rather that they thought a few steps ahead.”
Remote sensing technology indicated that between A.D. 350 and 900, the Maya built irrigation channels and terraces in and around the region’s towns, despite no indications of comparable expansion in the population centers.
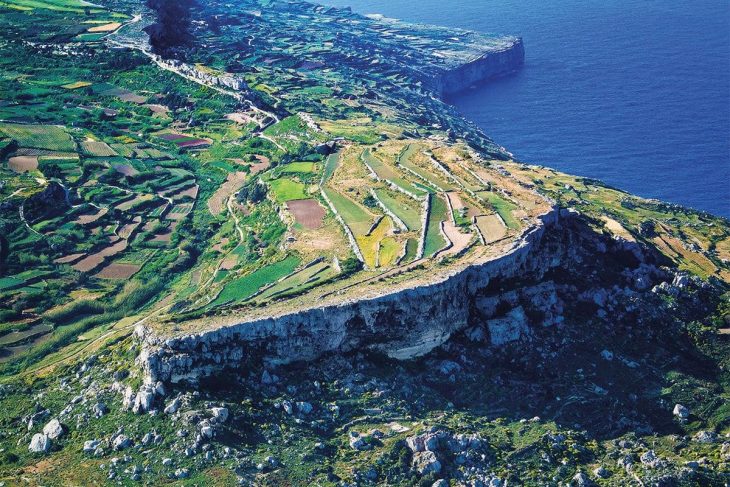
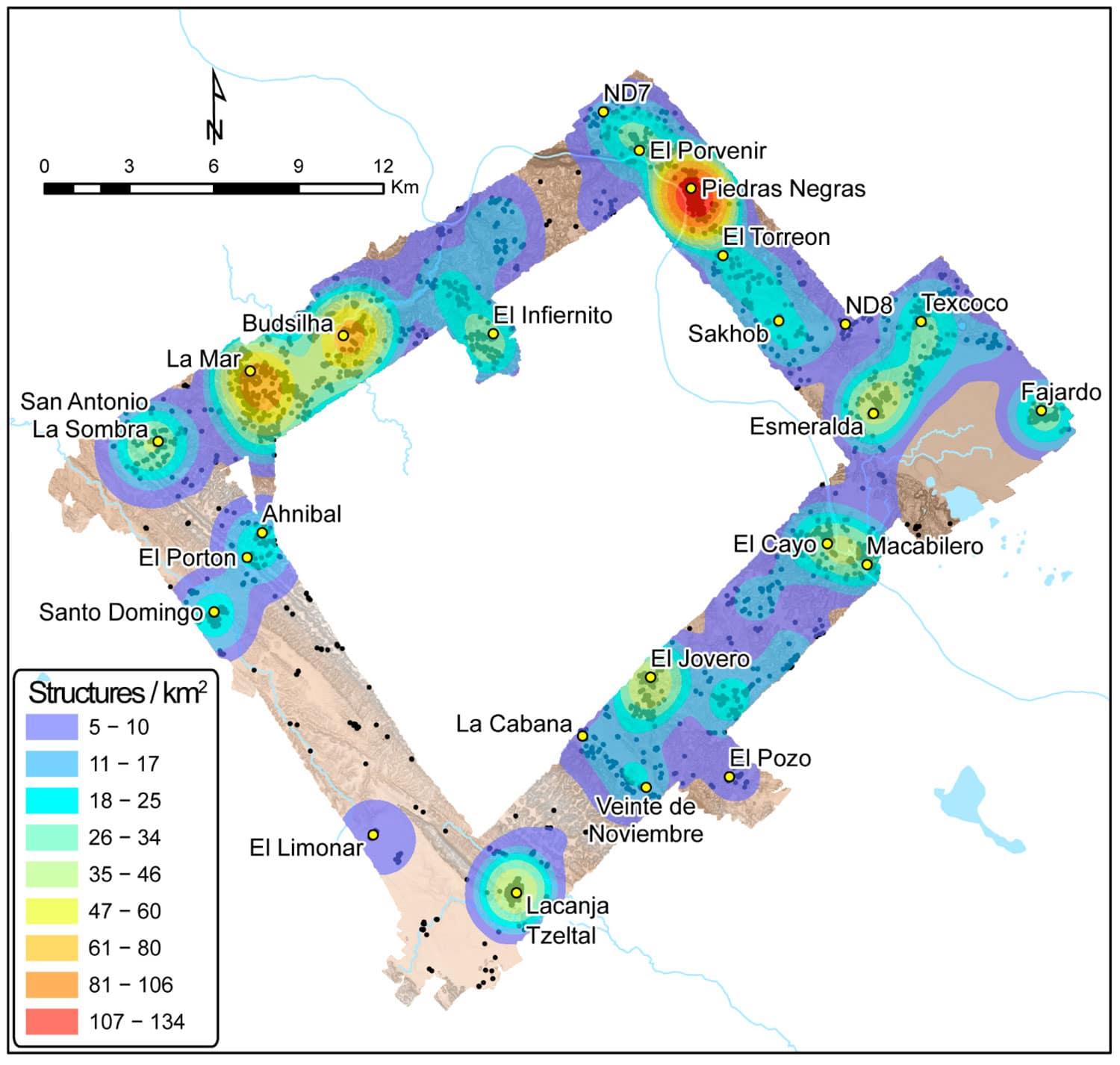
The lidar indicated signals of “agricultural intensification” — the alteration of land to boost the volume and predictability of crop production — in all three kingdoms. In ancient Maya kingdoms, where maize was the principal crop, agricultural intensification strategies included constructing terraces and developing water control systems with dams and channeled fields. The lidar, which penetrated the often-dense jungle, revealed substantial terracing and vast irrigation systems across the region, indicating that these kingdoms were not only prepared for population increase but also likely had food surpluses every year.
Maya farmers, the researchers explained, may have intended to produce surplus crops and prepare for population growth. Surplus food may have been sold in marketplaces as staples or as prepared food, Scherer added.
Today, Scherer said, significant parts of the region are being cleared for cattle ranching and palm oil plantations. But in areas where people still raise corn and other crops, they report that they have three harvests a year — and it’s likely that those high yields may be due in part to the channeling and other modifications that the ancient Maya made to the landscape.
“In conversations about contemporary climate or ecological crises, the Maya are often brought up as a cautionary tale: ‘They screwed up; we don’t want to repeat their mistakes,’” Scherer said. “But maybe the Maya were more forward-thinking than we give them credit for. Our survey shows there’s a good argument to be made that their agricultural practices were very much sustainable.”
The research group’s findings were published in the journal Remote Sensing.
Cover Photo: Lidar scans of the research area revealed the relative density of structures in Piedras Negras, La Mar, and Lacanjá Tzeltal, providing hints at these cities’ respective populations and food needs.The Brown University