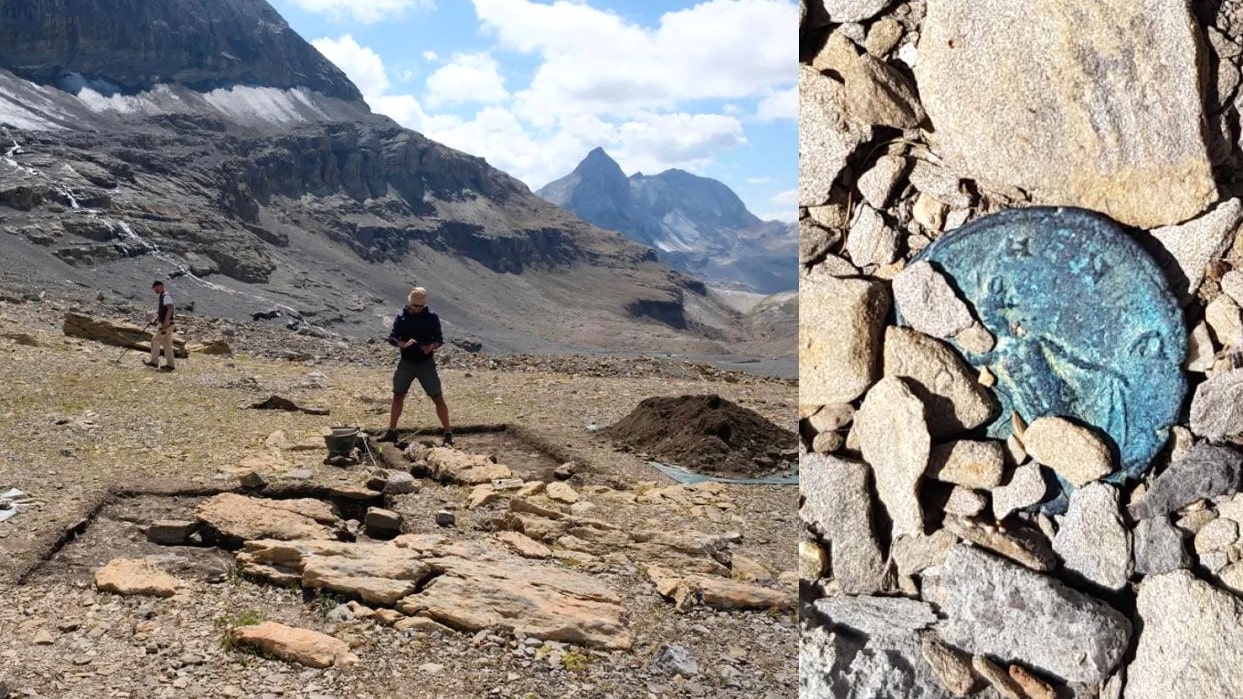
A trekking enthusiast stumbled upon an ancient Roman coin buried in rubble in a remote area high in the Alps in the Swiss Canton of Bern.
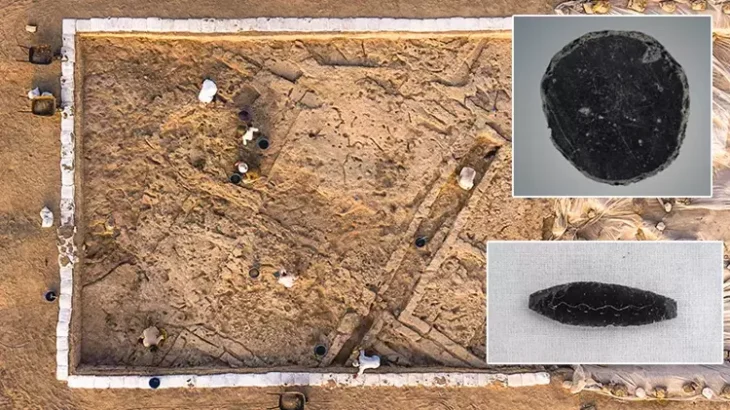
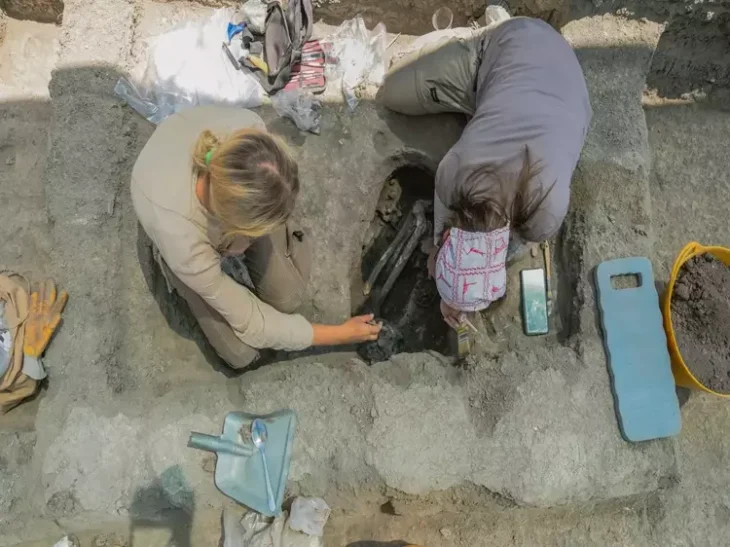
After reporting the finding to the local archeological unit, a whole hoard of ancient artifacts was found buried at the site, which archeologists now believe may have been a place of holy worship—a site to lay offerings to the Roman mountain gods.
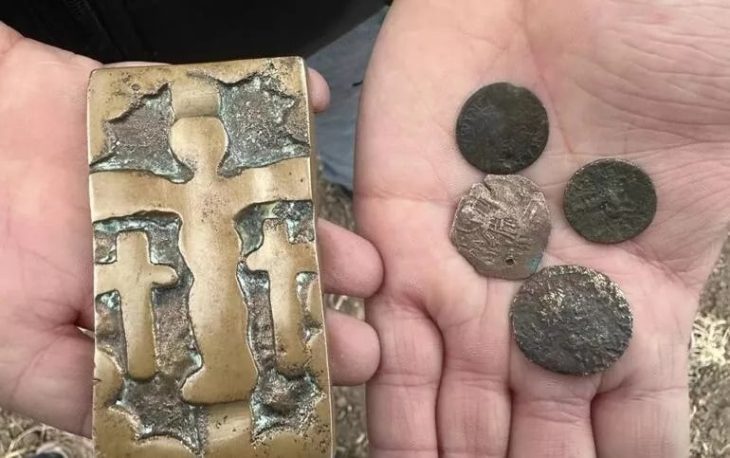
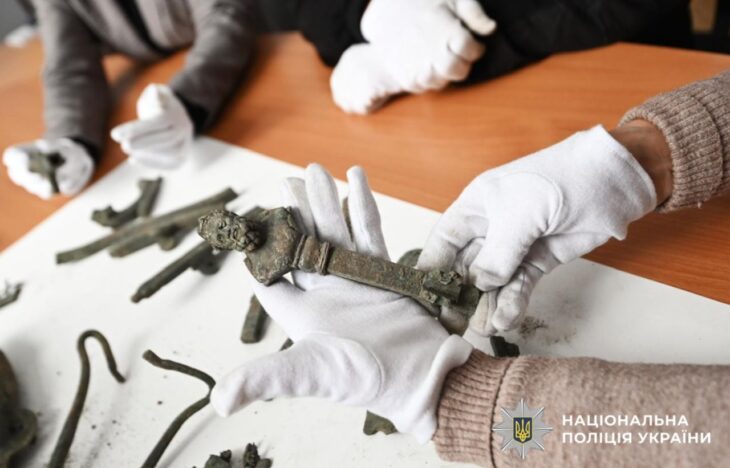
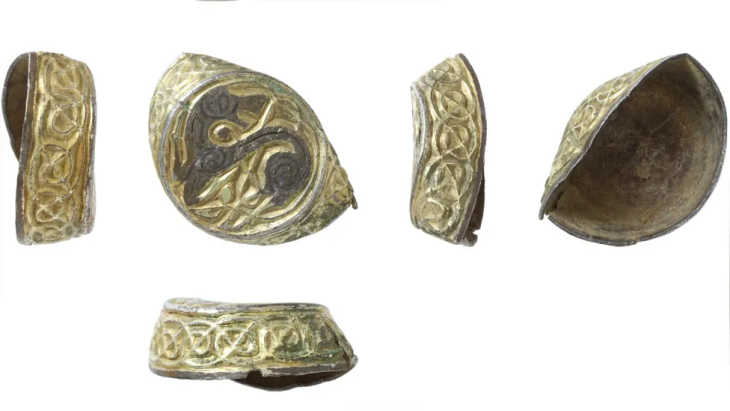
Since the hiker’s fortunate discovery, archaeologists have conducted two dig seasons and discovered one hundred additional Roman coins dating from the first to the fifth century A.D. The oldest is a Tiberian coin from 22 to 30 AD, and the most recent is an Arcadian coin from the eastern empire (r. 395-408 A.D.). A fibula from the first century B.C., 59 Roman shoe hobnails, and a piece of a bronze votive plate in the shape of a leaf were also discovered by the team.
“We do find single Roman coins occasionally in the Alps, but this site is unusual because of the amount of coins and the location,” Regula Gubler, the study’s scientific project manager, told Newsweek. “More common would be finds—coins, brooches—on mountain passes. This site however, is far from human habitation, today and in Roman times, at 2,590 meters above sea level [nearly 8,500 feet], and definitely not a pass.”
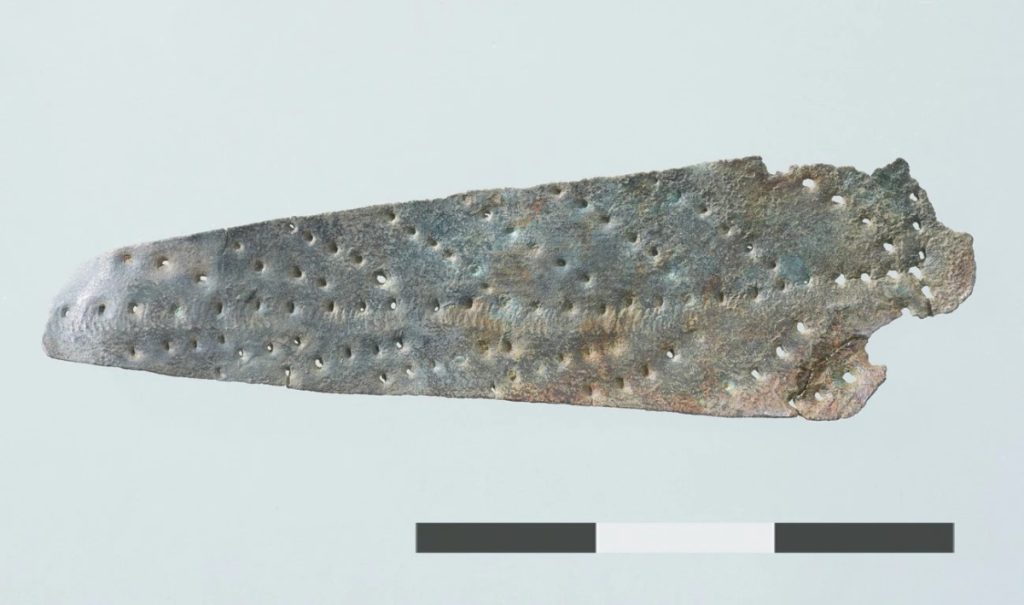

Gubler said that the site sits on a plateau between the mountain peaks of Ammertenhorn and Wildstrubel, which she described as “pretty impressive.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The unusual location of the site, as well as the concentrated collection of treasures that had amassed there, led the researchers to believe that this was a place of great religious significance.
“We are only at the beginning of the investigations, but we think it is a holy place, where people went to deposit votive offerings—mainly coins, but also other objects—asking the deities for things or thanking them,” Gubler said. “I guess a kind of pilgrimage.”

The town of Thun, which has several Roman temples, is only a little more than 12 miles away from the site. One of them contains an inscription that mentions female alpine deities, according to archaeologists.
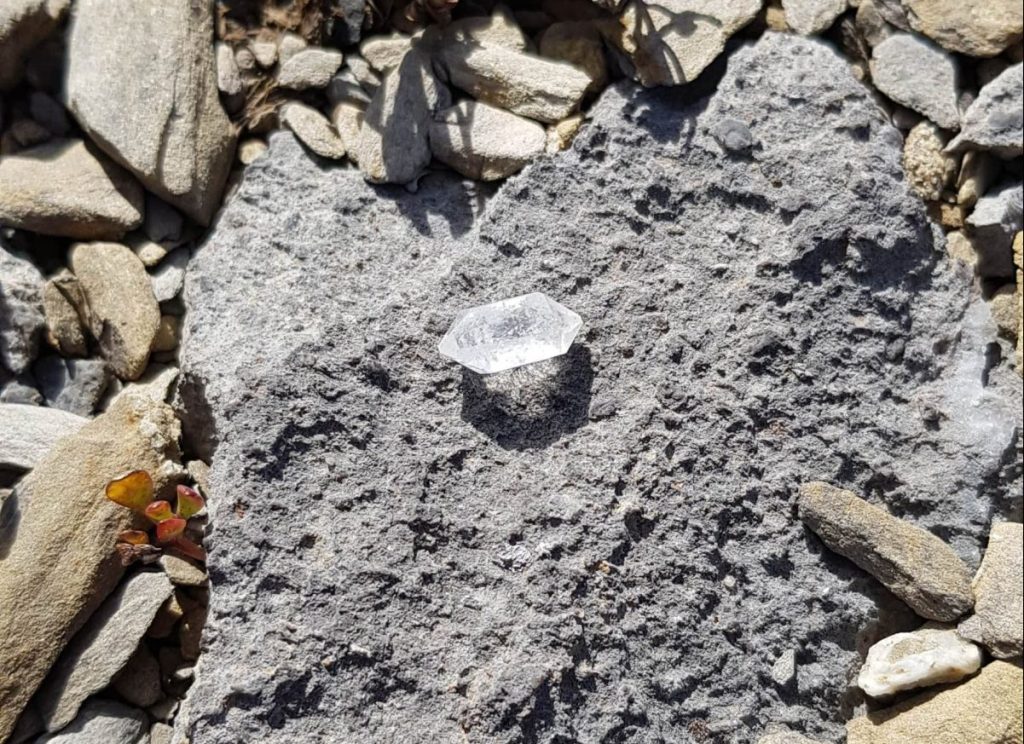
The prevalence of local rock crystals may have been part of the reason the location was seen as sacred.
The researchers will continue to investigate the site in order to learn more about its possible historical significance.
Cover Photo: Archaeological Service of the Canton of Bern