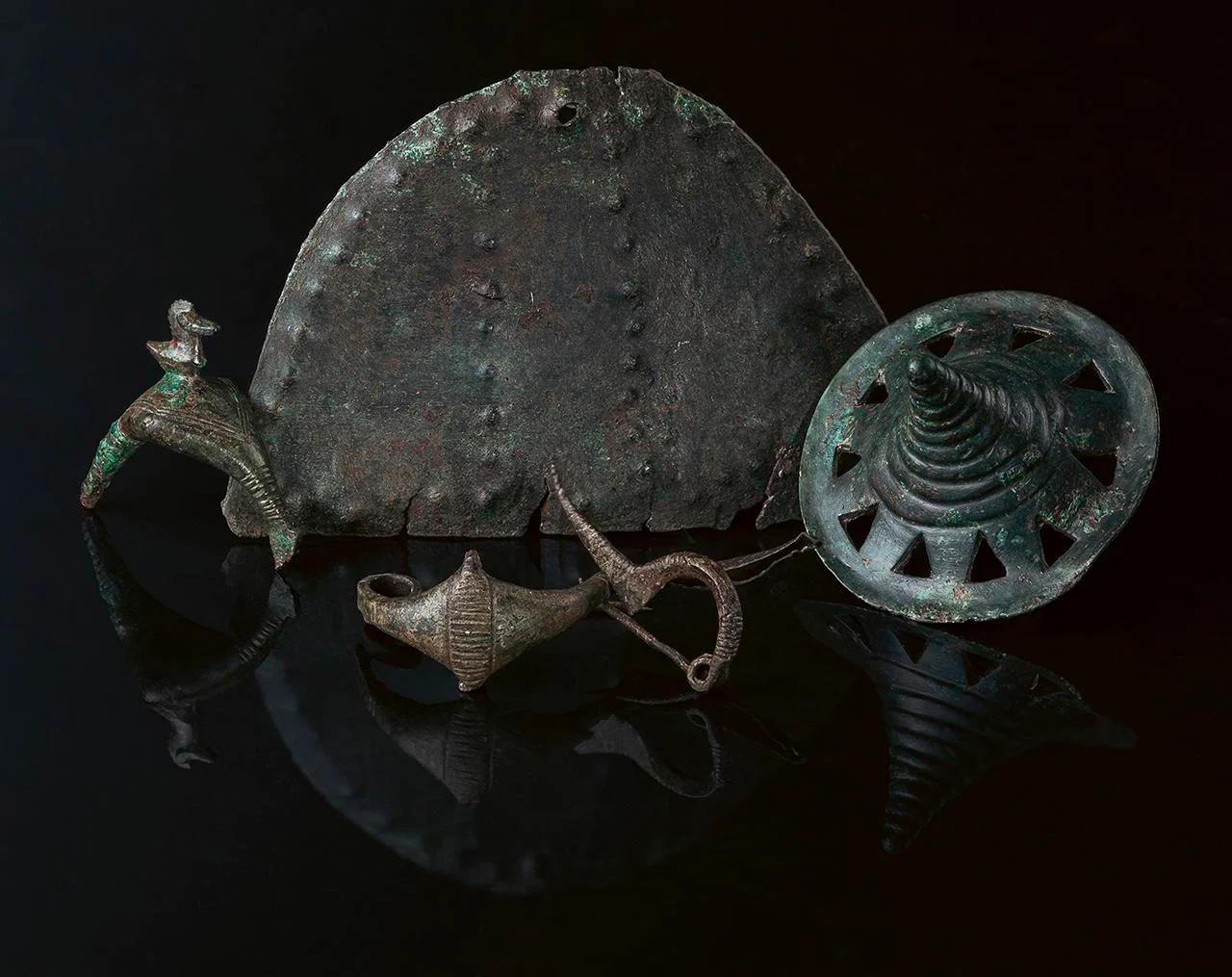
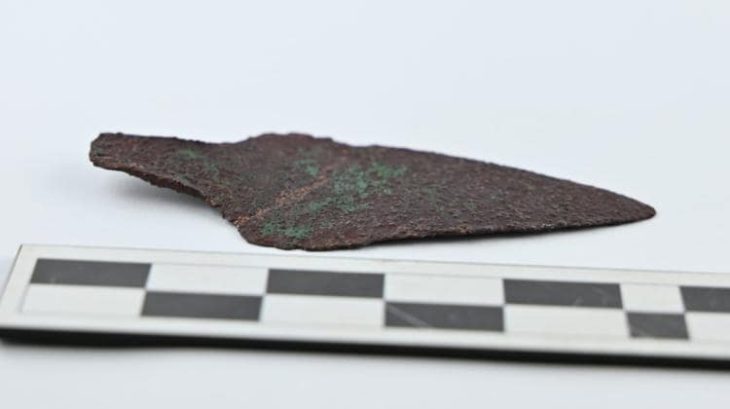
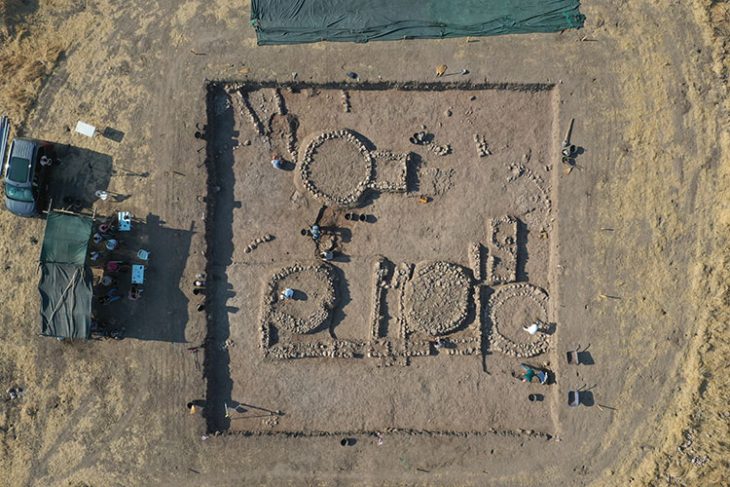A treasure trove of ancient metal artifacts, dating back over 3,000 years, has been unearthed at Somló Hill in western Hungary, shedding new light on the social and ritual practices of Bronze and Iron Age communities. The remarkable discoveries, comprising six distinct hoards, were made between 2023 and 2025 by archaeologists meticulously excavating the site. The findings, recently detailed in the journal Antiquity, highlight Somló Hill as a significant center during these pivotal periods.
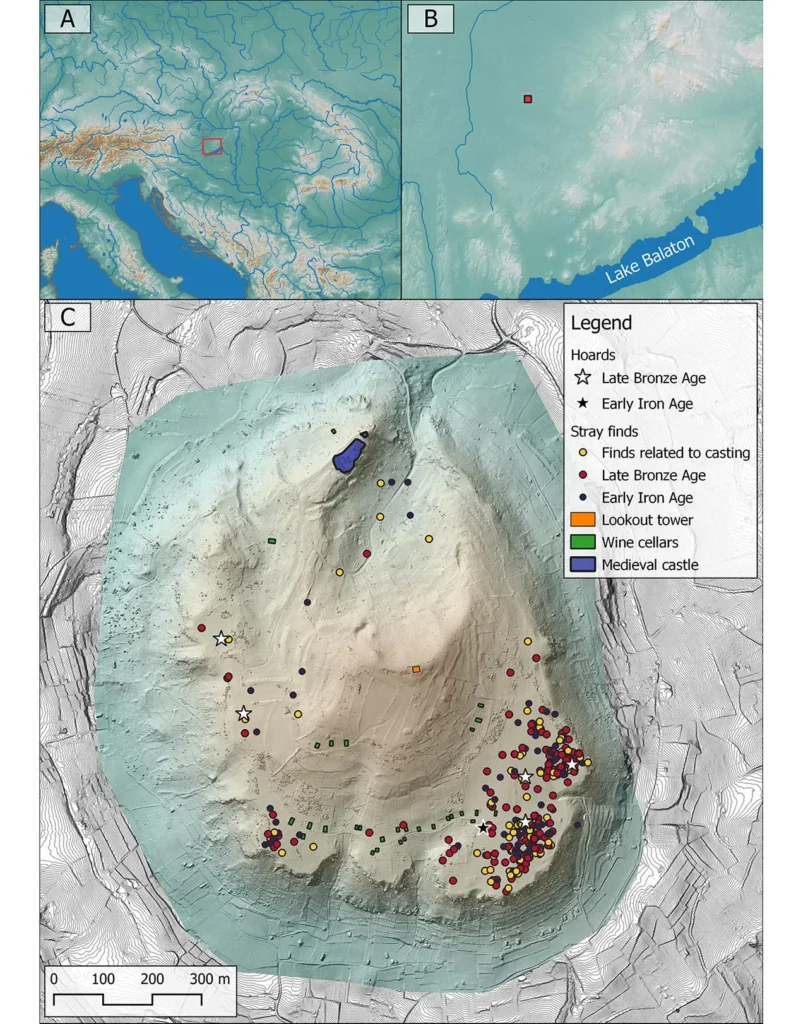
Rising prominently from the Veszprém County landscape, the 1,400-foot-high extinct volcanic butte of Somló Hill, now famed for its vineyards, has long hinted at its historical importance. While sporadic discoveries dating back to the 19th century suggested the site’s significance, systematic archaeological investigation remained limited until recent years. Now, a dedicated team led by archaeologist Bence Soós from the Hungarian National Museum’s Public Collection Center has revealed the hill as an exceptionally rich source of Late Bronze Age (1450–800 BCE) and Early Iron Age (800–450 BCE) materials.
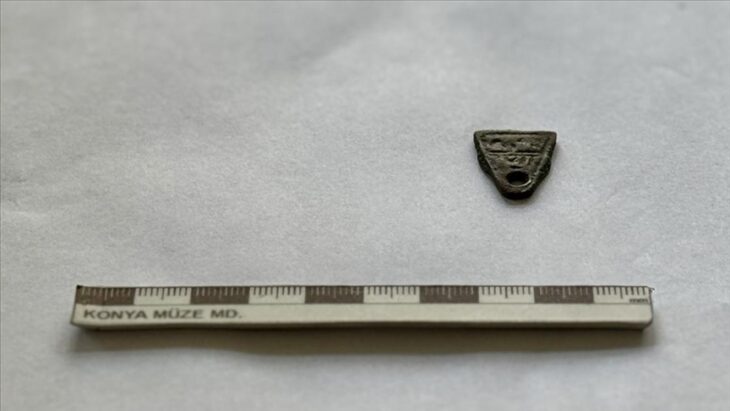
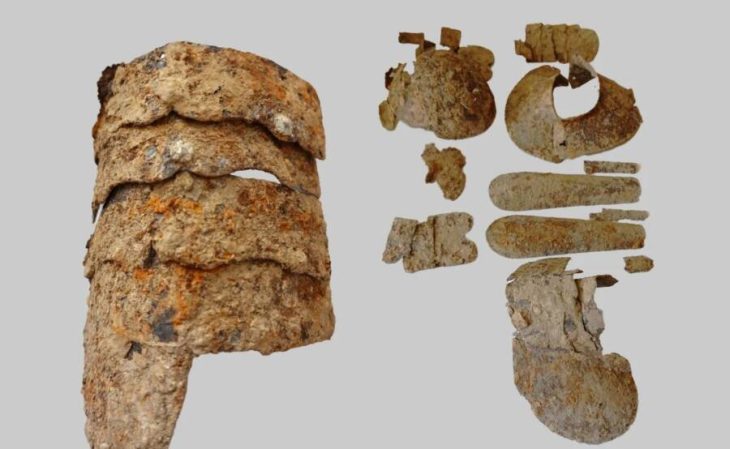
Employing cutting-edge survey techniques, including metal detecting, field-walking surveys, magnetic prospection, and airborne laser scanning (lidar), the research team meticulously mapped and analyzed the site. This comprehensive approach yielded over 900 metal objects, predominantly concentrated on the southeastern plateau of the hill. Notably, five of the six discovered hoards originate from the Late Bronze Age, with one dating to the Early Iron Age. These collections include an array of artifacts such as jewelry, brooches, decorative discs believed to be military adornments, and a rare Alpine-type spearhead found within Hoard I.
The exceptional preservation and depositional context of these finds are particularly noteworthy. In a groundbreaking discovery for the region, two of the hoards (III and V) were found carefully buried within ceramic pots – a practice long suspected but never definitively confirmed for this period in western Hungary. These ceramic vessels were meticulously excavated and subsequently subjected to computed tomography (CT) scanning at the University of Pannonia to analyze the internal arrangement of the objects. Furthermore, neutron tomography was performed on select artifacts to gain insights into their manufacturing techniques and identify any potential flaws.
Soós emphasized the unique significance of Hoard V, stating that it provides “the first evidence of local metal deposition customs during the transition between the Late Bronze and Early Iron Ages.” Beyond metalwork, this hoard also contained amber beads, pig and boar tusks, and fragments of textiles and leather, underscoring the intricate ritualistic nature of these deposits.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The continuous occupation of the hilltop during this transitional period, as evidenced by the hoards, challenges existing assumptions about settlement patterns in the region, according to the study’s authors. Ongoing typo-chronological and radiocarbon dating analyses, particularly of organic materials such as the bones discovered in Hoard I, are expected to establish a more precise timeline of the site’s occupation.
The deliberate organization and layering of objects within the hoards suggest a sophisticated system of ritual and symbolic behavior, potentially linked to an elite warrior class. Soós and his colleagues propose that Somló Hill offers a unique opportunity to redefine our understanding of hoarding traditions during the Hallstatt B period in Transdanubia.
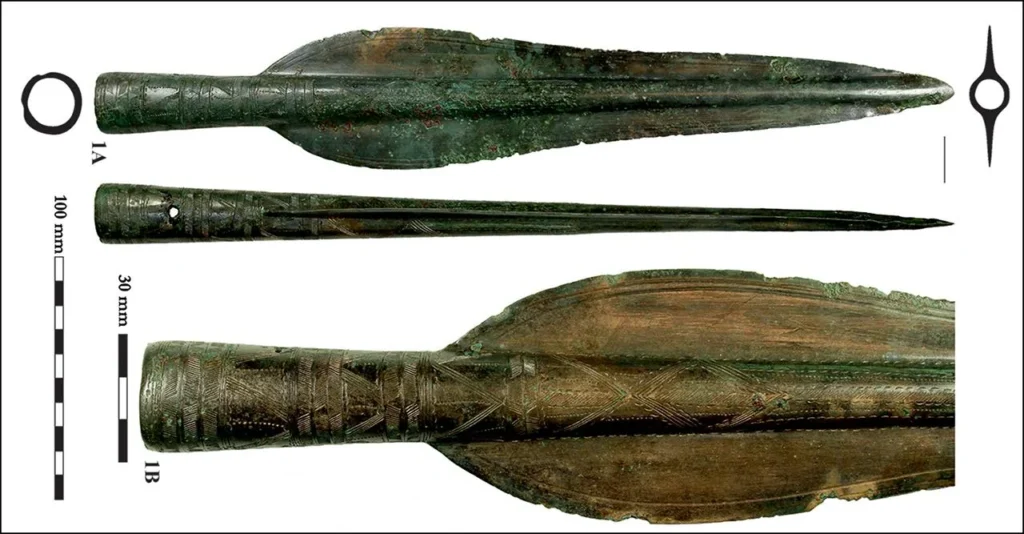

Furthermore, the research supports the idea that Somló Hill may have served as a central place within the Late Bronze Age settlement network, possibly functioning as a power center for tribal or clan societies. This is corroborated by earlier discoveries of monumental burial mounds in the vicinity, indicating the presence of high-status individuals. While the team has yet to confirm the existence of a metal-producing workshop, the unearthing of building fragments hints at a more permanent settlement.
The ongoing investigations at Somló Hill promise to further illuminate the chronology of its habitation and the fascinating traditions of metal hoarding that characterized this significant ancient site. Researchers are hopeful that future work will continue to unravel the mysteries held within this lone volcanic hill.
Soós, B., Péterváry, T., Mesterházy, G., Látos, T., Pető, Á., Pethe, M., … Tarbay, J. G. (2025). Later prehistoric hoarding and habitation on Somló Hill, western Hungary. Antiquity, 1–8. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.44
Some of the metal artifacts from the Early Iron Age discovered on Somló Hill, Hungary (photograph by László György). Credit: Bence Soós et al., Antiquity (2025)