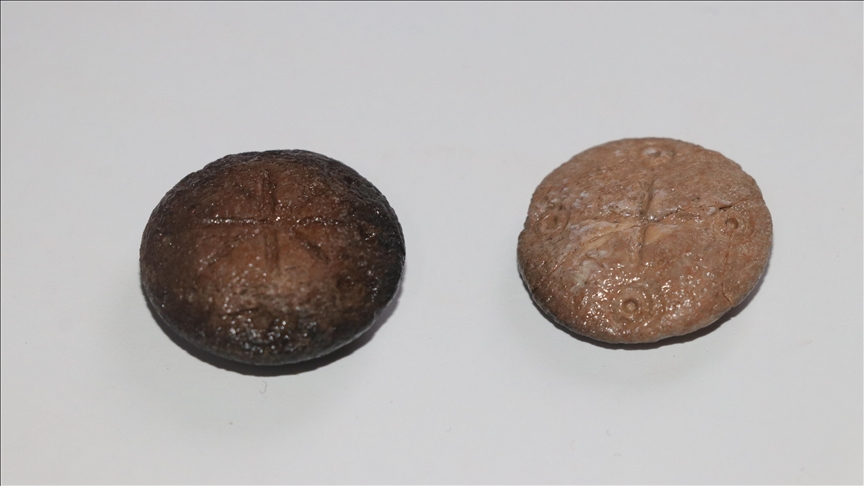
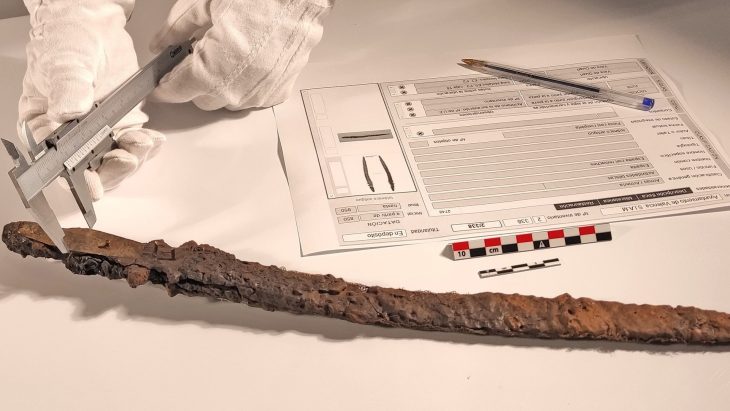
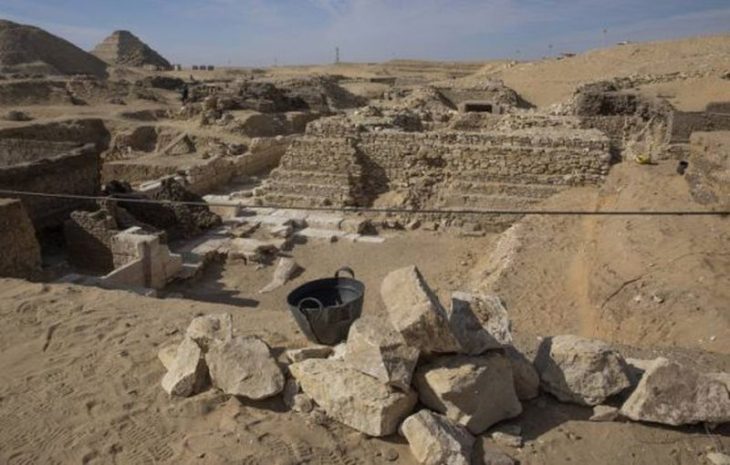
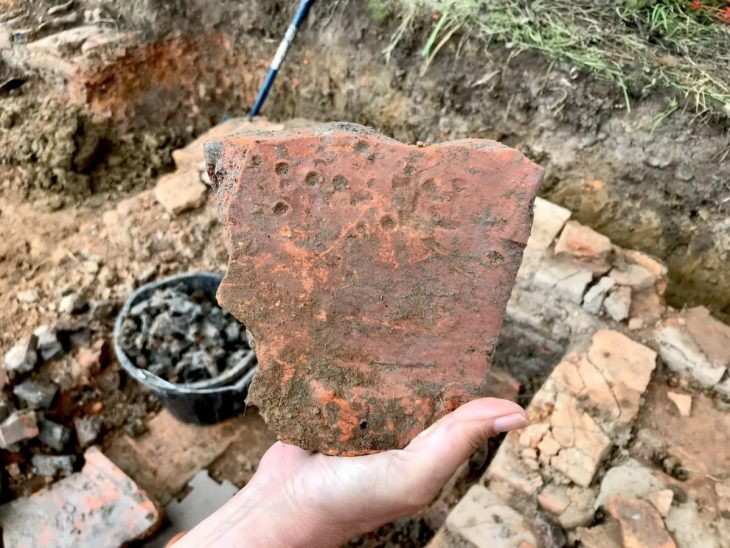
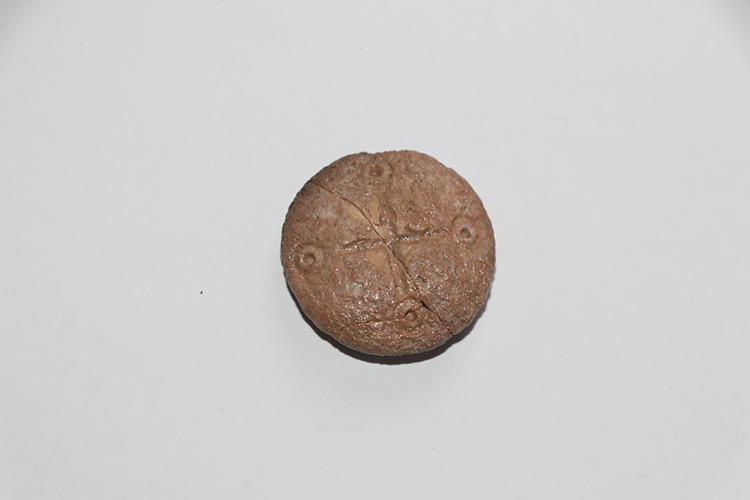
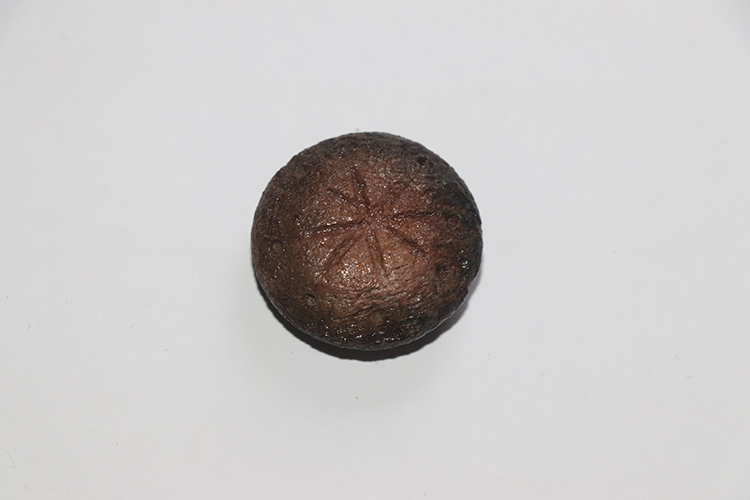
During the excavations in Hadrianopolis Ancient City in Eskipazar district of Karabük, 2 bone game stones belonging to the military strategy game, which are thought to belong to the 5th century, were unearthed.
Hadrianopolis in Paphlagonia was a city in southwestern Asia Minor, located approximately 3km west of the modern town of Eskipazar in the Karabuk Province. The city was named after the Roman emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century AD. The city of Hadrianopolis is also known as Caesarea and Proseilemmene and is famous for being the birthplace of two saints: Alypios the Stylite, and Stylianos of Paphlagonia.
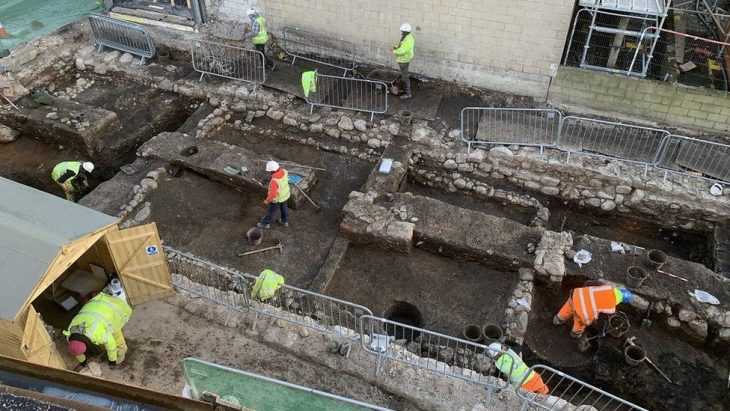
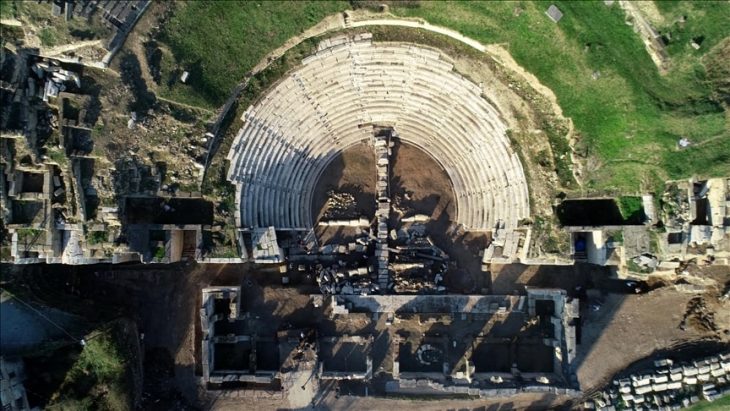
Ongoing excavation efforts, led by associate professor Ersin Çelikbaş from the Department of Archaeology at Karabük University’s Faculty of Literature, continue at the ancient city, which was used as a settlement during the late Chalcolithic, Roman, and early Byzantine periods.
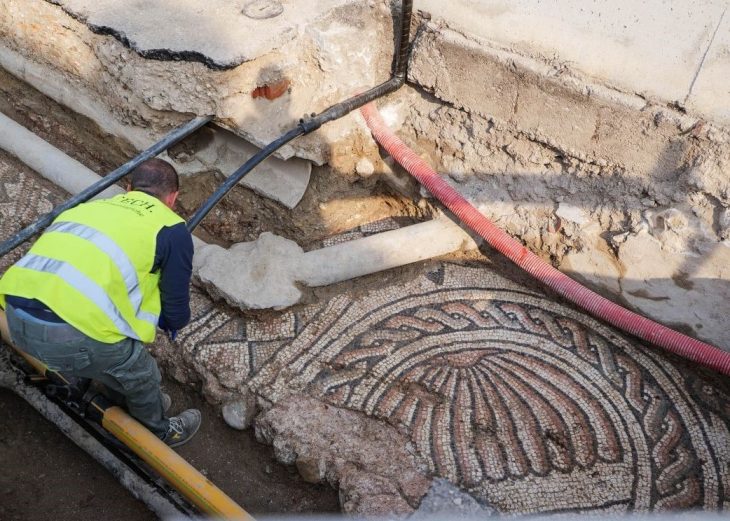
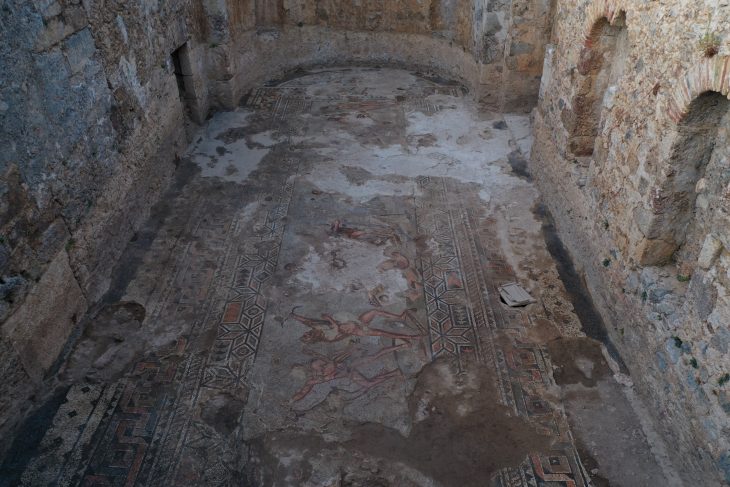
The ancient city of Hadrianopolis is called “Zeugma of Black Sea” because of its mosaics depicting many animals such as horses, elephants, panthers, deer and griffons.
The last discovery, together with previous findings, also points to the role of Hadrianopolis as a Roman military base in southern Paphlagonia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The site is thought to have been a Roman garrison, and it is located not far from the eastern edge of the great Roman Empire. In his previous statements, Çelikbaş had said that Rome had built this military base on the easternmost borders of the empire to defend against invasions from the Black Sea region. Researchers have previously discovered an iron Roman cavalry mask dating to the 3rd century AD in the region.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ersin Çelikbaş stated that they found 2 game stones and said, ‘These bone objects are in the form of lentils and discs. There is a 4-armed symbol on one stone and an 8-armed symbol on the other. These symbols show us that these stones could be game stones.’
Explaining that there were games played with bone stones in the past and that the stones they found belonged to a military strategy game, Çelikbaş continued as follows:

‘The discovery of strategy games in Hadrianopolis further concretises the existence of the military unit here because it is known that the strategy games played with bone stones in antiquity were ‘Ludus Latrunculi’ and ‘Doudecim Scripta’. Both games are based on a strategic basis. The ancient cities where these games emerged are also frequently encountered in Anatolia. It is also known that these games were strategy games that soldiers loved to play. Finds of this type reinforce the existence of a military unit in Hadrianopolis for many centuries. They clearly support the existence of a Roman headquarters, a Roman unit, and a Roman fortress in Hadrianopolis from the 2nd to the 5th century BC.’
Ludus latrunculi was a two-player strategy board game played throughout the Roman Empire. There are two rows of pieces facing each other, with sixteen pieces for each of the two players. The objective of the game is to seize every piece that the opposition has.
Doudecim Scripta was a board game popular during the Roman Empire. This Roman game is a relative, and probably ancestor, of backgammon. It is played on a board of three rows of twelve columns of playing spaces, and its name means “game of twelve lines”.
Cover Image Credit: Orhan Kuzu/AA