At a Chinese excavation site with Chinese and German researchers, evidence of a 2,700-year-old male facial cream was found. In their articles published in Archaeometry magazine, the group describes the items they found at the excavation site and the facial cream they discovered.
People have been using materials to color or alter their bodies for thousands of years. Evidence that Egyptians used cosmetics, for example, dates back over two thousand years, and women in China were found to use red cosmetic sticks to paint their faces by 1450 BC. As a result of this new study, researchers found evidence of the oldest use of cosmetics for Chinese men in the Liujiawa region in northern China. This is a cream that could have been used to make the face look white.
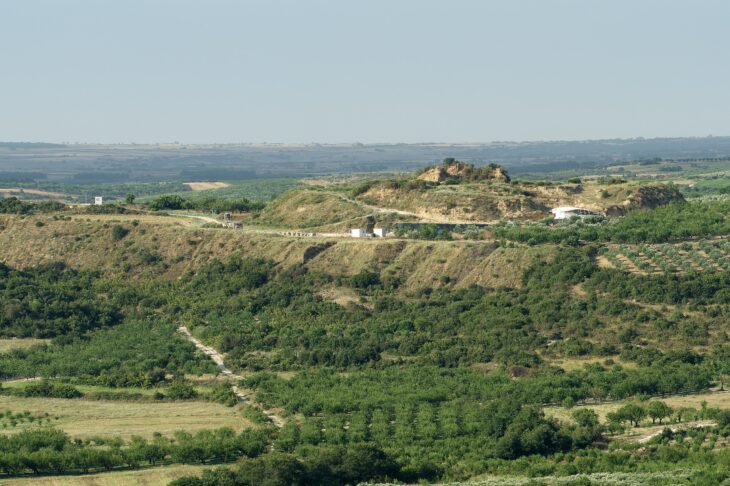
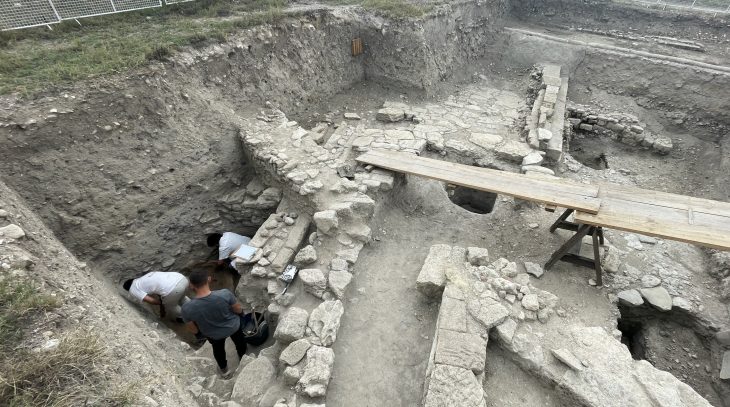
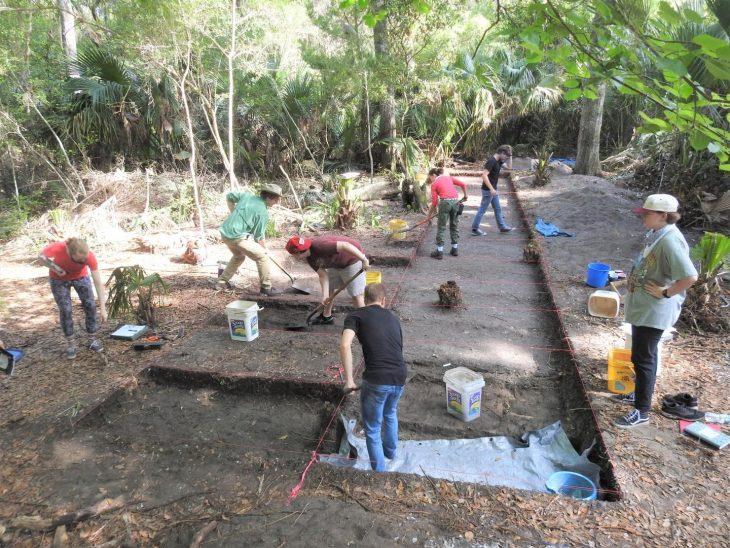
The team was working on part of the excavation site where the artifacts were dated to a point called the “Spring and Autumn period” in Chinese history. It includes a period of three hundred years between 771 and 476 B.C. The site was once home to a city called Liujiawa, the capital of a vassal state called Rui. The site was once home to a city called Liujiawa, the capital of a vassal state called Rui. The Spring and Autumn period ended when China was united under the Qin dynasty.
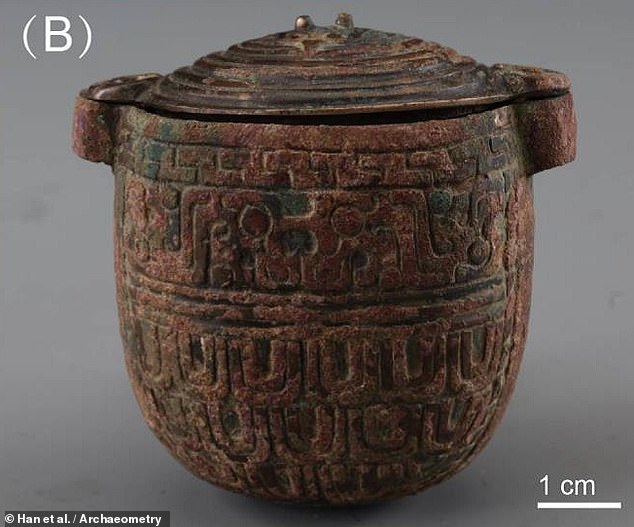

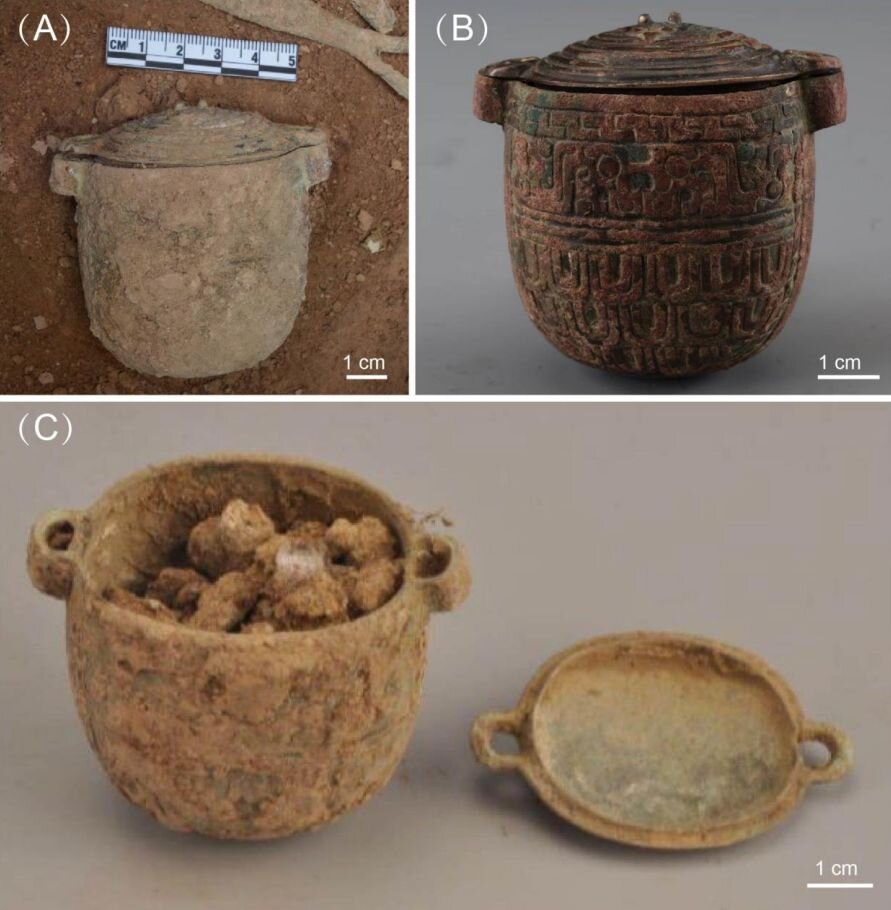
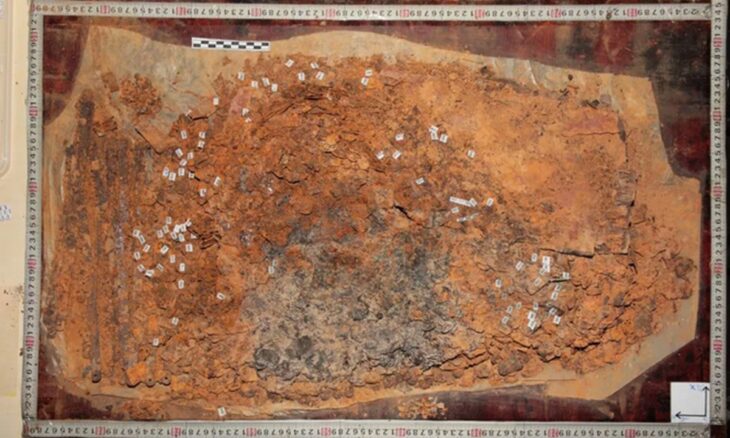
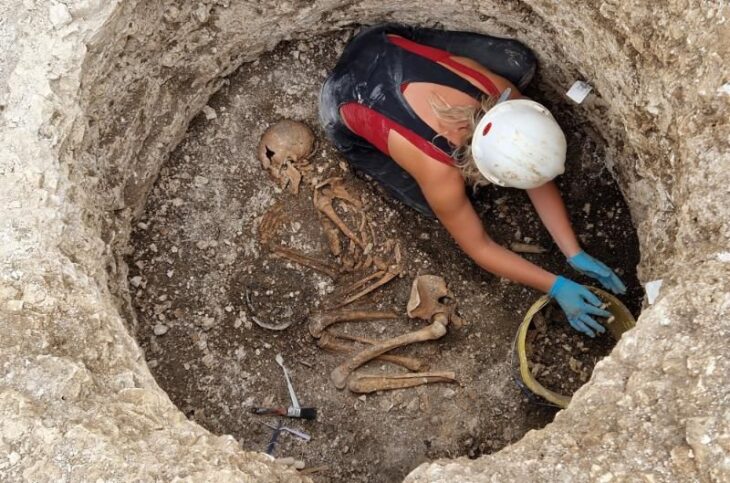
The researchers unearthed what they described as a Nobleman site at the site. They found bronze funeral weapons and a jar made of bronze, a soft, yellow-white material that researchers believe was a face cream. Analysis of the material showed that it is about 2,700 years old and was made from animal fat and lunar milk (a type of carbonate sludge found in some caves that turn into a white powder when dried, can be used as a cream). Researchers suggest that the nobleman used the cream on his face, perhaps as a different way to stand out from the public. They also suggest that it may have been used as part of religious ceremonies. Previous research had shown that caves were influenced by the religions of the time, which were believed to have minerals with magical properties.
The finding represents the earliest known use of a cosmetic for a male wearer in China.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
If the research interests you, you can visit the page below to read the full article. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/arcm.12659