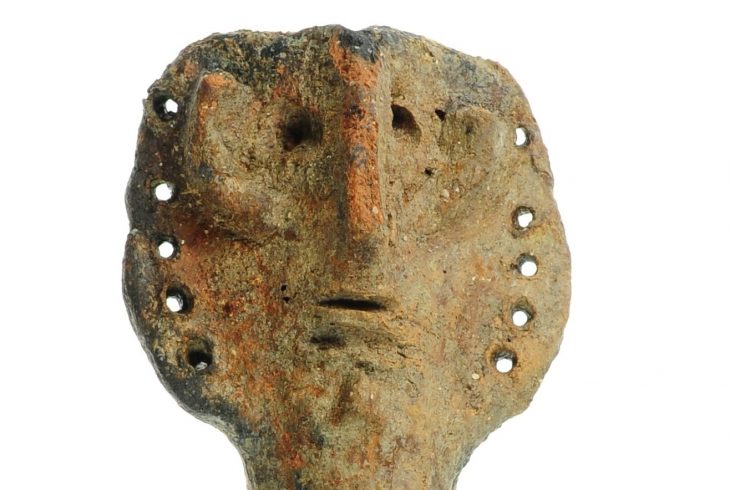
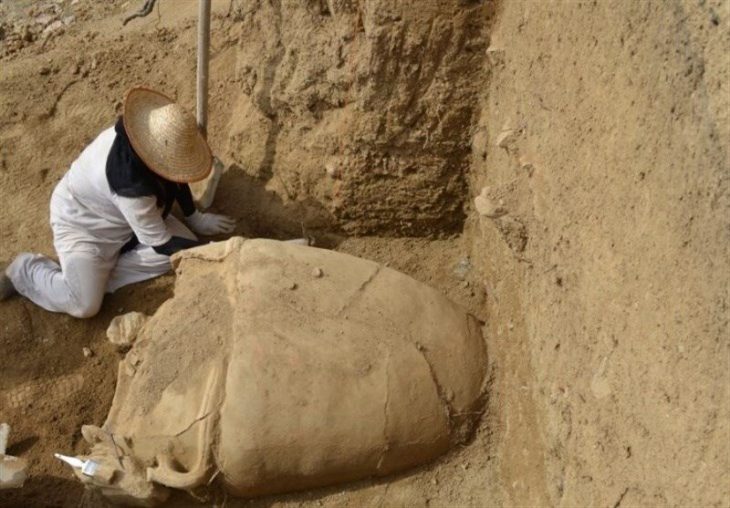
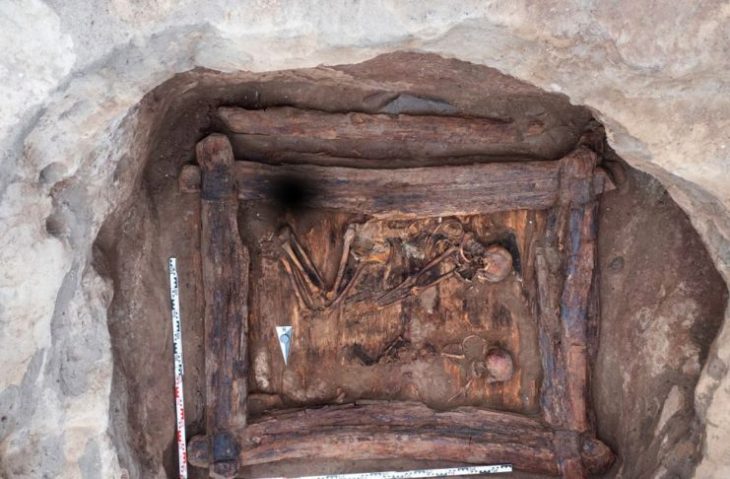
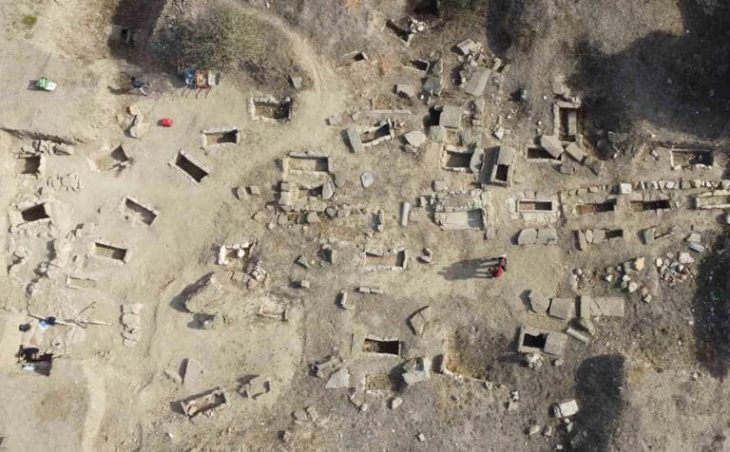
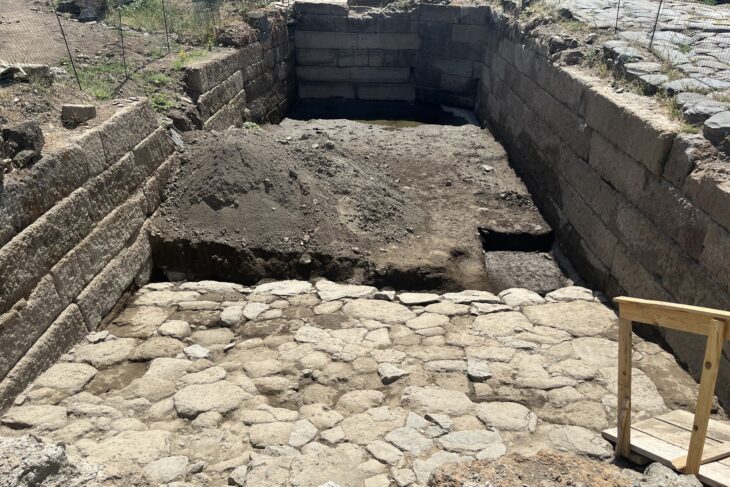
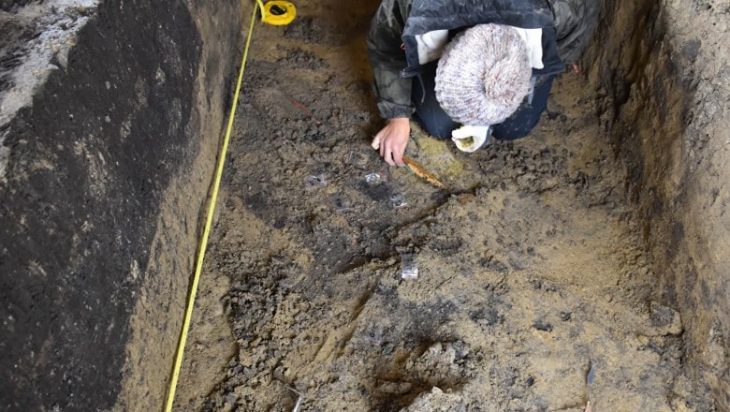
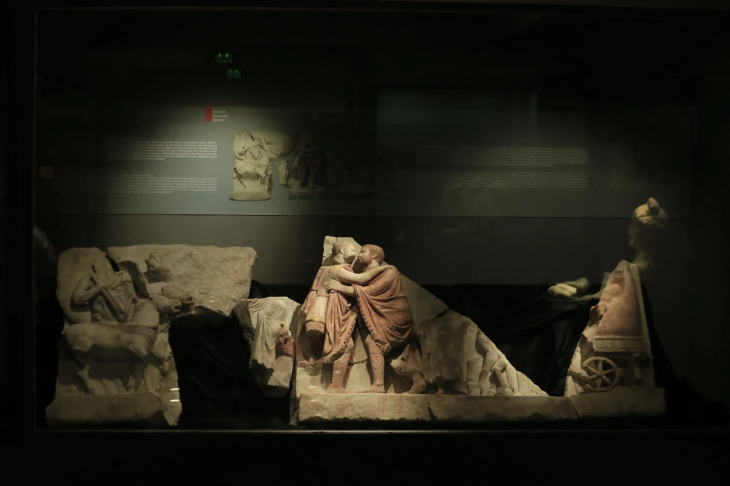
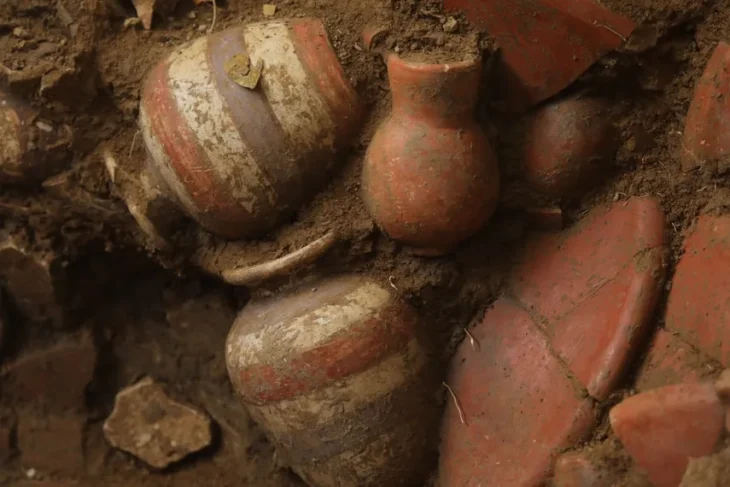
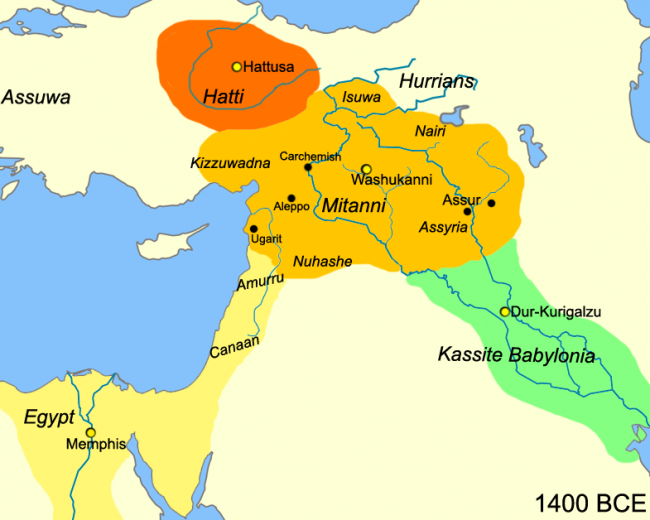
Hurrians; They became a state organization with a warrior and ruling class of Indo-Aryan origin who came from North-West Mesopotamia to today’s Mardin towards the end of the 16th century BC. This state was called Mitanni State as an official name.
A mixed people has emerged, in which the majority of the people are Hurrians and the ruling class consists of the Mitannis. The Land of Mitanni, where this mixed population lived, is approximate as of It became a major political power in the second half of the BC16th century. Mitanni kings adopted Hurrian as their language.
Vashukanni (Ṷašukanni), is capital of the Mitanni state. The Mitanni State began to be effective in the west of the Euphrates, thus becoming the third largest power in the political scene of the period, along with Egypt and the Hittite. Kirta and Shuttarna (Šuttarna), known as the oldest Hurri kings, are generally known from seal pressures’. The inscription “Šu-ut-tar-n [a] DUMU Ki-ir-ta LUGAL Ma-i-ta-ni” (King of Maitani, son of Kirta, Shuttarna (Šuttarna)) in stamp impressions found in Alalah (Alalaḫ) is being read. Kirta, mentioned in these tablets belonging to the period of King Sauştatar (Sauštatar); Using the seal belonging to Şuttarna (Šuttarna) perhaps indicates that this king was the founder of the Mitanni State.
The Mitanni geography is generally located between the Euphrates curve and the upper parts of the Tigris, with the triangle formed by the Habur branches in the middle. The Mitanni Dynasty, at its height, controlled the trade routes from Habur to Mari and from the Euphrates to Carchemish. The dynasty also held Control of the Upper Tigris in Ninive and the tributaries that feed it.
Mitanni allies, Kizzuwatna in Southeastern Anatolia; Mukish (Alalah – Açana) in the west of the Asi River, between Ugarit and Qanta; It is the Kingdom of Niya that controls the eastern shore of the Asi River from Alalah downwards to Aleppo, Ebla and Hama and from there to Qanta and Kadesh. Mitanni lands in the north of Syria are bordered by Eastern Anatolia in the west and extend to the Nuzi (today’s Kirkuk) and Tigris River in the east. It spread from Aleppo in the south to Mari on the Euphrates in the east.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
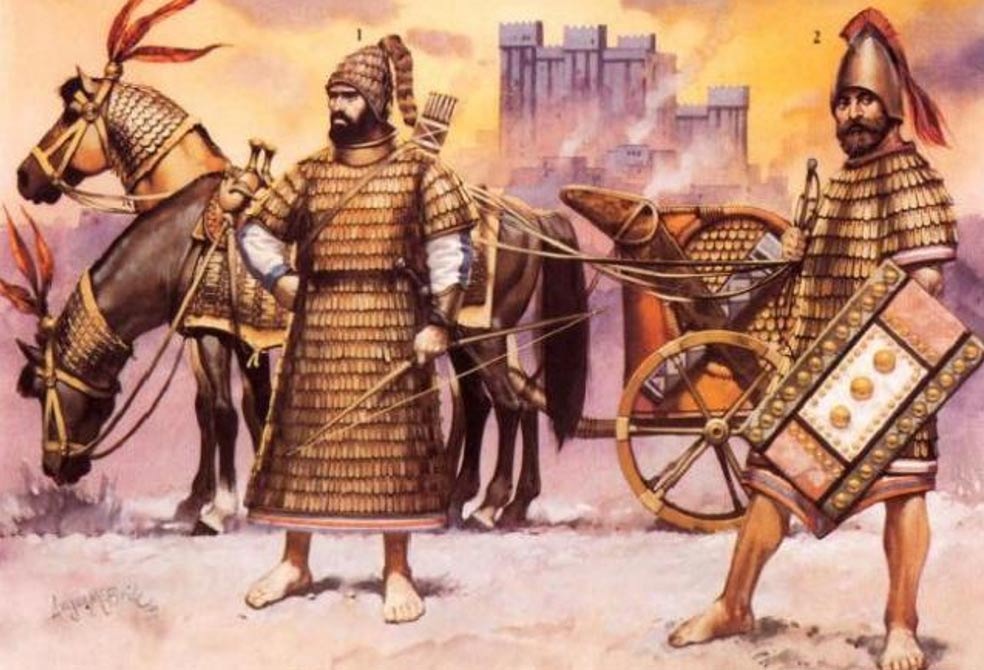
This whole region was suitable for agriculture. Cattle, sheep, horses and goats were raised, and the Mitanni were famous for horse riding and carriages. Using light chariots developed by themselves rather than solid wooden wheels, as the Sumerians used, enabled the cars to maneuver faster and more comfortably.
Today, the oldest horse training booklet in the world was found during the excavation of Hattusa archives near Boğazkale. This booklet dates from 1345 BC and consists of four tablets (1080 lines) and was written by a horse trainer named Kikkuli. In his introductory sentence, Kikkuli writes: “Kikkuli, the master horse trainer of the lands of Mitanni, speaks” and then details the appropriate training to be given to horses.
In the 16th century BC, the most well-known kings appear to be Kirta, Shuttarna and Barratarna. King Shaushtatar (reign about 1430) extended the borders of Mitanni to Alalah, Nuzi, Assyria and Kizzuwatna . During the period of III. Tuthmosis (1479-1425), Egypt defeated Mitanni in the city of Aleppo, which was under its rule, as a result of its long struggle to take the Syrian region under its control.
As part of the agreement between the Egyptian Dynasties and Mitanni in order to balance the power of the two nations, Taduhepa, the daughter of King Tushratta of Mitanni, and III. It was decided that Amenhotep would marry. This agreement was made during the power struggle between Tusratta and Shuttarna (also known as Artatama II), a relative of the former king, that continued in Washukanni. While Egypt supported Tushratta in this power struggle, Hittite King I. Suppiluliuma II. He supported Artatama.
Fearing the growing power of the Hittites, Tushratta stood tall to succeed, despite withdrawing Egyptian support. Another problem for Tušratta was that I. Suppiluliuma threatened the lands of Mitanni with his alliance with the king of Kizzuwatna. However, the move that made Tušratta ineffective was realized with the attack of I.Šuppiluliuma. Having achieved a successful result from this attack, I. Šuppiluliuma had a treaty text prepared in relation to the fate of Mitanni, in which the king to be ascended to the throne of Mitanni was determined.
It is understood from the text of this treaty that Tušratta’s son Mattiwaza (Šattiwaza) was appointed as the king of Mitanni.( (Letters of the Tusratta king of Mitanni, pp. 161-162). Suppiluliuma, with diplomatic weariness and the confidence of Egypt’s no longer reciprocating, directed his military forces to Washukanni and turned this city into ruins. Tushratta killed by his son; possibly to save the city with minimal damage. After this defeat, Mitanni was ruled by the Hittite kings.
As a result; After the capture of Wassukanni by the I Suppulium, the Hittites settled new rulers in Mitanni towns, and the Assyrians regained control of the region they lost to Mitanni. Tusratta was killed and his son Shattiwaza he became heir the Hittite Suppiluliuma (1344 – 1322 BC). At the same time, the rebel Artatama became the unimportant king of a reborn Assyrian led by Assyria-Uballit I (1364-1328 BC). Wassukanni, BC. It was recaptured by the Assyrian king Adad-Nirari around 1290.
During the period of its existence, the Kingdom of Mitanni has experienced many events and has had a great impact on the region where it is located and has become a kingdom that has made a name for itself.
Source: YILDIRIM, N. (2017) ‘‘ Mitanni Kralı Tuşratta’nın Mektupları Çerçevesinde Diplomatik Evlilikler Üzerine Bir Değerlendirme’’ s. 151-16
EDULJEE, K.E. (2005) ‘‘ Indo-Iranians Of Asia Minor’’