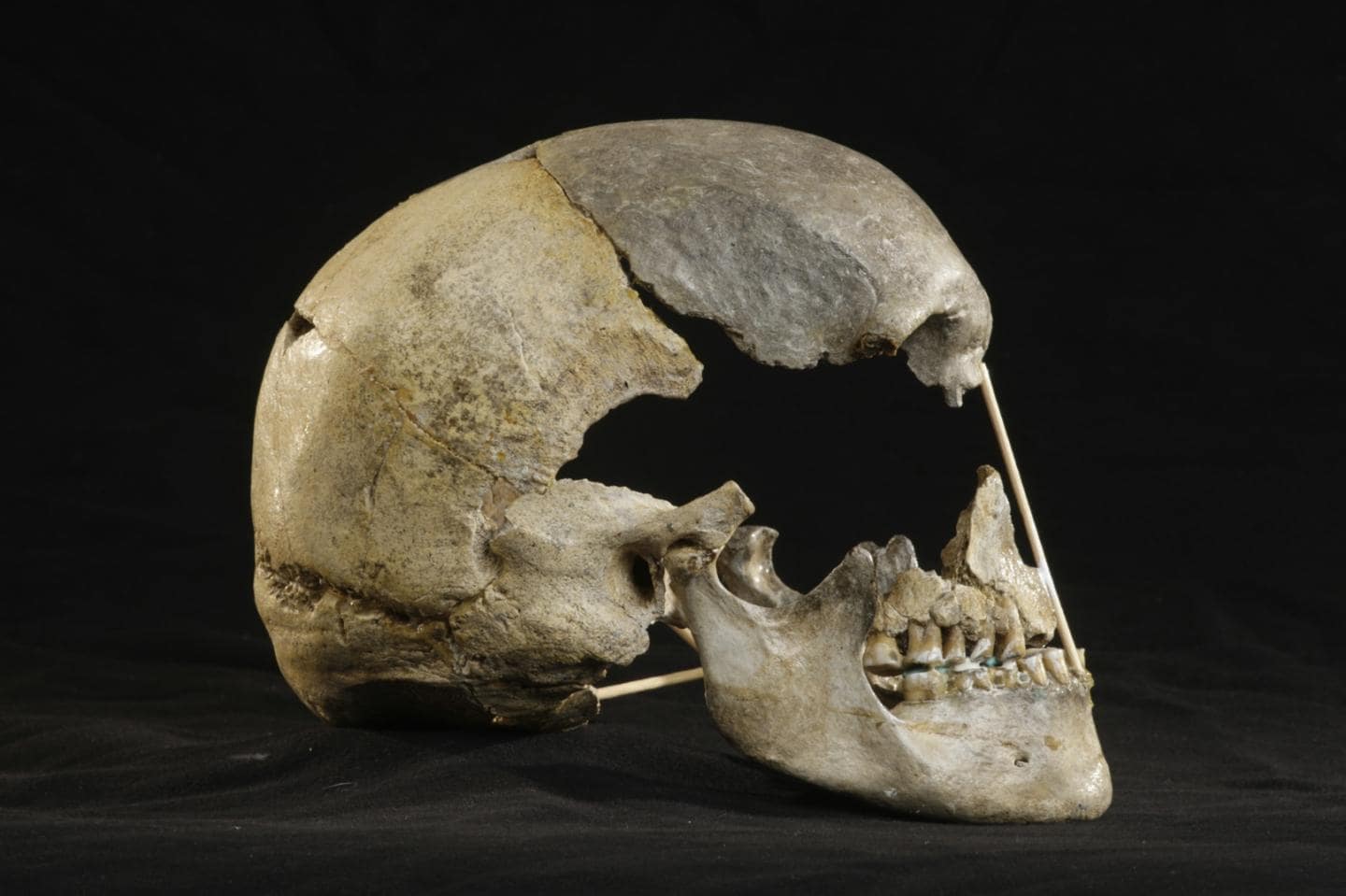
The fossilized skull of a woman in the Czech Republic provided the oldest modern human genome to date, which has been reconstructed to represent a population that arose before the ancestors of today’s Europeans and Asians split.
Ancient DNA from Neanderthals and early modern humans has recently shown that these groups likely interbred crossed somewhere in the Middle East after modern humans left Africa some 50,000 years ago. As a result, everyone outside of Africa carries 2% to 3% of Neanderthal DNA. In the modern human genome, these Neandertal DNA fragments become shorter and shorter with the passage of time, and their length can be used to estimate a person’s survival time. The archaeological data released last year further showed that modern humans already existed in Southeast Europe 47-43,000 years ago, but due to the lack of fairly complete human fossils and the lack of genomic DNA, people do not know who these early human colonists were. -Or their relationship with ancient and contemporary human groups.
In a new study published in “Nature Ecology and Evolution”, an international research team reported the oldest possibility to date to reconstruct the modern human genome. Researchers call it Zlatýkůň (the golden horse of the Czech Republic). It was the first female discovered in the Czech Republic. Its Neanderthal DNA fragments are longer than the 45,000-year-old Ust’-Ishim in Siberia, the oldest modern human genome to date. Analysis shows that she is part of a part of the population, and these populations were formed before the split between Europeans and Asians today.
A recent anthropological study based on the shape of the Zlatýkůň skull shows that the species is similar to people who lived in Europe before the last glacier peak at least 30,000 years ago, but radiocarbon dating has produced sporadic results, irregular of which 15,000 years ago. It wasn’t until Jaroslav Brůžek from the Faculty of Science, Prague and Petr Velemínský of Prague’s National Museum collaborated with the genetics laboratories of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History that a clearer picture came into view.
“We found evidence of cow DNA contamination in the analyzed bone, which suggests that a bovine-based glue used in the past to consolidate the skull was returning radiocarbon dates younger than the fossil’s true age,” says Cosimo Posth, co-lead author of the study. Post was formerly a research group leader at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History and is currently a Professor of Archaeo- and Palaeogenetics at the University of Tübingen.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
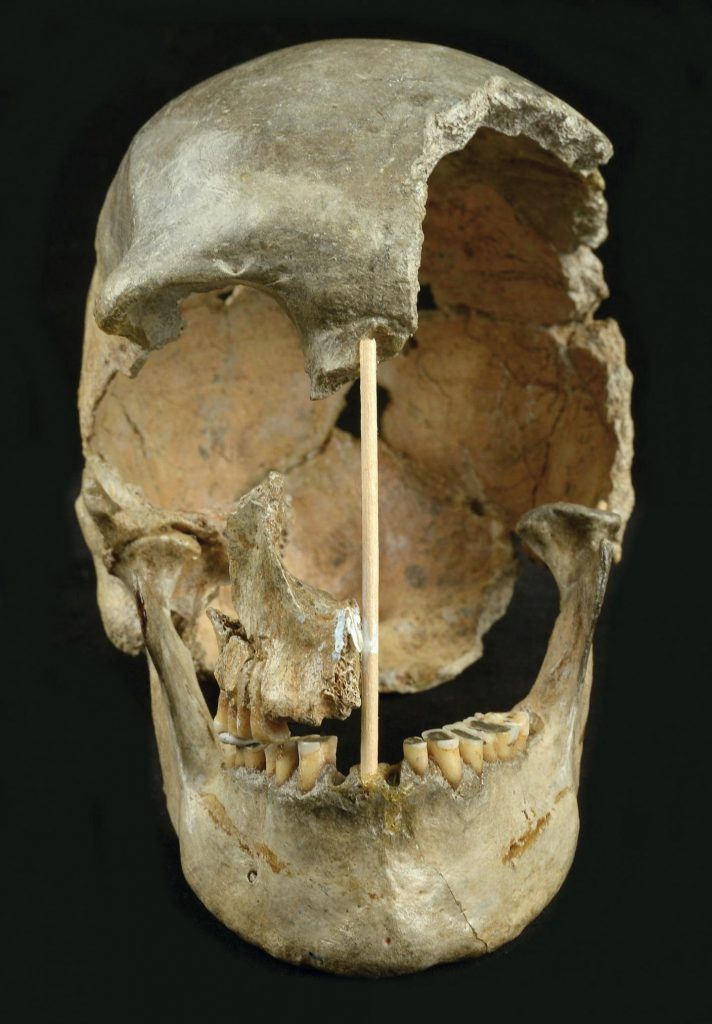
However, it was Neandertal DNA that led the team to reach the main conclusions about the age of the fossil. Zlatýkůň carries the same amount of Neandertal DNA in her genome as Ust Ishim or other modern humans outside of Africa, but the fragments of Neandertal descent are longer on average.
“The results of our DNA analysis show that Zlatý kůň lived closer in time to the admixture event with Neanderthals,” says Kay Prüfer, co-lead author of the study.
The scientists were able to estimate that Zlatý kůň lived approximately 2,000 years after the last admixture. Based on these findings, the team argues that Zlatý kůň represents the oldest human genome to date, roughly the same age as – if not a few hundred years older than – Ust’-Ishim.
“It is quite intriguing that the earliest modern humans in Europe ultimately didn’t succeed! Just as with Ust’-Ishim and the so far oldest European skull from Oase 1, Zlatý kůň shows no genetic continuity with modern humans that lived in Europe after 40,000 years ago,” says Johannes Krause, senior author of the study and director at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
One possible explanation for the discontinuity is the Campanian Ignimbrite volcanic eruption roughly 39,000 years ago, which severely affected climate in the northern hemisphere and may have reduced the survival chances of Neanderthals and early modern humans in large parts of Ice Age Europe.
As advances in ancient DNA reveal more about the story of our species, future genetic studies of other early European individuals will help to reconstruct the history and decline of the first modern humans to expand out of Africa and into Eurasia before the formation of modern-day non-African populations.
Source: MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR THE SCIENCE OF HUMAN HISTORY