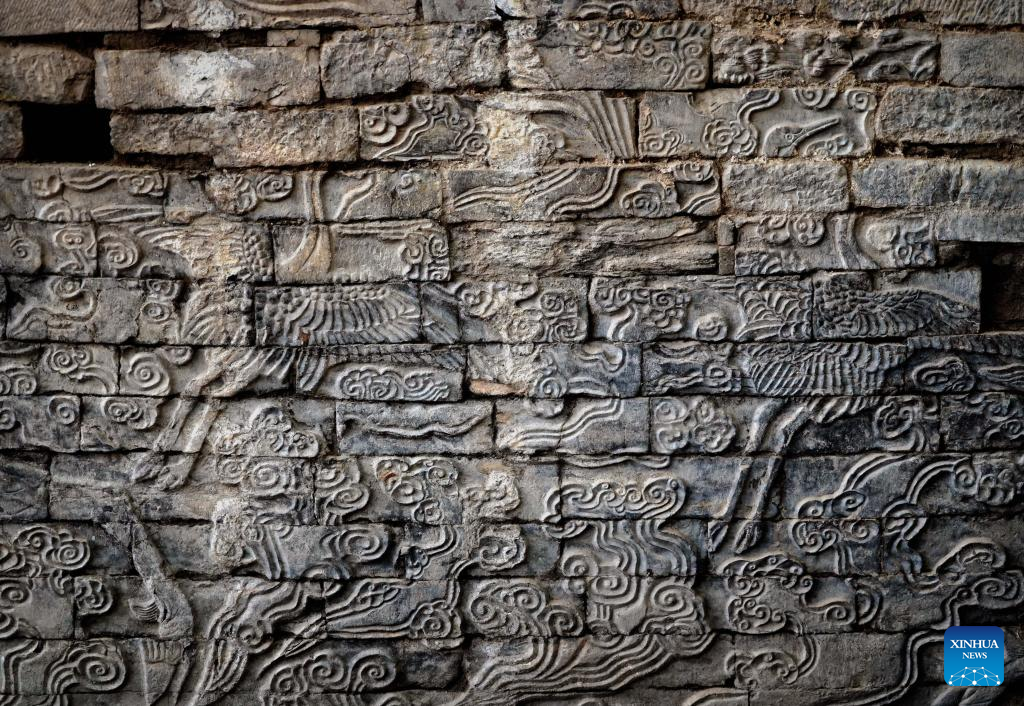
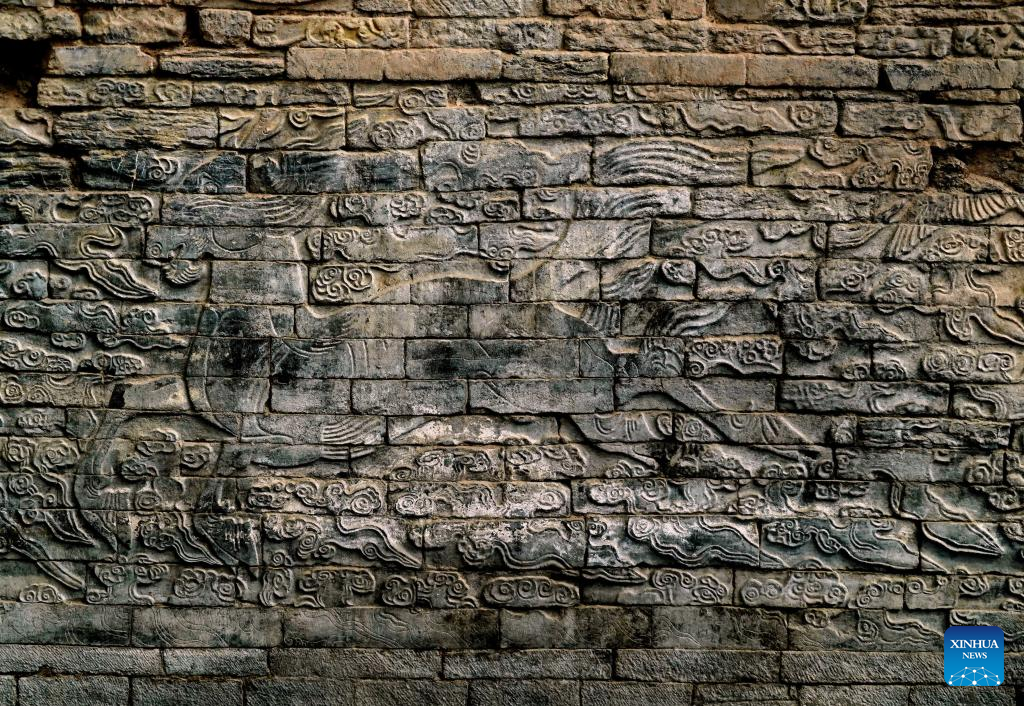
Two stone murals from the Northern Song Dynasty (960-1127) have been discovered in Henan Province, central China, and are the largest of their kind ever discovered in the country.
China’s Song dynasty (960-1279) saw enormous scientific advances, a flourishing of the arts, and an increase in the popularity of trade guilds, paper currency, public education, and social welfare. The Song dynasty era, along with its predecessor, the Tang dynasty (618-906), is regarded as a defining cultural epoch in imperial China’s history.
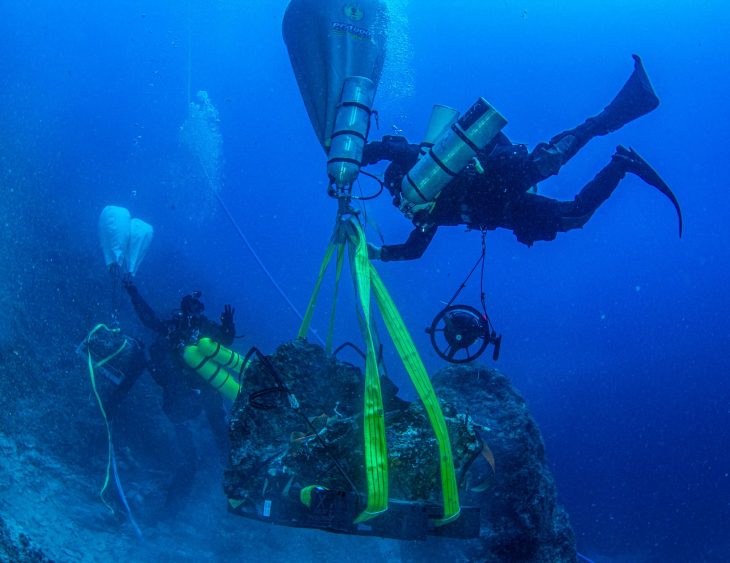
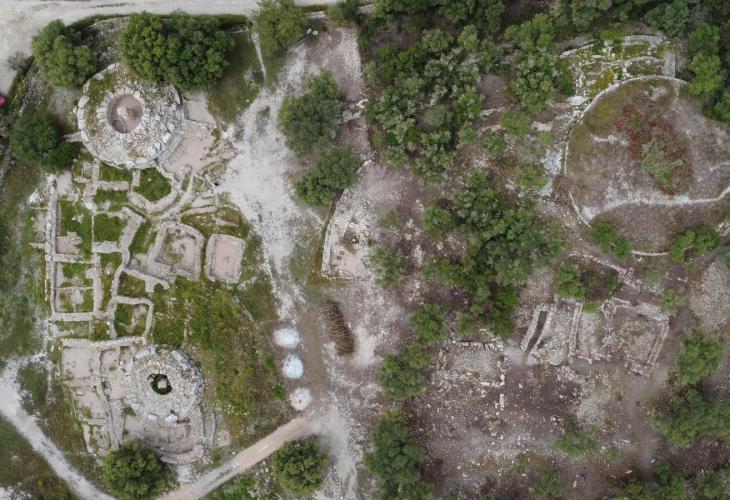
The murals, discovered in Kaifeng City’s Zhouqiao relics site, are symmetrically distributed along the northern and southern banks of the Zhouqiao Bridge’s east side.
The murals are 3.3 meters in height, and it has been revealed that the excavated length of the south bank mural is 23.2 meters, while that of the northern one is 21.2 meters. The stone murals are engraved with auspicious patterns of traditional Chinese culture such as seahorses, flying cranes, and clouds.

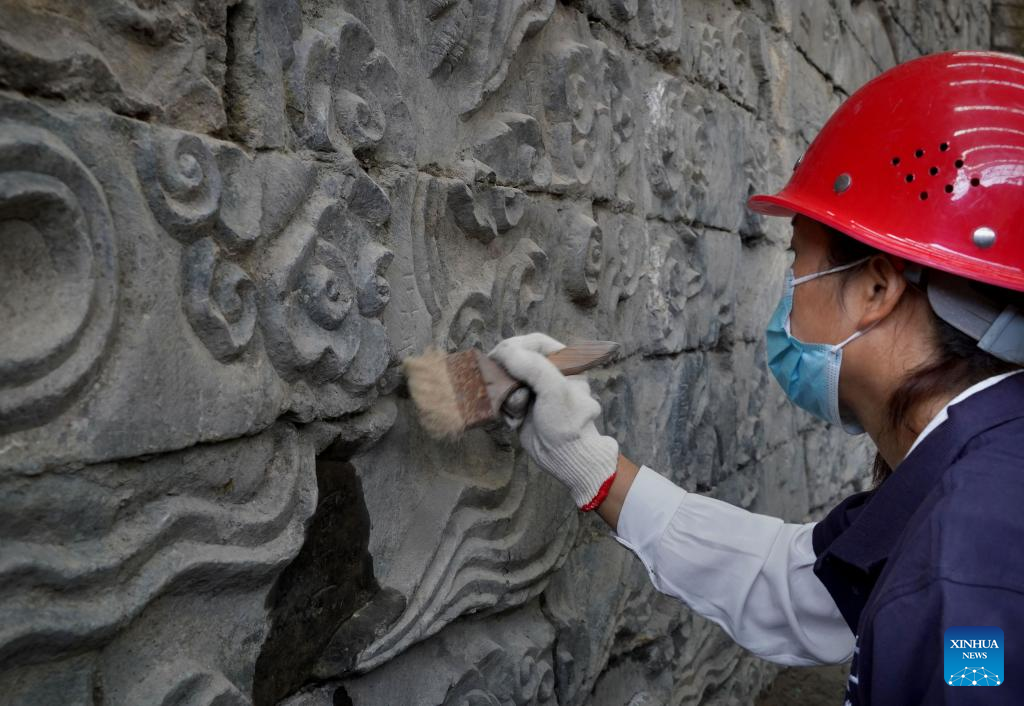
Further excavation and cleanup work is still ongoing, according to Zhou Runshan, the excavation project’s head, who added that the total length of a single mural is estimated to be around 30 meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It is estimated that the total length of the stone murals is expected to reach about 100 meters and the total carved area will reach around 400 square meters upon complete excavation of the murals on both east and west sides of the bridge, Zhou added.
“In terms of scale, subject and style, the stone murals can represent the highest standards of the stonework system and the highest level of carving techniques during the Northern Song Dynasty,” said Zheng Yan, a professor at Peking University’s School of Arts.
“It is an important discovery that enriches and rewrites the art history of the Song Dynasty,” he said.

Artists of the Song dynasty experimented with novel themes and methods in ceramics and painting. Paradoxically, the Song’s fascination with science and meticulous world observation led to large-scale, grand landscape paintings that meticulously explore the world. Porcelain techniques and new glazes both flourished. It seems that they were also quite good at stone processing techniques.
Zhouqiao Bridge was built between 780 and 783 in the Tang Dynasty (618-907) across the Grand Canal, a vast waterway connecting the northern and southern parts of China. It was a landmark structure in the central axis of Kaifeng City and was buried in 1642 by mud and sand due to the flooding of the Yellow River. Archaeological excavation of the Zhouqiao site was launched in 2018.
So far, a total of 4,400 square meters of the site have been excavated, and 117 sites of remains and ruins have been found.