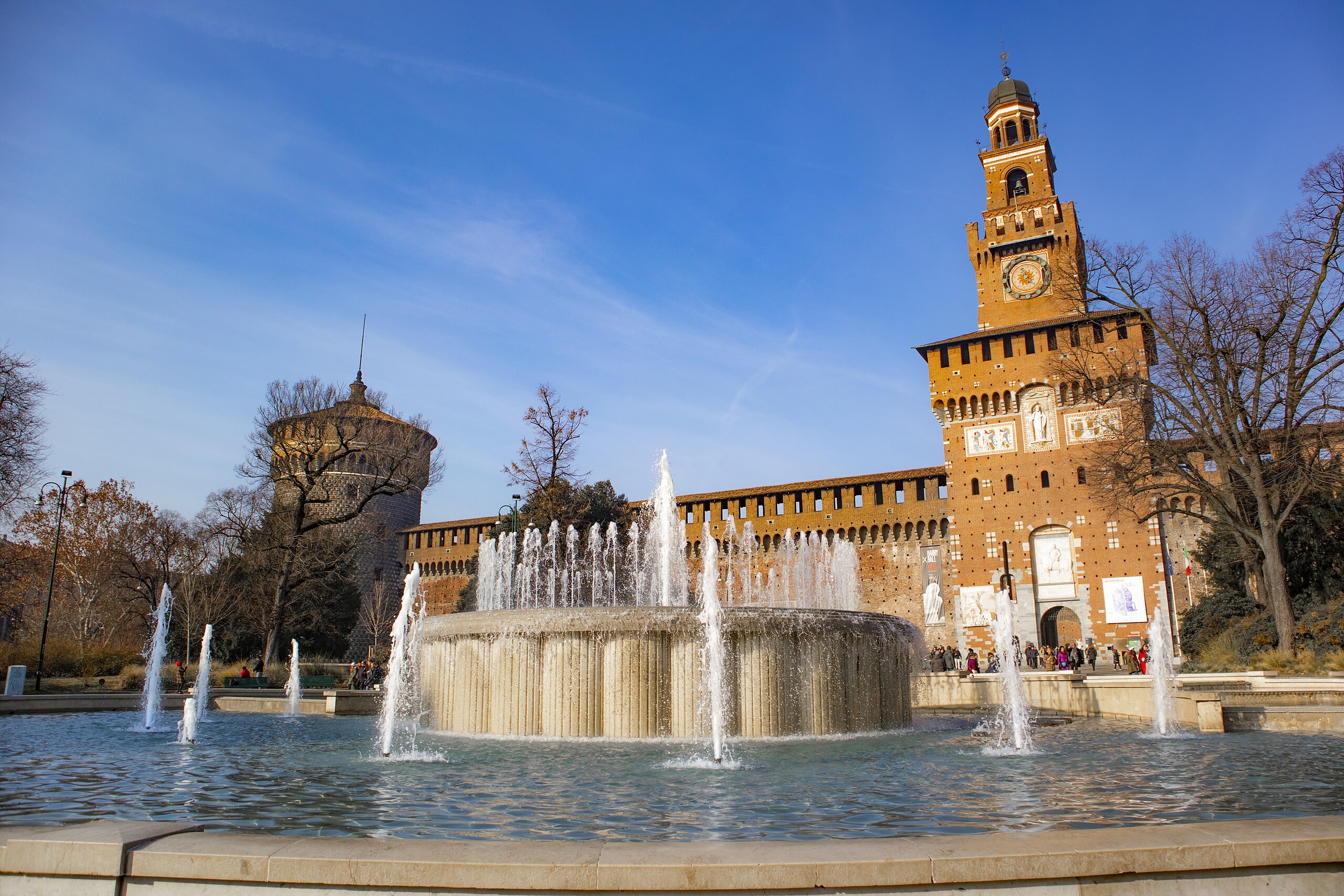
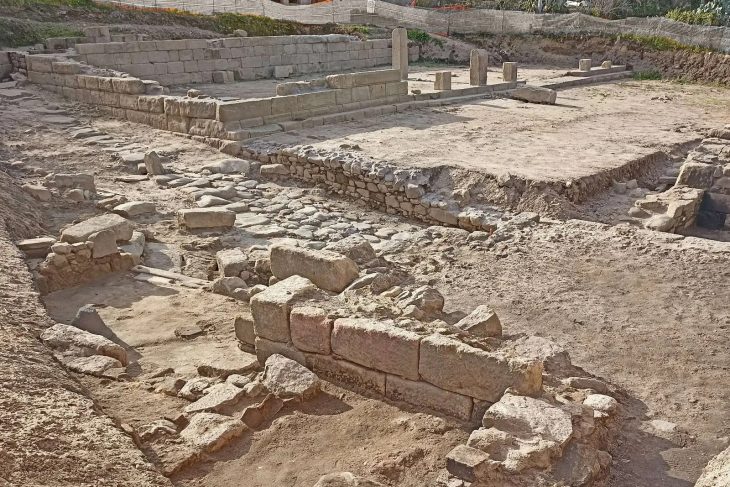
As part of a PhD thesis, an innovative technological investigation conducted by the Politecnico di Milano, in collaboration with the Sforza Castle and with the technical support of Codevintec, revealed numerous hidden passages under the Sforza Castle. These structures hint at secret passageways depicted in the drawings of renowned artist and engineer Leonardo da Vinci.
As a symbol of Italian history, the castle has long captivated the attention of historians, engineers, and architects. Since its construction in the 15th century, it has functioned as a fortress, residence, and seat of power in Milan.
According to researchers from the Politecnico di Milano (Polytechnic University of Milan), some of the tunnels were probably used by the military, while another that was formerly connected to a nearby church was used by a grieving duke to sneak into his wife’s grave.
Numerous legends have been created over the years regarding its underground chambers. In one of these stories, Ludovico il Moro, Duke of Milan, is said to have visited his wife, Beatrice d’Este, through a secret passageway. Renowned polymath Leonardo da Vinci’s drawings also featured the underground passage.
The duke is said to have never fully recovered from the loss—entering, in the words of the historian Luciano Chiappini, “an almost maddening mourning” (involving the deification of his wife, around which he created something of a cult) that is suspected to have contributed to his downfall a few years later.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
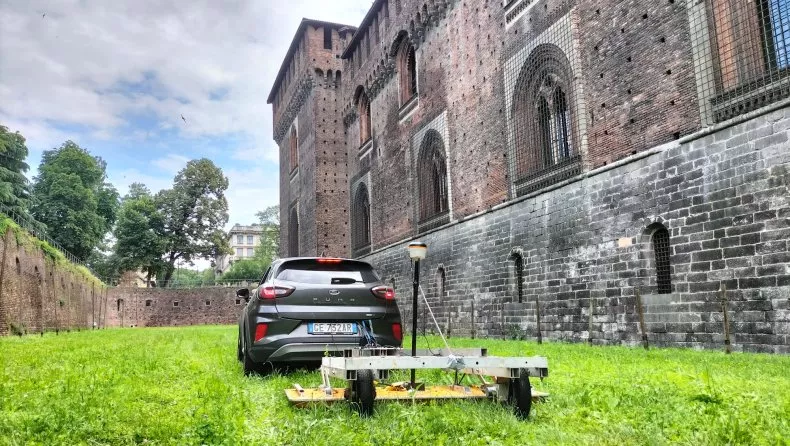

This passage, immortalized in Leonardo’s drawings, now, thanks to technology, it seems that its existence can be confirmed. But there are numerous secret walkways.
Now, a study applying advanced ground-penetrating radar technology provides fresh evidence that such underground corridors and similar architectural features may indeed exist beneath the castle.
The investigation used advanced technologies, including ground penetrating radars and laser scanners, to accurately map and document the Castle’s subsurface and its underground structures. These instruments made it possible to reveal cavities and underground walkways at a depth of a few decimeters.
“The aim is to create a digital twin of the Sforza Castle,” said Franco Guzzetti, a geomatics professor at the university, in a statement.
This, he added, will be a model “that not only shows the current appearance of the castle, but also allows us to explore the past by revealing ancient structures that are no longer visible.”
The information gathered has not only provided historical documentation but also created new prospects for the Castle’s tourism development. Visitors would be able to explore underground spaces and inaccessible historical locations through the use of augmented reality technologies and the development of virtual pathways, providing an immersive experience that blends innovation and history.
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia Commons CC BY-SA 4.0