Archaeologists have unearthed 130 dwellings at an Early Bronze Age monument in Germany, indicating that the ‘Stonehenge’ was once home to a population.
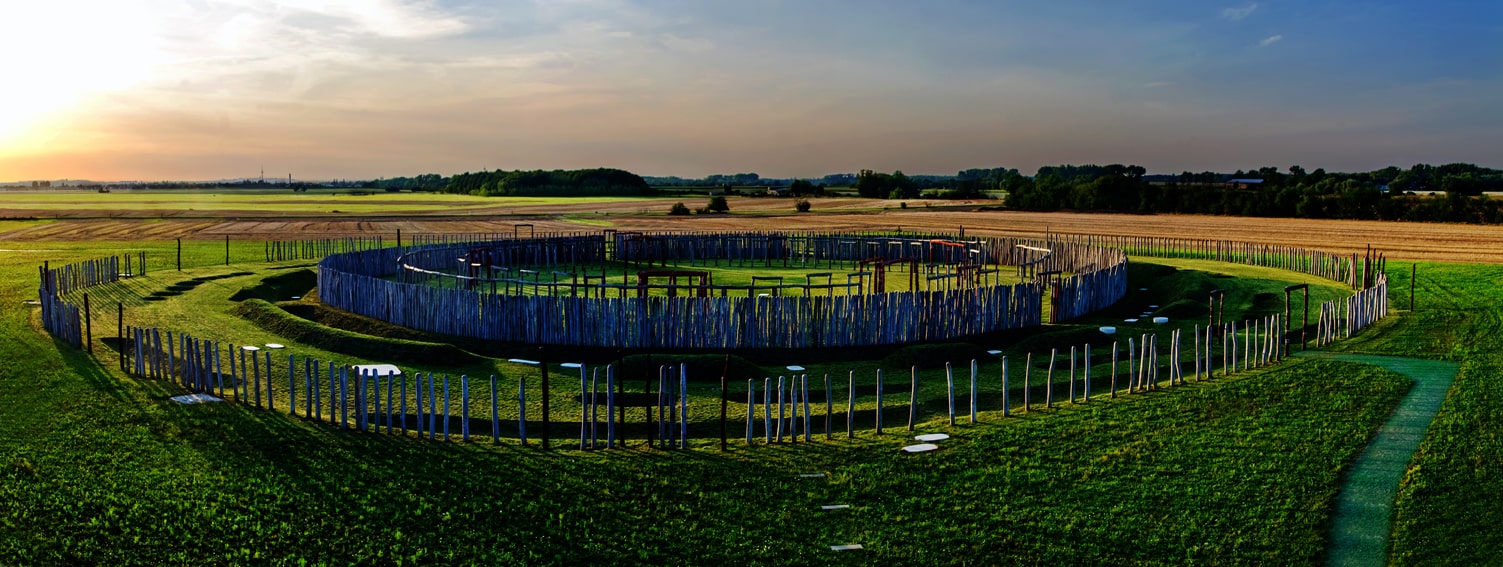
Ringheiligtum Pömmelte, German meaning ‘Ring Sanctuary of Pömmelte,’ is an ancient archaeological site in the village of Pömmelte, 85 kilometers from Berlin. The site was discovered in 1991 through aerial photographs.
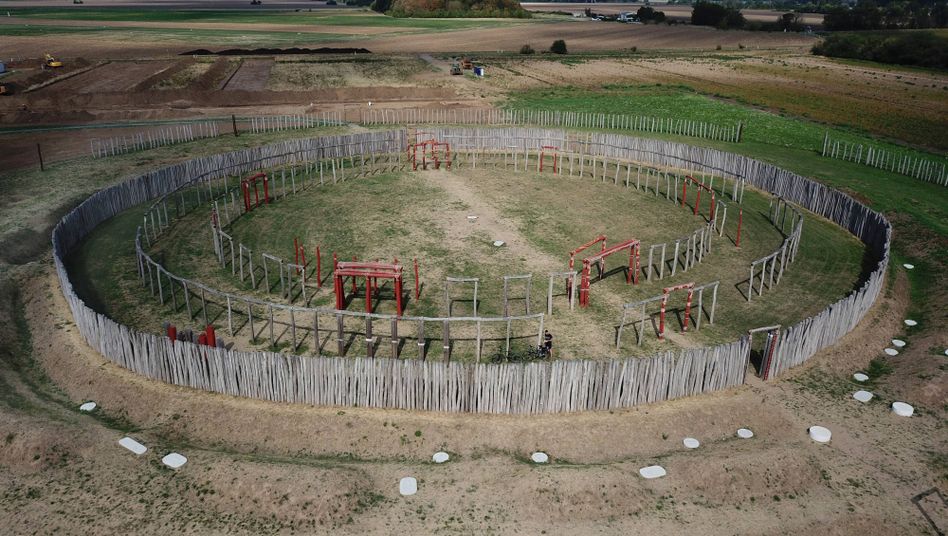
The monument is made up of seven rings of palisades, ditches, and elevated banks, all of which have a succession of wooden posts. Ringheiligtum Pömmelte, according to archaeologists, was an astronomical observatory and ceremonial center, akin to Stonehenge in Wiltshire, England.
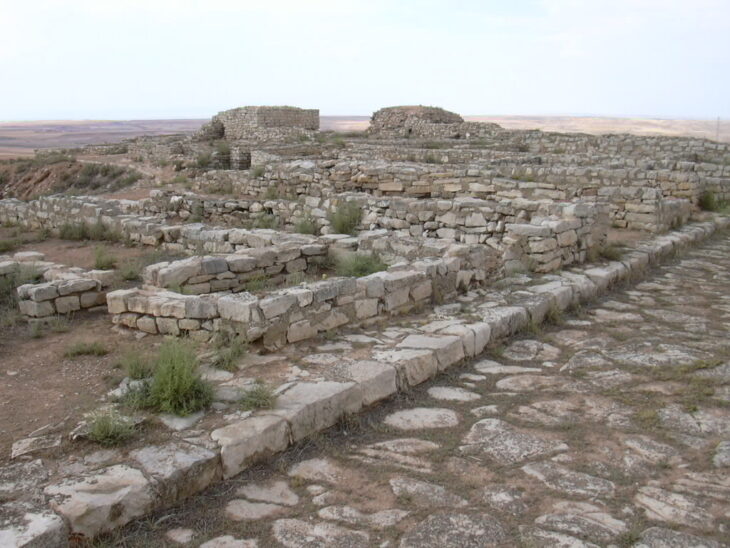
A team of academics from the Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg discovered a residential area surrounding the monument during the most recent excavation of the site. It was always considered that the monument was a ceremonial place, but this is the first time they’ve found evidence of permanent habitation in the area.

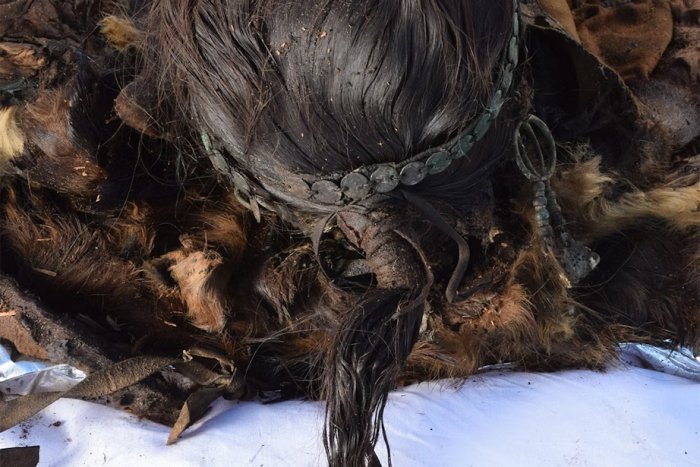
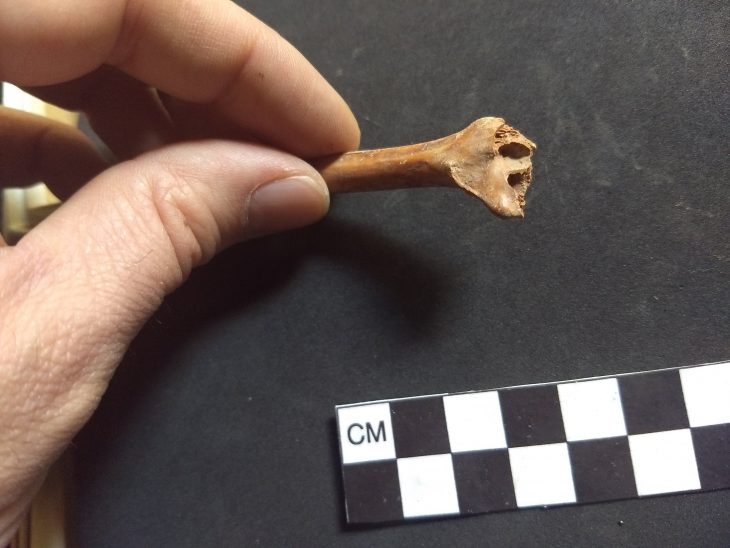
Previous excavations uncovered dismembered corpses of children and women, some of whom died with severe head injuries and rib fractures. Ringheiligtum Pömmelte was always thought to be a seasonal ceremonial place or used to memorialize religious festivals and burial ceremonies, with no trace of permanent occupancy in the vicinity.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Archaeologists uncovered two house dwellings, 20 ditches, and two tombs during the most recent set of excavations, which began in May 2021. As the excavations advanced, further burial sites and almost 80 full house plans were discovered, resulting in a total of 130 homes being recognized.
The structures date from several eras, with some from the early phase of the monument’s creation and sharing traits with the Bell Beaker culture of 2800 BC, while the majority of homes have been designated as Unetic culture of 2200 BC.
Excavations will continue until October 2021, with the goal of better understanding the Unetice culture’s social and religious milieu, as well as determining the connections between the habitation area and the ceremonial enclosure.
Source: Dailymail