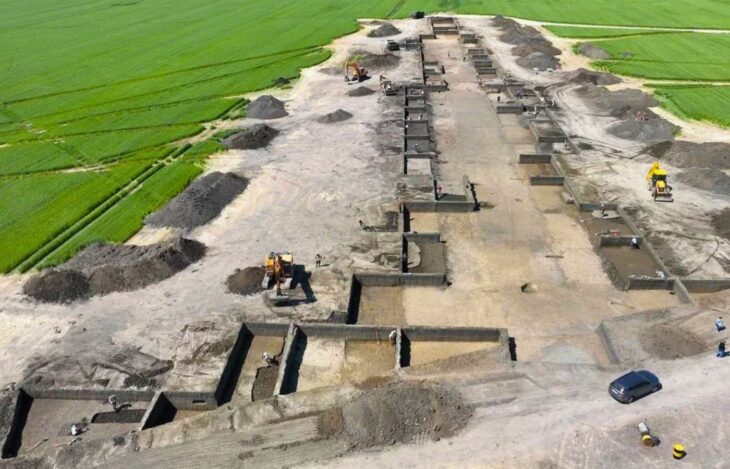
Archaeologists have recently made a groundbreaking discovery in northwestern Arabia, unearthing immense fortifications that date back an astonishing 4,000 years.
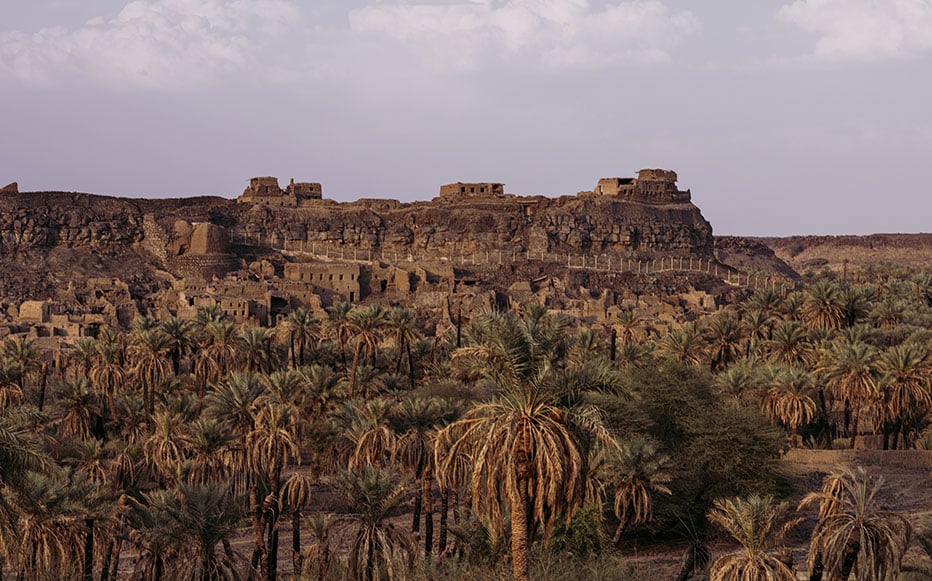
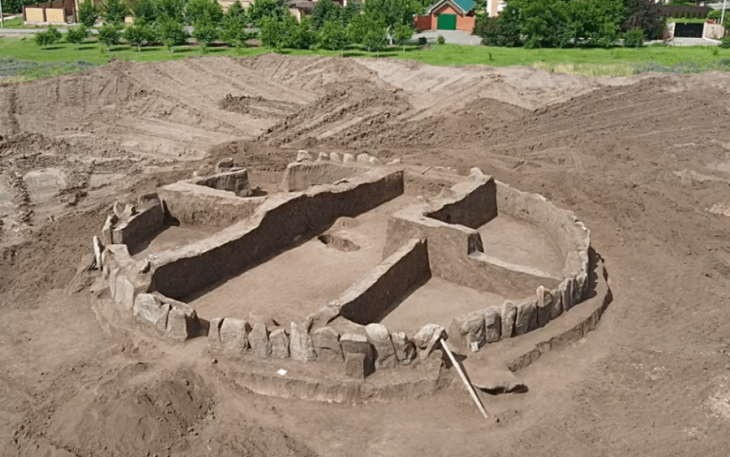
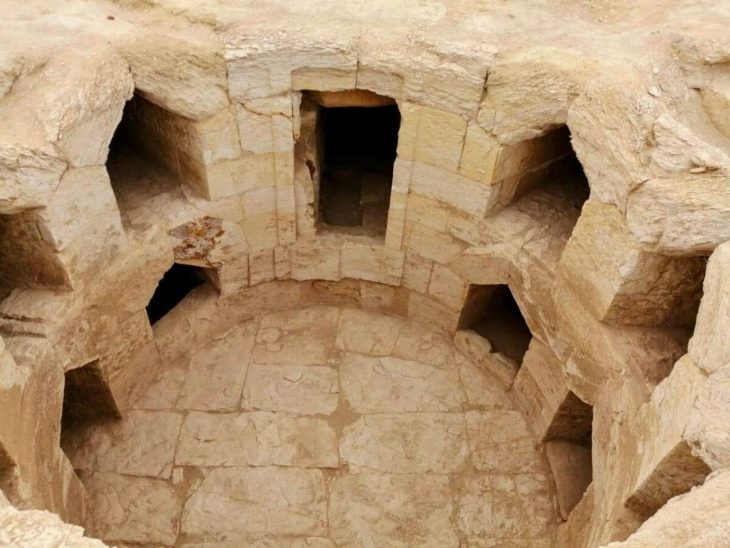
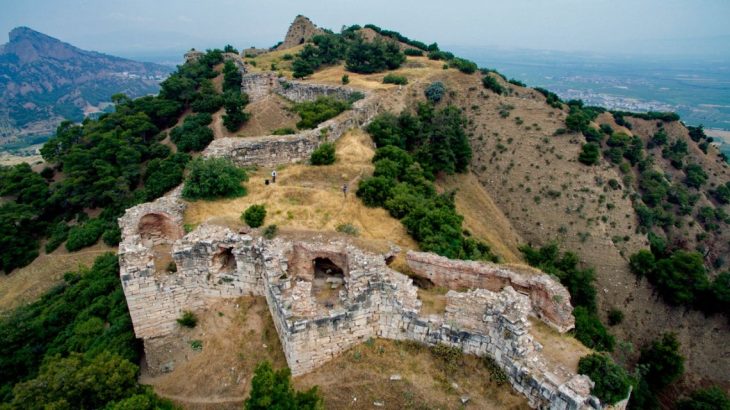
The North Arabian Desert oases were inhabited by sedentary populations in the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE. A fortification enclosing the Khaybar Oasis—one of the longest known going back to this period—was just revealed by a team of scientists from the CNRS1 and the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU).
This new walled oasis, alongside Tayma, is one of Saudi Arabia’s two largest. While a number of walled oases dating back to the Bronze Age have previously been documented, this significant discovery sheds new light on human occupation in northwestern Arabia and provides a better understanding of local social complexity during the pre-Islamic period.
By studying the architectural features and layout of the fortifications, archaeologists can gain insights into the social structure, military strategies, and economic activities of the ancient inhabitants. This information helps piece together the puzzle of their daily lives and interactions with neighboring civilizations.
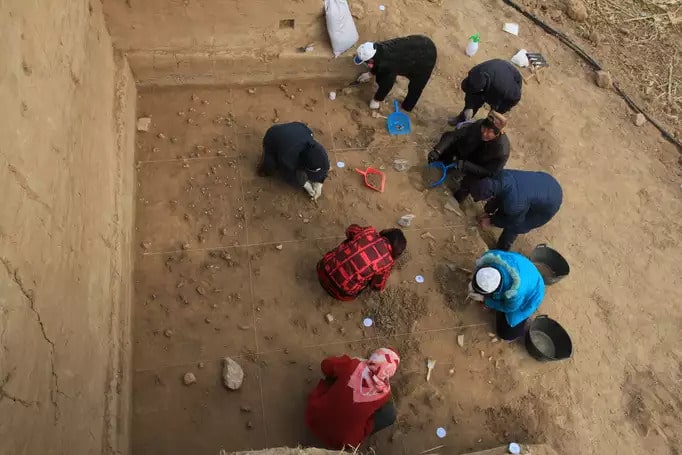
The fortifications are presently being excavated, under the direction of a committed group of archaeologists and researchers. To guarantee the structures’ preservation and accurate interpretation, the procedure entails meticulous mapping, documentation, and analysis of the structures. Sophisticated methods like remote sensing and 3D scanning are being used to produce intricate digital models of the fortifications. This makes it possible to comprehend their building techniques and architectural elements on a deeper level.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
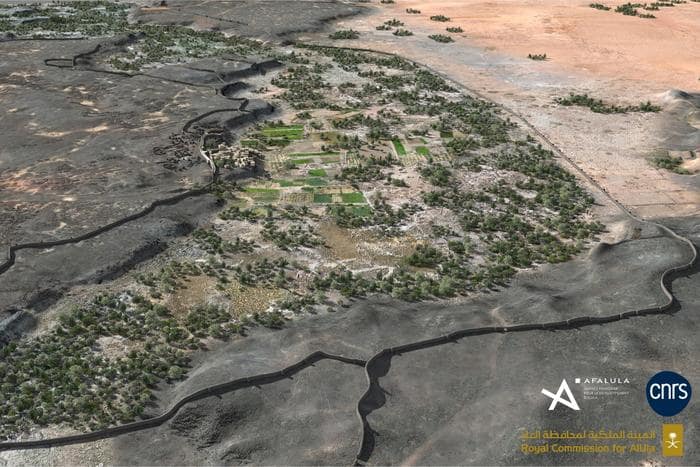

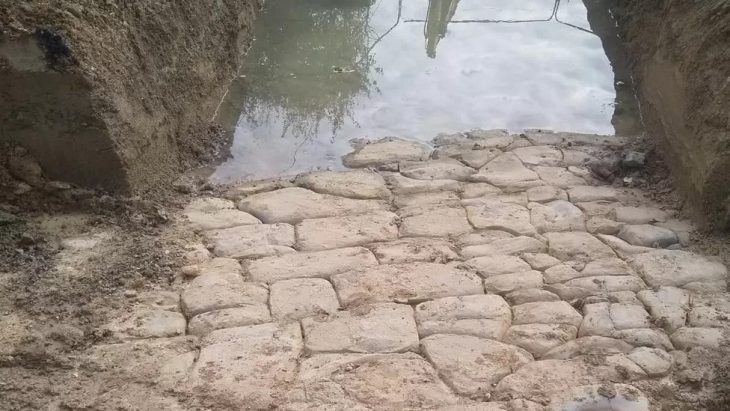
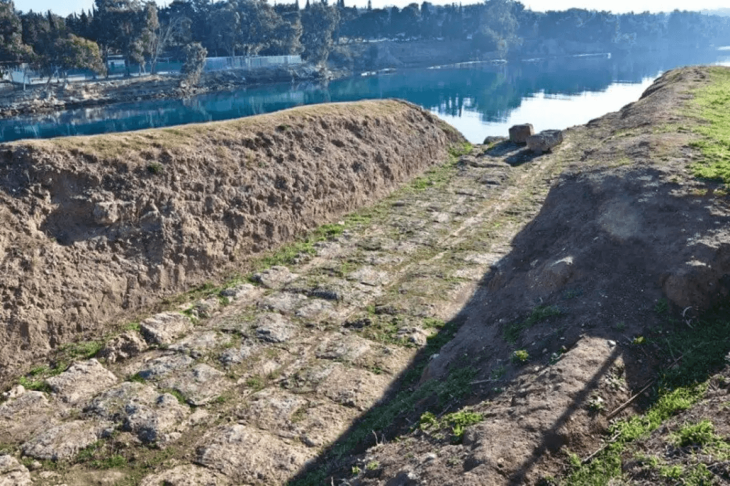
Cross-referencing field surveys and remote sensing data with architectural studies, the team estimated the original dimensions of the fortifications at 14.5 kilometres in length, between 1.70 and 2.40 metres in thickness, and approximately 5 metres in height. Preserved today over a little less than half of its original length (41%, 5.9 km and 74 bastions), this colossal edifice enclosed a rural and sedentary territory of nearly 1,100 hectares. The fortification’s date of construction is estimated between 2250 and 1950 BCE, on the basis of radiocarbon dating of samples collected during excavations.
While the study confirms that the Khaybar Oasis was clearly part of a network of walled oases in northwestern Arabia, the discovery of this rampart raises questions about why it was built and the nature of the populations who built it, particularly their interactions with populations outside the oasis.
Furthermore, the discovery of these massive fortifications opens up new avenues of research in archaeology. It encourages further exploration of the region in search of additional ancient sites and artifacts that can help us better understand the past.
This archaeological discovery paves the way for major advances in understanding the prehistoric, pre-Islamic, and Islamic past of the north-western Arabian Peninsula.
A study describing this work is published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
Cover Photo: ExperienceAlUla