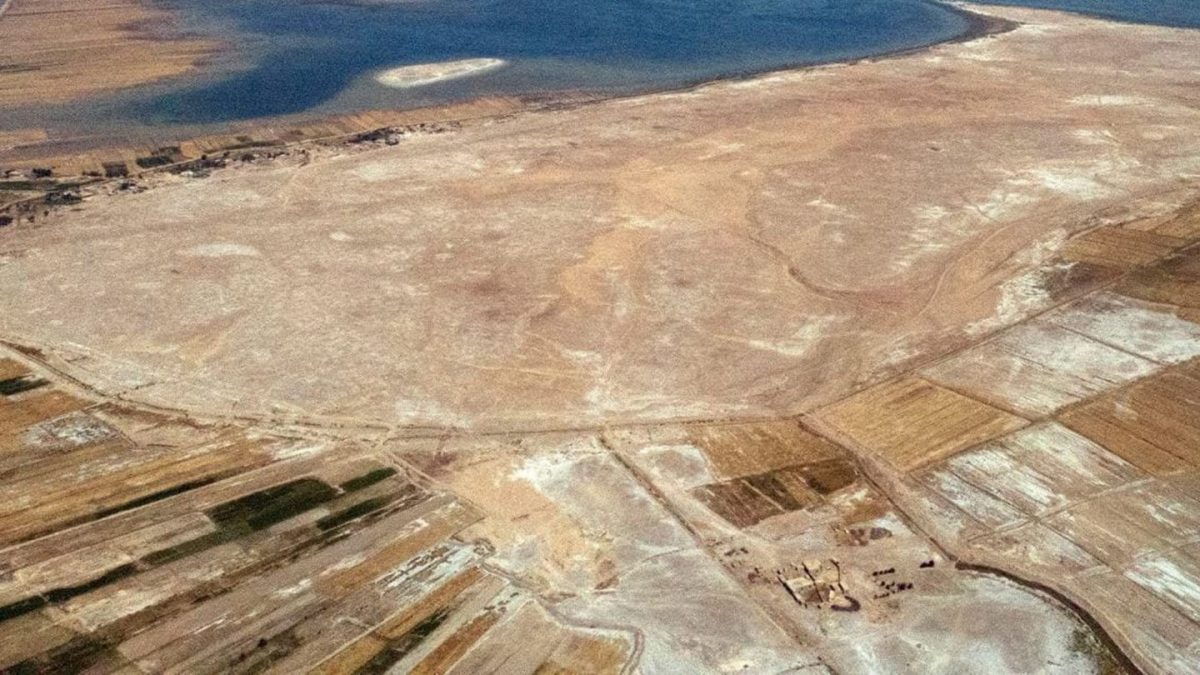
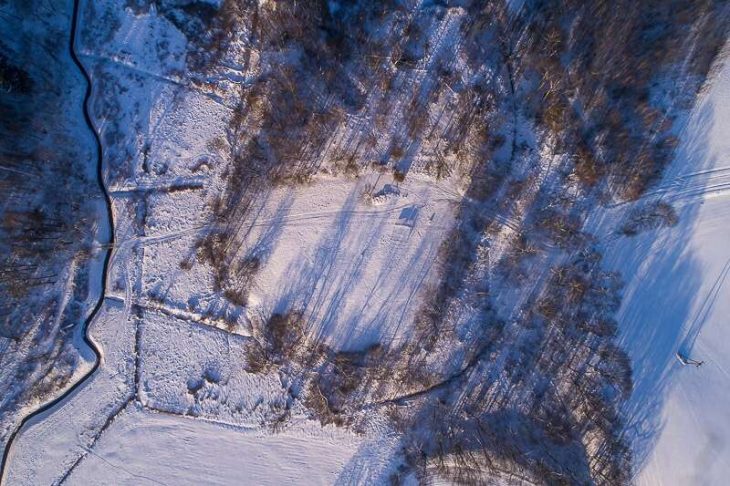
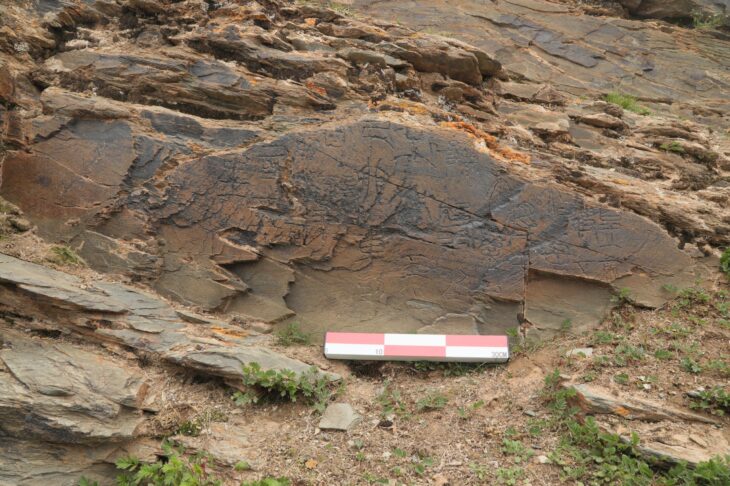
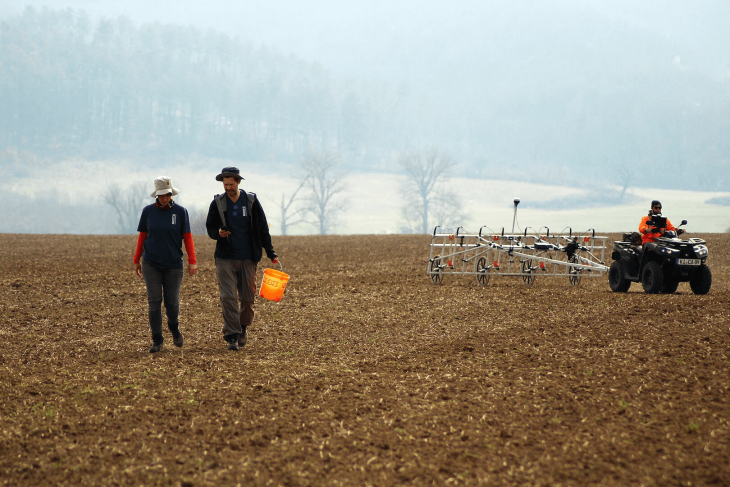
A drone survey of Lagash, a site located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, revealed that the 4,900-year-old settlement was built on four marsh islands.
The gathering of extensive data from large-scale remote sensing has “helped to rehydrate an ancient southern Mesopotamian city, tagging it as what amounted to a Venice of the Fertile Crescent. Identifying the watery nature of this early metropolis has important implications for how urban life flourished nearly 5,000 years ago between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, where modern-day Iraq lies,” Science News reports.
Emily Hammer, an anthropological archaeologist at the University of Pennsylvania, explained that remote-sensing data, collected mainly by a specially equipped drone, provides evidence of a vast urban settlement called Lagash, which was largely made up of four marsh islands connected by waterways.
These findings add important details to the growing consensus that southern Mesopotamian cities did not, contrary to popular belief, expand outward from the temple and administrative districts into irrigated farmlands surrounded by a single city wall.
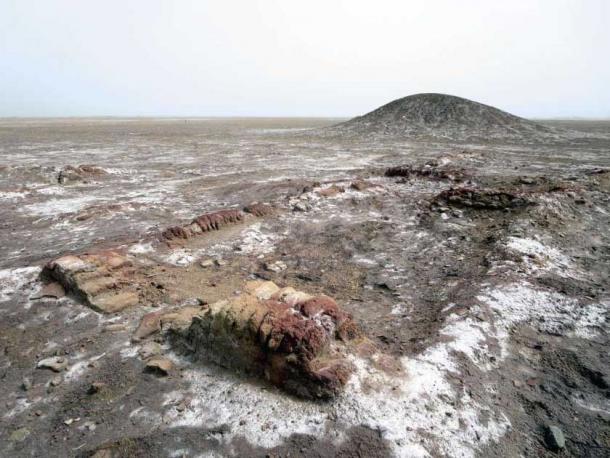

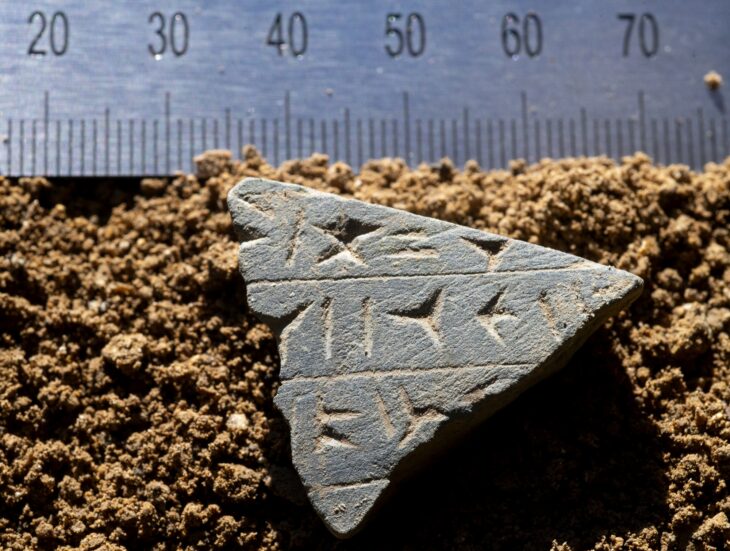
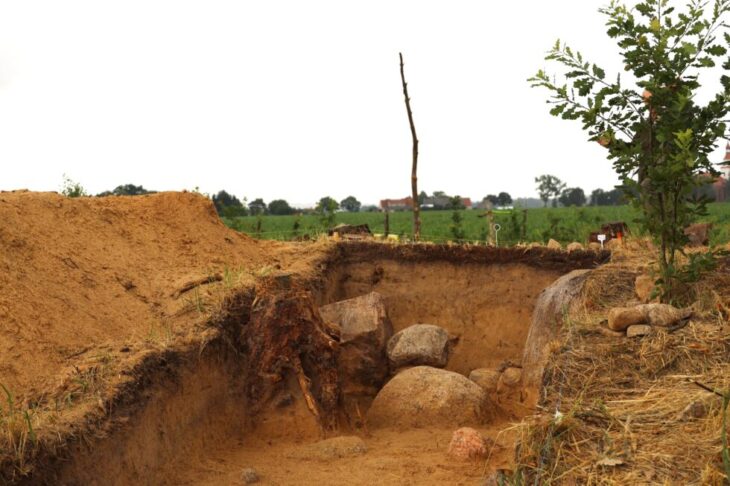
Lagash, which is now known as Tell al-Hiba, was most likely established between 4,900 and 4,600 years ago. Excavated more than 40 years ago for the first time, it was learned that this site was abandoned around 3,600 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Previous analysis by other anthropologists, historians, and scientists indicate that Lagash was built on raised mounds in the marshes, and possibly consisted of 33 small, marsh islands.
“There could have been multiple evolving ways for Lagash to be a city of marsh islands as human occupation and environmental change reshaped the landscape,” Emily Hammer says.
“The standard model of third millennium BCE Mesopotamian cities presents them as nuclear, compact settlements set within an irrigated agricultural hinterland, expanding continuously from a monumental religious complex. This reconstruction holds enormous influence in the comparative global study of early urbanism. UAV photos and magnetic gradiometry data captured at Lagash (Tell al-Hiba) show dense architecture and related paleoenvironmental features over c. 300 ha, revealing a city that does not conform to the standard model.”
Early Dynastic Lagash (2900–2350 BCE) was composed of spatially discrete sectors bounded by multiple surrounding walls and/or watercourses and separated by open spaces.
In fact, Lagash is characterized by dense architecture spread out over 300 hectares (approximately). Evidence also points to marshy and watery local environmental factors. This led Hammer to conclude that the city sectors originated as marsh islands.
For example, canals have been spotted on one of the islands, which may have focused on fishing and collecting reeds for construction. Evidence of gated walls, city streets, and large kilns have been found on two other islands.
Drone photos also show harbors that could connect city sectors via boat travel. The remains of potential footbridges have also been discovered, but only excavations can shed more light on the subject.
Cover Photo: LAGASH ARCHAEOLOGICAL PROJECT