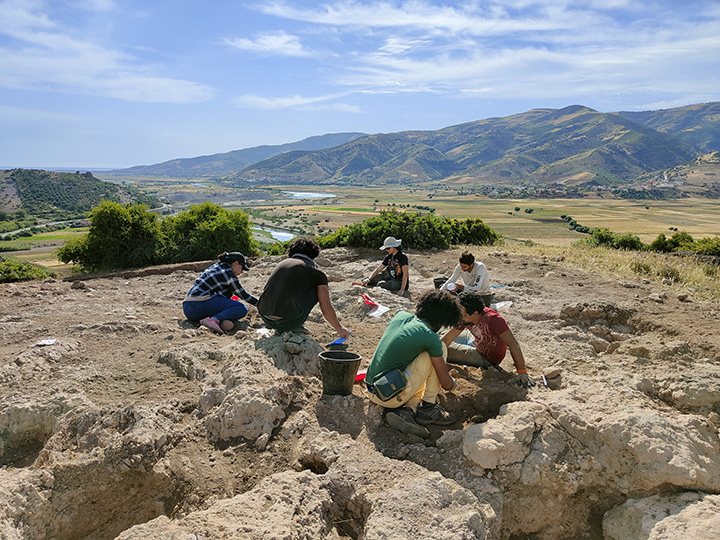
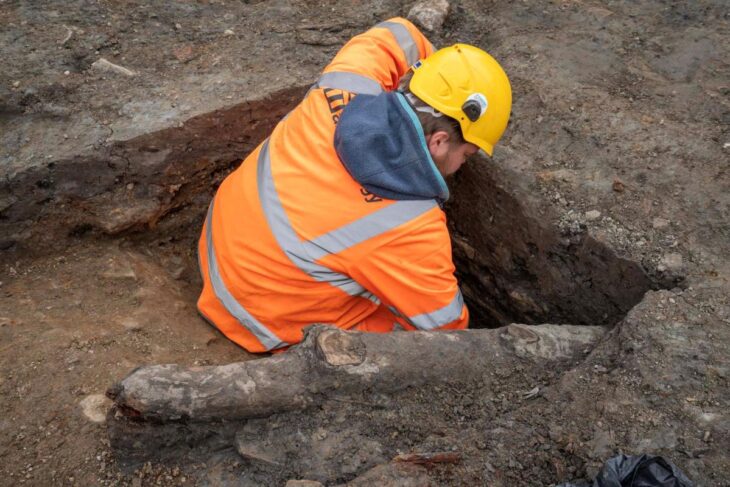
Researchers at the University of Barcelona have made a remarkable discovery: the first Bronze Age settlement in the Maghreb region of North Africa.
This significant finding, published in the journal Antiquity, challenges long-held beliefs that the area was largely uninhabited until the arrival of the Phoenicians around 800 BC.
Excavations at Kach Kouch, located in northwest Morocco, have uncovered evidence of human occupation dating from 2200 to 600 BC, making it the earliest known site of this period in Mediterranean Africa, excluding Egypt. This discovery addresses the longstanding mystery surrounding the absence of archaeological evidence from the Bronze Age in northern Africa.
Researchers noted that the Bronze Age (circa 2200–800 BC) and Early Iron Age (circa 800–550 BC) were critical periods for the development of complex social and political structures along the western Mediterranean. Despite this, the African Mediterranean coast west of Egypt has been largely overlooked in terms of its indigenous contributions to these historical developments.
In an effort to rectify this oversight, the research team, led by Ph.D. student Hamza Benattia Melgarejo, focused on the Maghreb region near the Strait of Gibraltar, a crucial maritime link between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic. The Kach Kouch site, covering approximately one hectare, is situated just six miles from the coast and 19 miles southeast of Tétouan.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
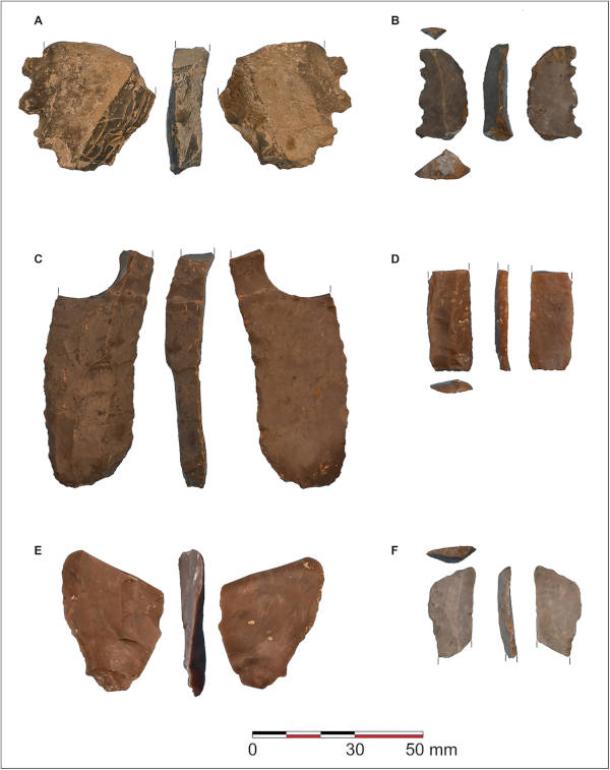

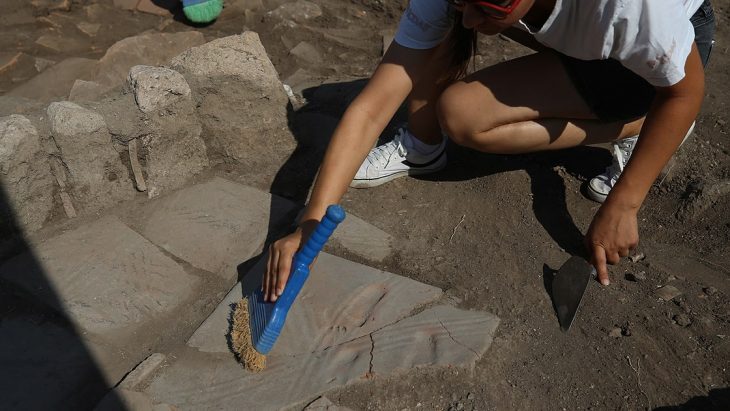
The excavations revealed multiple phases of occupation. The earliest phase, from 2200 to 2000 BC, although limited in evidence, indicates a contemporary presence during the transition from the Bronze Age to Iberia. The second phase, spanning 1300 to 900 BC, marked a flourishing agricultural community, showcasing the first definitive signs of sedentary life in the Maghreb prior to Phoenician influence. Artifacts such as wooden mud-brick structures, rock-cut silos, and grinding stones point to a robust agricultural economy based on barley, wheat, and livestock.
The third phase, from 800 to 600 BC, highlights the adaptability of Kach Kouch’s inhabitants, who incorporated cultural innovations from the eastern Mediterranean, including wheel-thrown pottery and iron tools. This blend of local and foreign practices underscores the community’s active engagement in Mediterranean trade networks.
Benattia Melgarejo emphasized the importance of this discovery, stating, “Kach Kouch is one of the first well-documented examples of continuous settlement in the Maghreb, revealing a history of dynamic local communities that were far from isolated.” The findings aim to correct historical biases and illustrate the Maghreb’s active participation in Mediterranean social, cultural, and economic exchanges.
The researchers believe that Kach Kouch is just the beginning of uncovering the rich history of the region. “This site is a significant step towards understanding the Maghreb’s role in the broader Mediterranean narrative,” Benattia concluded, suggesting that further discoveries may continue to reshape our understanding of North Africa’s past.
Benattia, H., Bokbot, Y., Onrubia-Pintado, J., Benerradi, M., Bougariane, B., Bouhamidi, B., … Broodbank, C. (2025). Rethinking late prehistoric Mediterranean Africa: architecture, farming and materiality at Kach Kouch, Morocco. Antiquity, 1–21. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.10
Cover Image Credit: Kach Kouch is located ten kilometres from the present-day coast, near the Strait of Gibraltar, and thirty kilometres southeast of Tétouan. Credit: University of Barcelona