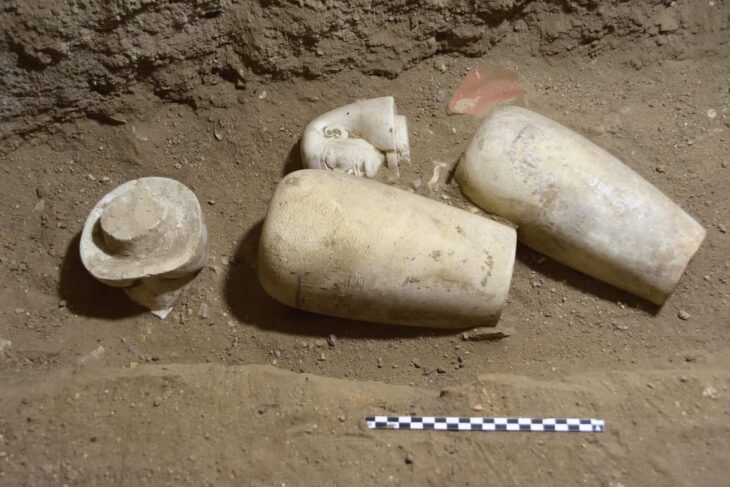
A team of scientists has discovered and analyzed the first direct evidence of basketry among hunter-gatherer societies and early farmers in southern Europe, (9,500 and 6,200 years ago), in the Cueva de los Murciélagos of Albuñol (Granada, Spain).
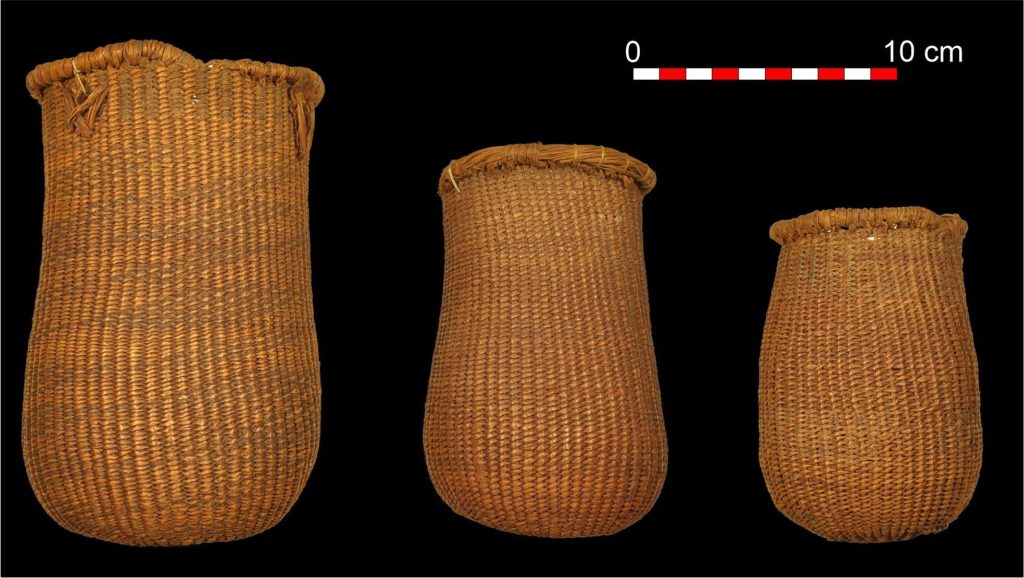
Intricate baskets and shoes found show that people living in Europe thousands of years ago were skilled at weaving objects from plant fibers.
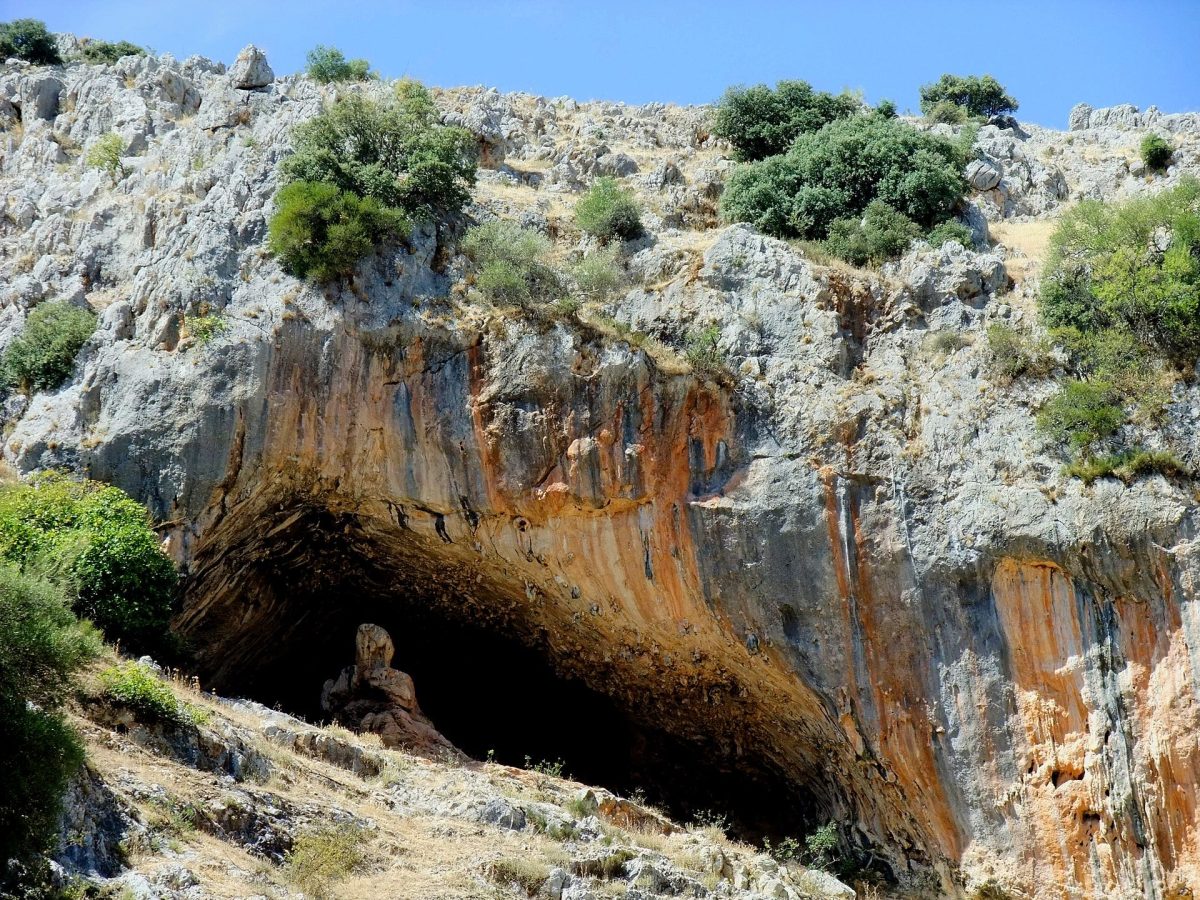
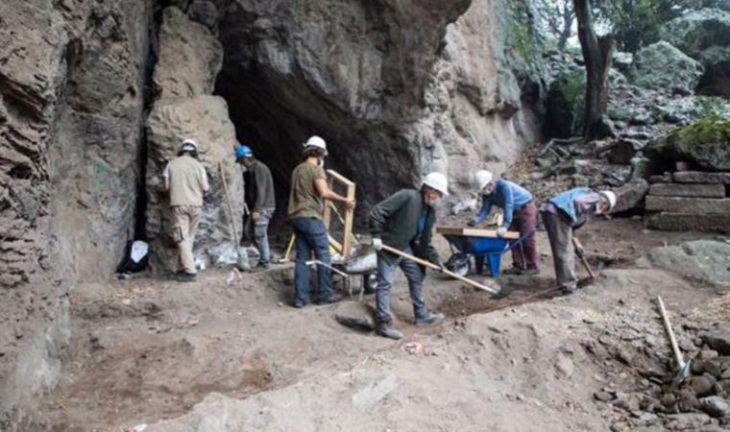
Cueva de los Murciélagos, or the Cave of the Bats, is a cave system in southwest Spain discovered during mining activities in the 19th century. The cave’s excavations have revealed several mummified corpses alongside objects including baskets, sandals and a wooden hammer.
This site is one of the most emblematic archaeological sites of prehistoric times in the Iberian Peninsula due to the unique preservation of organic materials found there.
Francisco Martínez Sevilla at the University of Alcalá in Spain and his colleagues have now analysed 76 of these artefacts. The study has been published in Science Advances.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
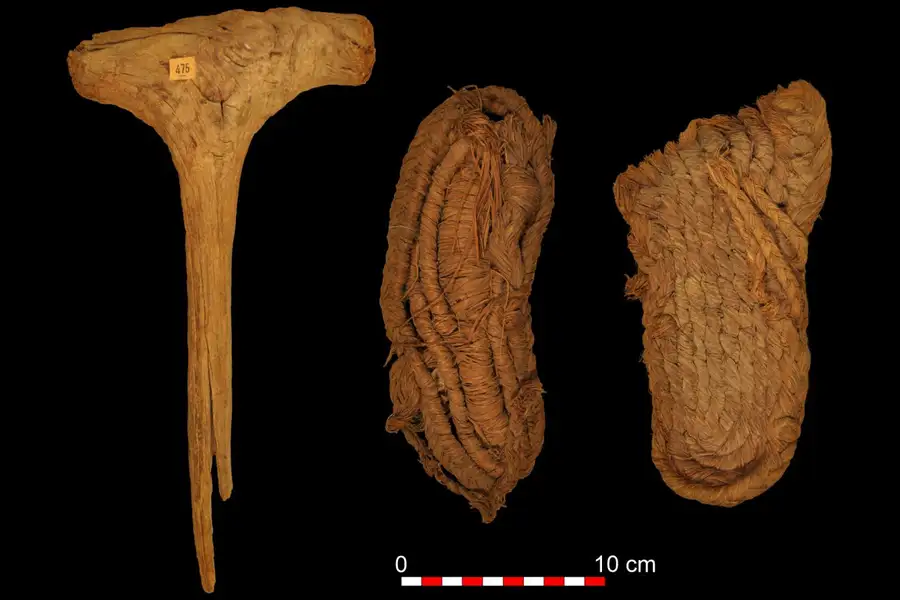

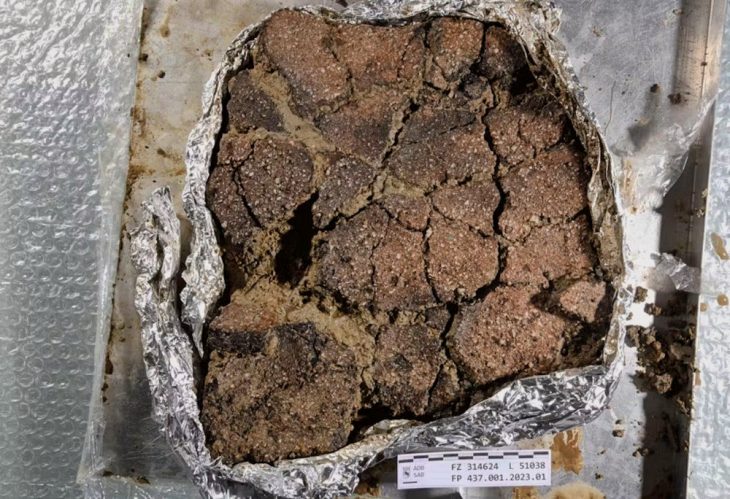
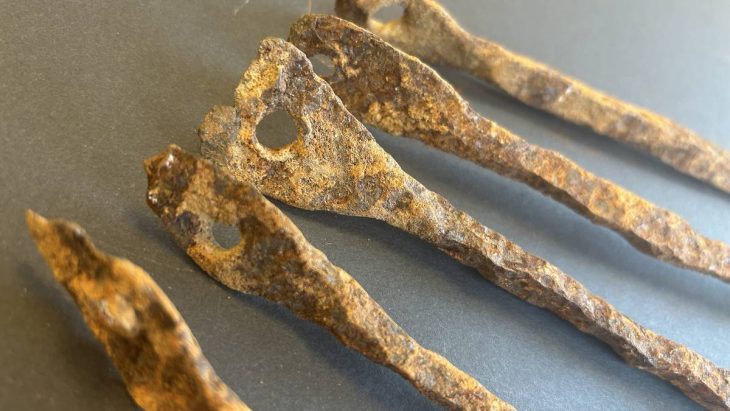
Around 65 of the items were found to be made from a fiber called esparto grass. This includes a set of baskets, with either a flat or a more cylindrical shape, as well as sandals that were made by crushing and twisting the esparto. The other artifacts are made of wood and include tools such as a hammer and digging sticks.
The team carbon-dated 14 of these objects and found that they belonged to one of two time periods: 7950 to 7360 BC or 4370 to 3740 BC.
Francisco Martínez Sevilla, a researcher at the Department of Prehistory at the University of Alcalá, says older objects were created by hunter-gatherers in the Mesolithic age, while later objects were probably used by Neolithic farmers.
The oldest dated sandal was found to be around 6000 years old, which makes it the oldest shoe ever found in Europe, says Martínez Sevilla.

“The use of vegetal fibres in Europe is older than we expected,” says team member Maria Herrero-Otal at the Autonomous University of Barcelona in Spain. “We imagine the Mesolithic populations as simpler, but it seems that they were much more complex than we thought.”
Francisco Martínez Sevilla says, “the new dating of the esparto baskets from the Cueva de los Murciélagos of Albuñol opens a window of opportunity to understanding the last hunter-gatherer societies of the early Holocene.”
“The quality and technological complexity of the basketry makes us question the simplistic assumptions we have about human communities prior to the arrival of agriculture in southern Europe. This work and the project that is being developed places the Cueva de los Murciélagos as a unique site in Europe to study the organic materials of prehistoric populations.”
Cueva de los Murciélagos is located on the coast of Granada, to the south of the Sierra Nevada and 2 kilometers from the town of Albuñol.