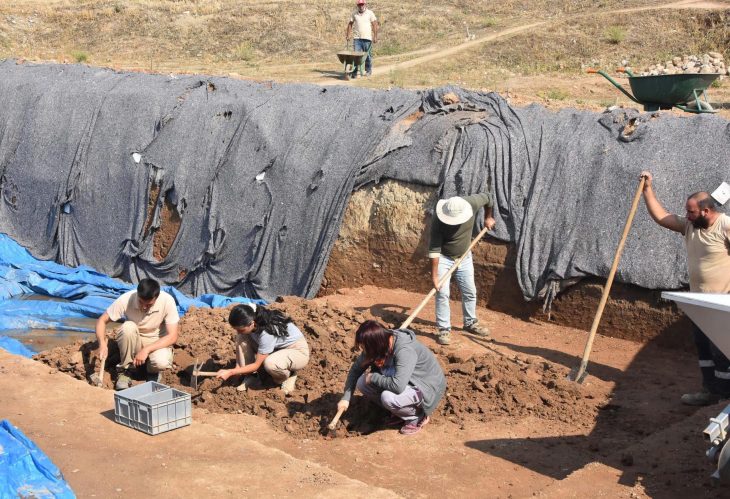
The joint Polish-Omani archaeology team has discovered a 4,000-year-old stone board game whilst excavating a Bronze Age and Iron Age settlement near the village of Ayn Bani Saidah in Oman.
Located near the village of Ayn Bani Saidah, the find was described as “the most exciting and unexpected find ever” according to the Polish Center for Mediterranean Archaeology (CAŚ) at the University of Warsaw, which published the findings on Tuesday.
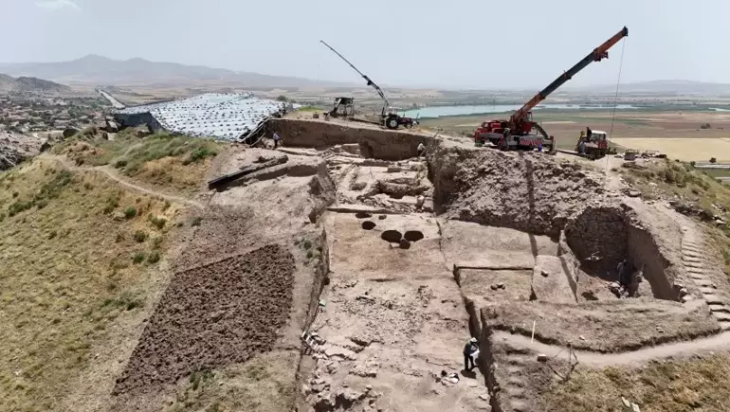
Excavations were carried out as part of an Omani-Polish project dubbed “The development of settlements in the mountains of northern Oman in the Bronze and Iron Ages” by the Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology (CAS) at the University of Warsaw.
The project investigates the development and forms of settlement in one of the least studied corners of Oman: the mountain valleys of the Northern Hajar range.
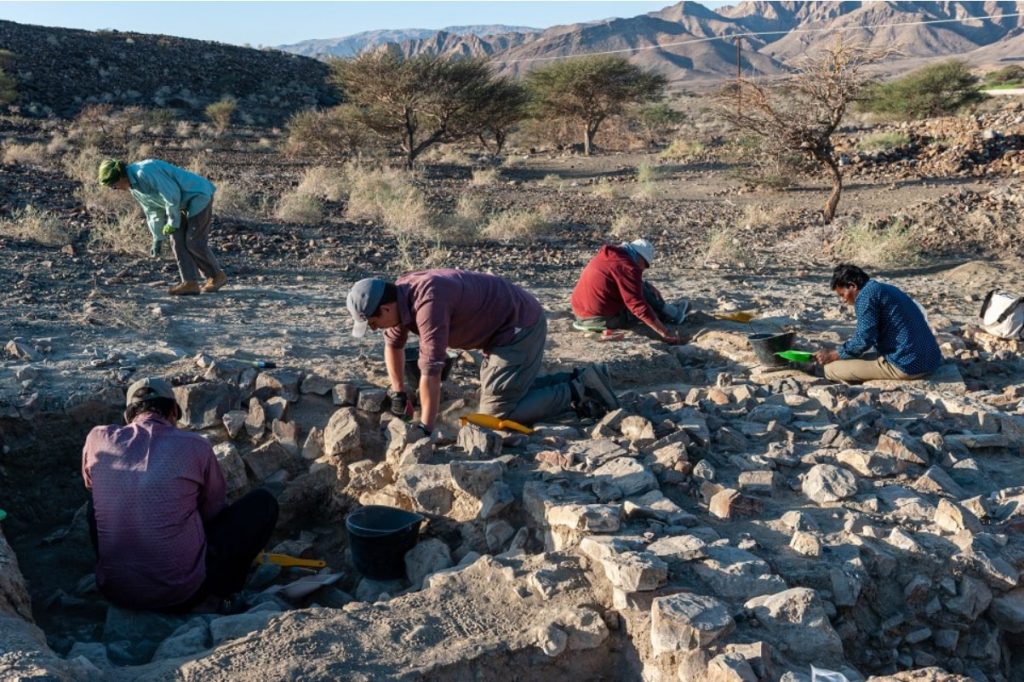

The valley is a micro-region with numerous archaeological artifacts found along with a 10-kilometer-long L-shaped dip between massifs of the Jebel Hajar Mountain range. This was a key highway in ancient times, linking Bat in the south, Buraimi, and Al-Ayn in the north, and the seashore at Sohar in the east.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
As part of the study, researchers identified an ancient settlement from the so-called Umm Al-Nar period (2500-2000BC), where they unearthed remnants of large circular towers and Bronze Age structures.
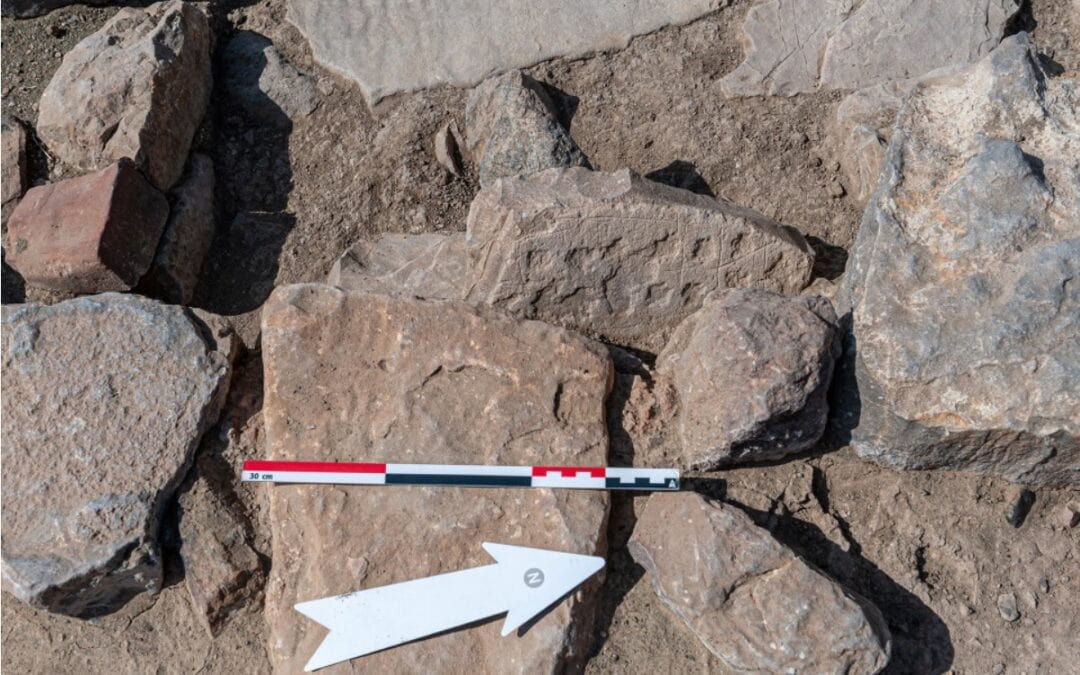
The most interesting discovery is a stone board game with marked fields and cup holes, which is comparable to games seen in India, Mesopotamia, and the Eastern Mediterranean basin.
The most renowned example of a similar gaming board – also dating back nearly 4,000 years – was discovered at the Royal Cemetery at Ur in what is now southern Iraq.
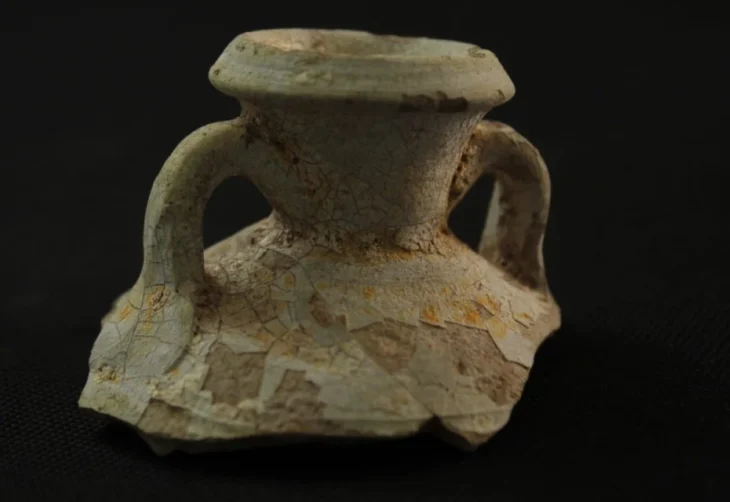
The discoveries were made last month and in addition to the stone game board, evidence was also found of copper smelting. Researchers said this discovery shows that the ancient settlement participated in the lucrative trade mentioned in Mesopotamian written sources.
Next year, the team will continue work in the Qumayrah Valley, both in Ayn Bani Saidah and in Bilt, on the other end of the valley where further Umm an-Nar remains are located.