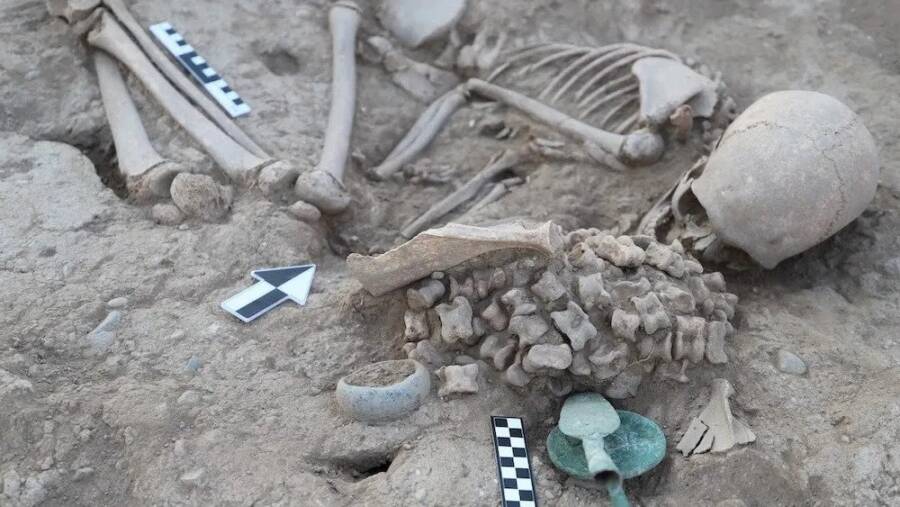
Archaeologists in eastern Kazakhstan have unearthed a Bronze Age burial mound of a girl surrounded by various grave goods in the Ainabulak-Temirsu Necropolis.
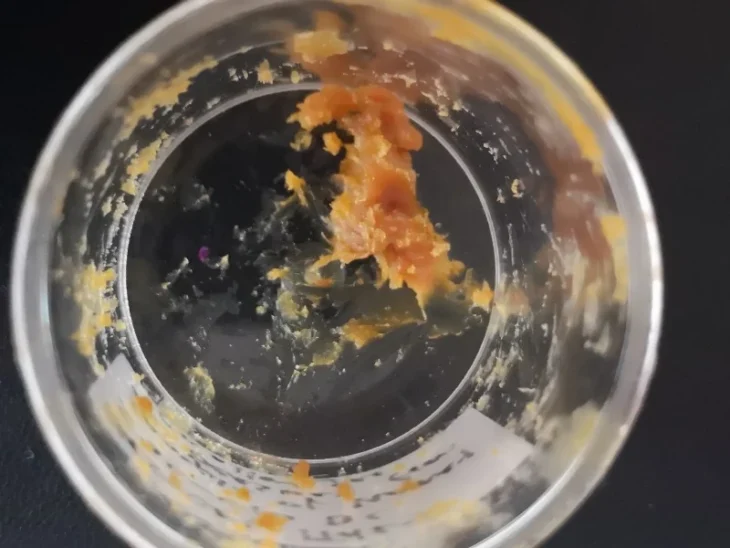
The young girl was laid to rest with a number of peculiar grave goods, including 180 animal ankle bones and a small, exquisite silver accessory depicting a frog on a disc.
The excavations are carried out together with experts from the University of Cambridge and under the direction of Rinat Zhumatayev, Head of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University (KazNU) Archaeology, Ethnology, and Muzology Department. The ongoing excavations have gained momentum since 2016 when the journey to explore the region’s historical treasures commenced in the Zaisan district, spearheaded by Abdesh Toleubaev.
According to The Astana Times, an English-language news outlet in Kazakhstan, the girl’s grave is located near Ainabulak village in the east of the country and dates from Central Asia’s Bronze Age, which lasted from roughly 3200 B.C.E. until 1000 B.C.E.
Speaking to LiveScience, Rinat Zhumatayev, an archaeologist who led the excavation and heads the Department of Archaeology, Ethnology and Museology at Al-Farabi Kazakh National University in Kazakhstan, said: “She was buried on her left side, bent over. Small wire earrings were in both ears and beads around her neck.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
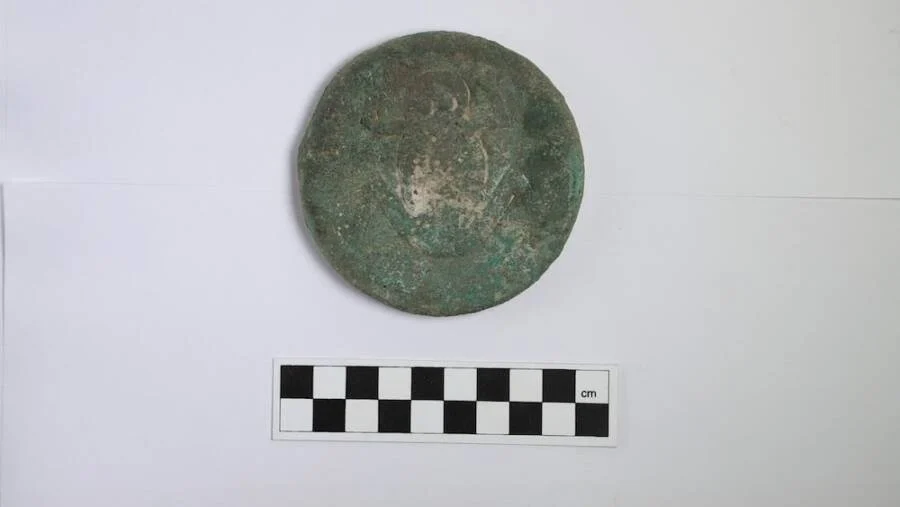

The frog-adorned artifact carries immense significance. Scholars associate the frog motif with water-related rituals found in China and Egypt, adding an intriguing layer to the ongoing research. According to the researchers, this is the first example discovered in Kazakhstan and may be associated with the image of a woman in labour and the cult of water.
The sheer volume of animal bone fragments buried in the burial mound also piqued researchers’ interest. The number of bones buried with this person was extravagant compared to other graves on the Eurasian steppe that contained animal remains, frequently in child and adolescent burials.
Some scientists think that the burial of astragalus bones was part of a “cult practice” and that the bones were used during meditation. However, other researchers view the bones as “symbols of well-being” and “good luck” that served as a “wish for a successful transition from [one] world to others,” Zhumatayev said.
“Our exploration is far from over. By the year’s end, we anticipate unveiling our findings and publishing a comprehensive scientific article,” shared Rinat Zhumatayev.