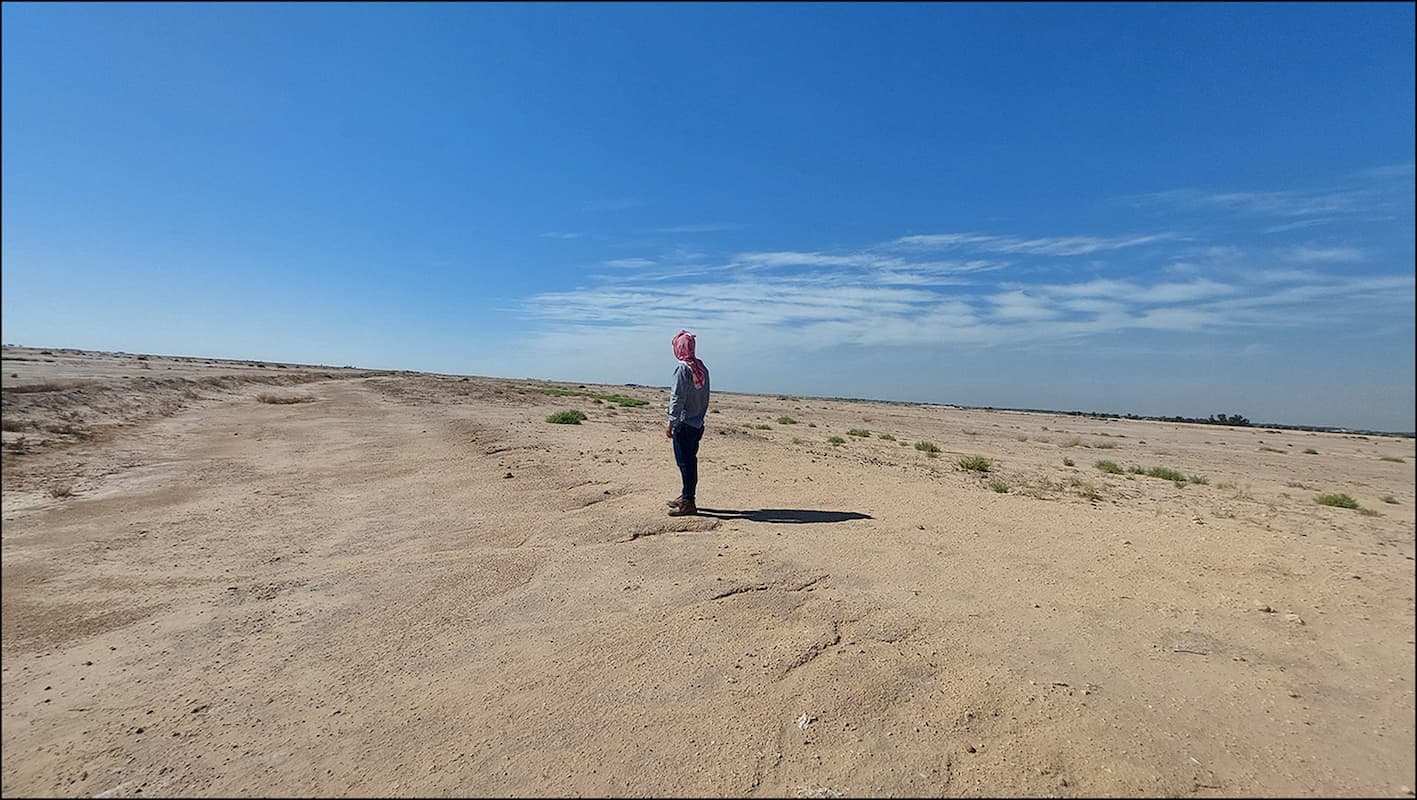
Archaeologists from Durham University in the UK and the University of Al-Qadisiyah have identified the site of the historic Battle of al-Qadisiyyah in what is now Iraq by comparing historical accounts with declassified images from US spy satellites.
The team used declassified U.S. spy satellite imagery from the 1970s, which is now in the public domain, and compared it to modern-day images and historical texts.
Known as a pivotal conflict in the spread of Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, this conflict, which lasted from 637 to 638 CE, ended in a resounding victory for the Muslim Arabs. Even though this event was significant historically, its precise location had not been determined until now because there was insufficient archaeological evidence.
This battle played a central role in the early Islamic expansion, leading to a decisive Arab Muslim victory over the Sasanian Empire and clearing the way for Islam’s spread into Persia and beyond.
Dr. William Deadman, a specialist in archaeological remote sensing, was undertaking a remote survey to map out the Darb Zubaydah a pilgrimage route from Iraq’s Kufa to Mecca in Saudi Arabia– the pilgrimage route when the discovery was made.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
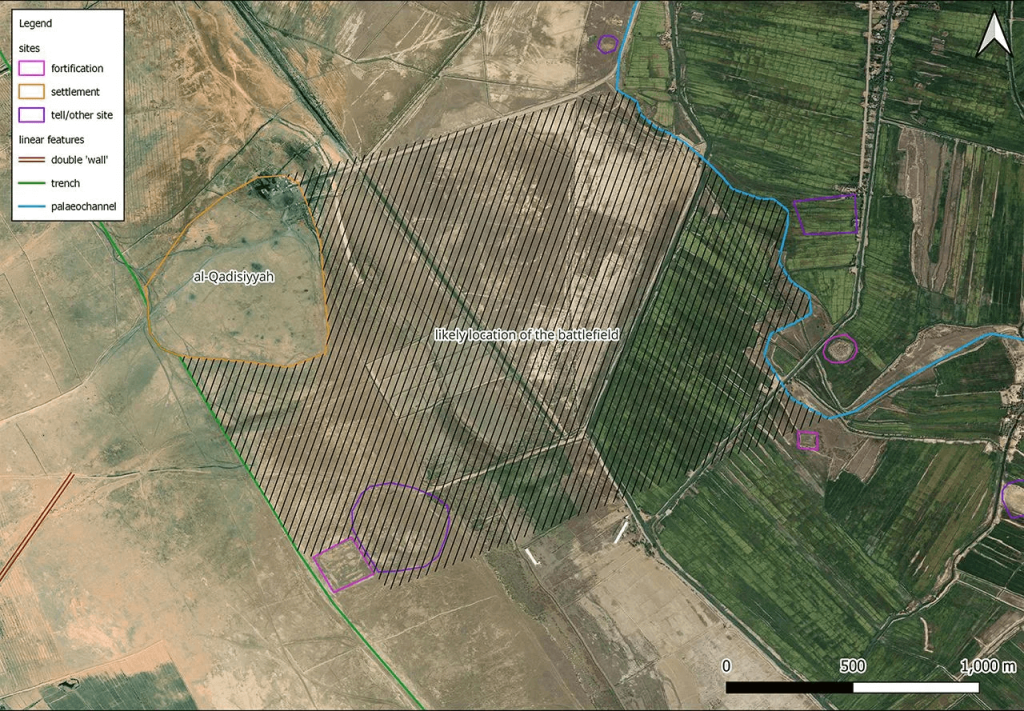
The researchers think they have located the battlefield in Iraq’s Najaf Governorate, about 30 kilometers south of Kufa, by comparing historical texts with declassified satellite images from the Cold War. Previously, the precise location was not clear, with maps placing it within a radius of 10-20 kilometers, which Dr. Deadman described as a “huge” margin of error. He said the exact location of the battlefield had been tied down “quite precisely” to within perhaps 1 kilometer.
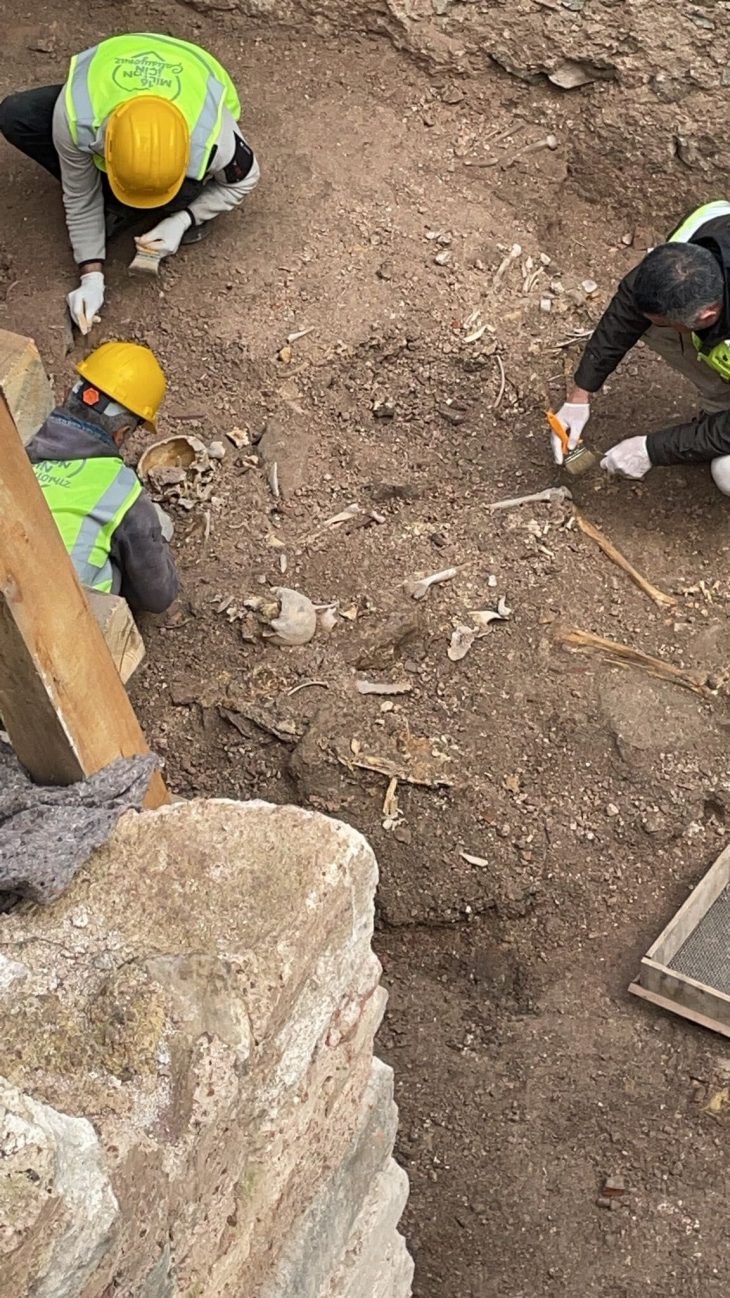
During their survey work, the team identified a six-mile-long double wall feature linking a military complex on the desert fringe and a large settlement on the edge of the southern Mesopotamian floodplain. This finding corresponded remarkably well to details within the rich body of historical sources relevant to the battle of al-Qadisiyyah and the stopping points along the Darb Zubaydah.
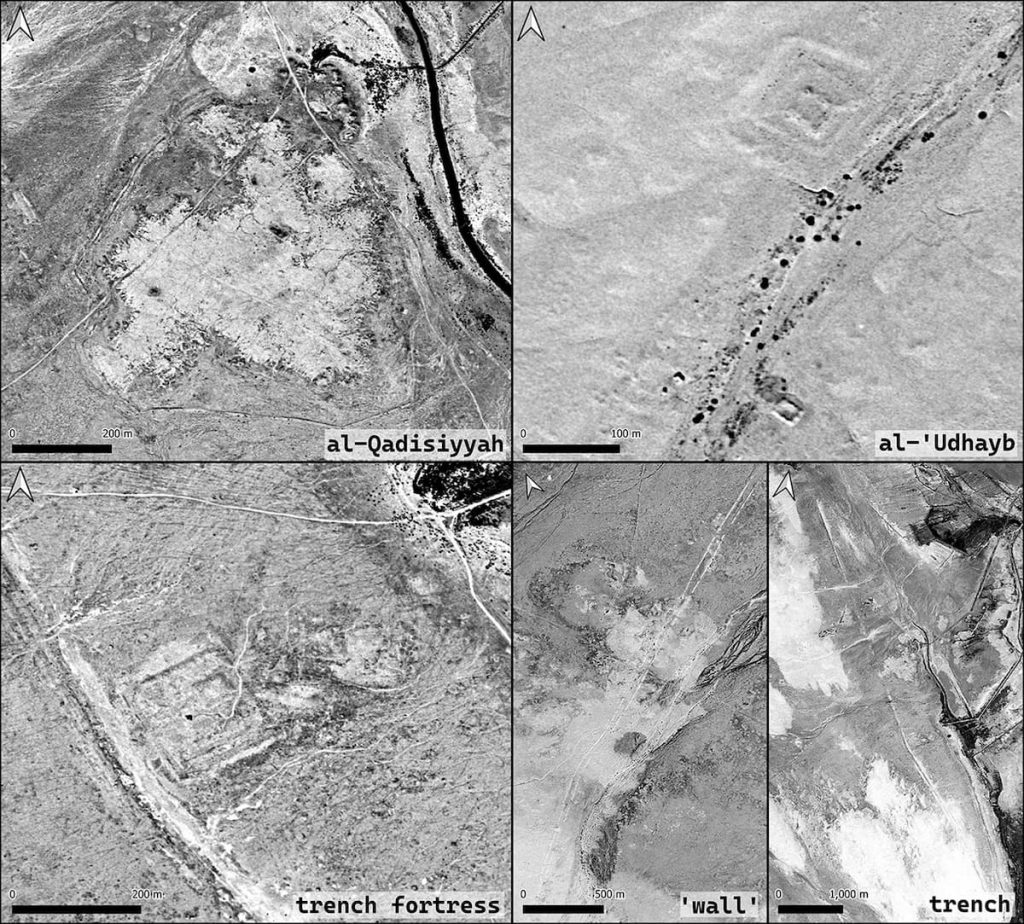

Ground surveys carried out by Iraqi researchers, including Dr. Jaafar Jotheri and Dr. Rajwan Almayali from the University of Al-Qadisiyah, uncovered physical evidence that supports the findings. Additionally, the team was able to locate al-Qadisiyyah and al-‘Udhayb, two stopping points along the Darb Zubaydah, with confidence.
The research was part of the wider Endangered Archaeology in the Middle East and North Africa (EAMENA) project, which focuses on the endangered archaeology of the region and was launched in 2015 to document endangered archaeological sites. The project is a collaboration between the universities of Oxford, Durham, and Leicester, and is funded by Arcadia.
Read the full article in Antiquity.
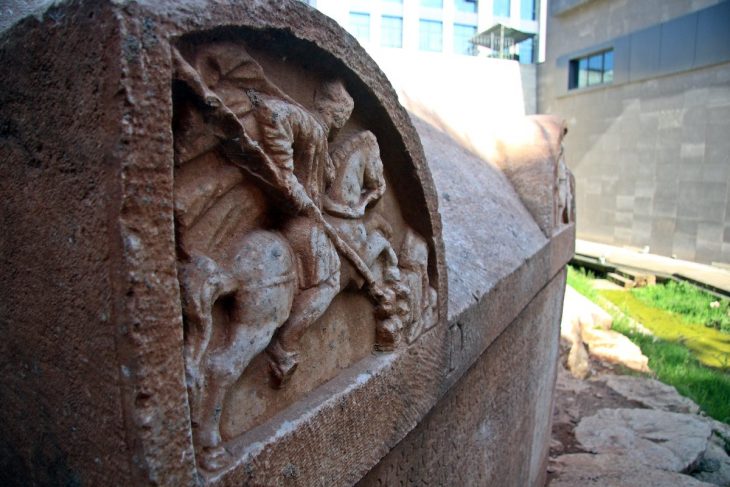
Cover Image Credit: View of the al-Qadisiyyah battlefield. J. Jotheri
















