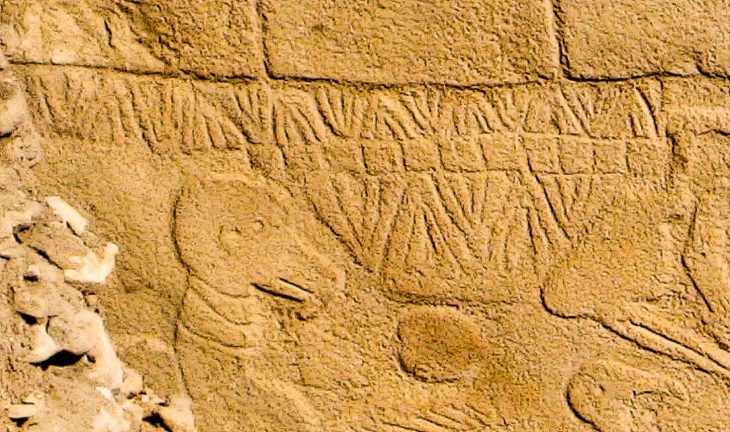
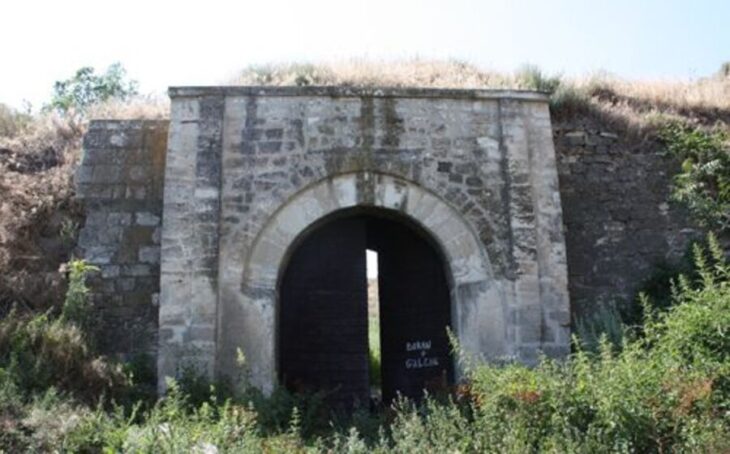
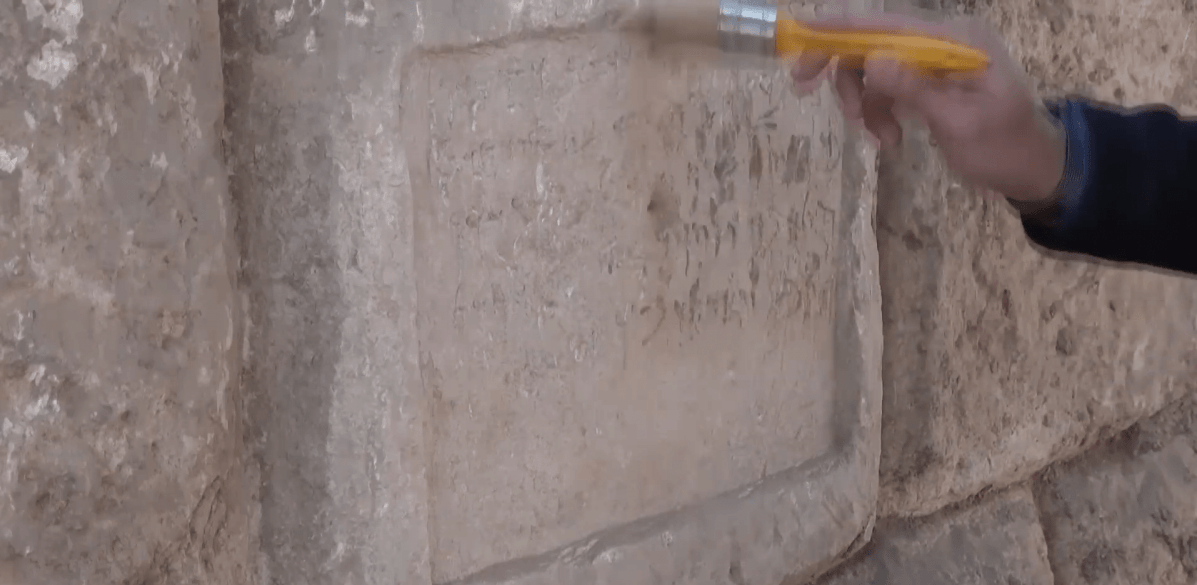Four inscriptions written in Aramaic were discovered in the ancient city with a grid plan, located on an area of approximately 270 hectares in Erciş district of Van province in eastern Turkey. The inscriptions are expected to shed light on the history of the ancient city.
It is aimed to obtain important information about the mysterious structure of the city, which is thought to be the first example of the modern mass housing concept in Eastern Anatolia, with the solution of the Aramaic written inscriptions under protection.
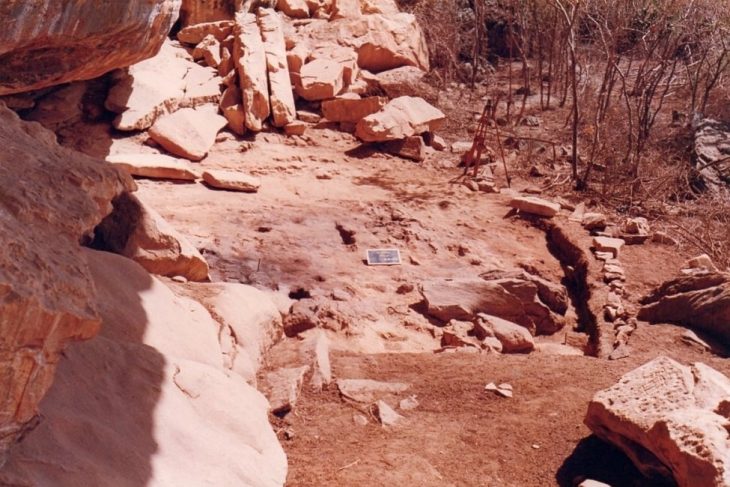
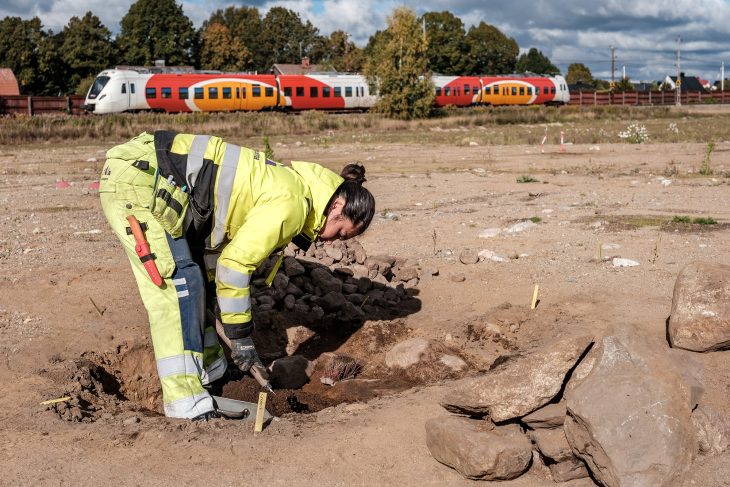
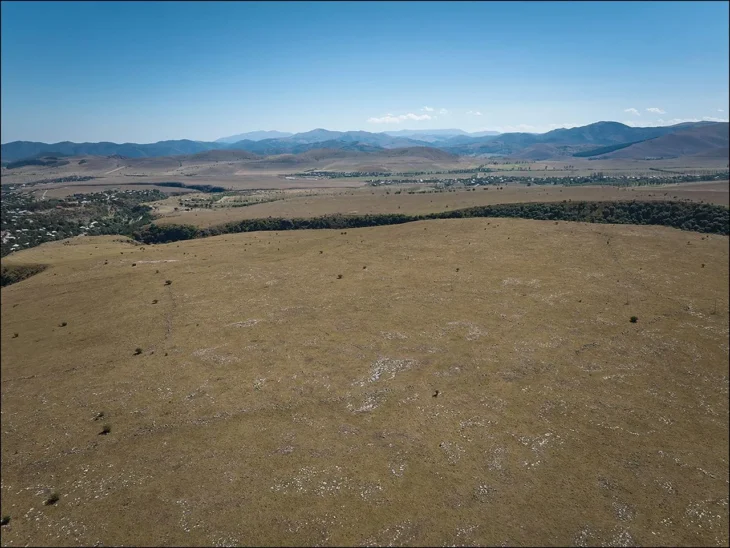
On Zernaki Tepe, in the Yukarı Işıklı neighborhood of Erciş District, excavations are being conducted with the approval of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism in the ruins of the grid-planned historical city, which attracts attention with its approximate 2.5 km length and 1.5 km width.
During the excavations carried out under Van Museum Director Erol Uslu, 4 inscriptions were found, which are considered to belong to the Parthian Empire.
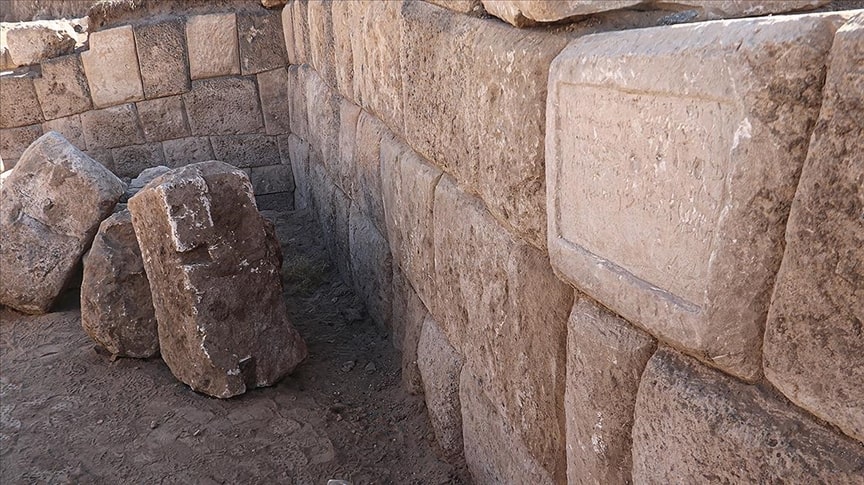

Uslu told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they resumed the rescue excavation work, which was suspended last year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Stating that the unearthed artifacts gave essential clues about the history of the city, Uslu said that some of the walls were unearthed as a result of the works.
Noting that there is no area to point to a door in front of the eastern wall, Uslu gave the following information:
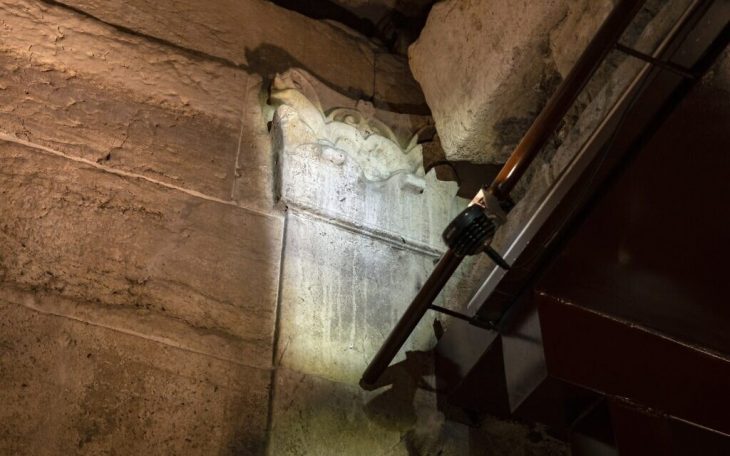
“Four inscriptions with Aramaic inscriptions carved into the surface of the outer walls were found. Scientific studies are continuing on these inscriptions. Four inscriptions need to be analyzed and translated in order to provide a clear periodical information. The first data is that this structure belongs to the Parthian Empire period. It must say that there are serious data and findings that the Persians and Parthians established dominance in this region after the Urartian period. Apart from the ancient city of Zernaki Tepe, no architectural remains from the Parthian Empire period have been recorded in the museum records to date. We saw that these typefaces, which we define as Aramaic, were used for the first time in this ancient city.”
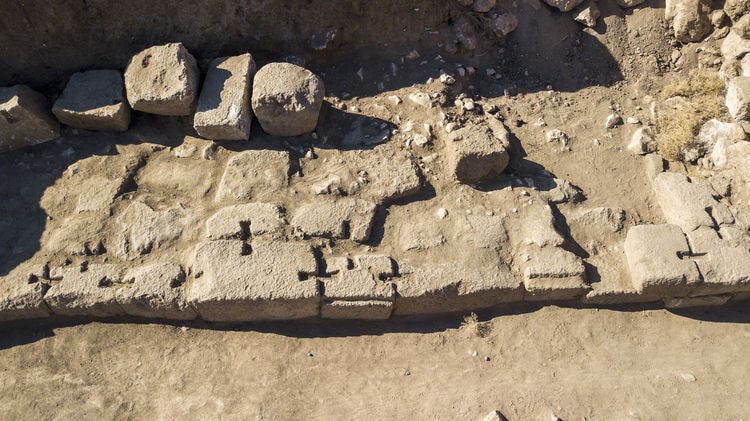

“For the first time, Aramaic inscriptions were found on a wall in the Eastern Anatolia Region”
Professor Rafet Çavuşoğlu, who was the scientific advisor of the excavation, stated that they concentrated the excavations on the northern wall of the city and they encountered four inscriptions that they considered important here.
Stating that an expert team continues to work on the solution of the inscriptions, Çavuşoğlu said:
“They seem to be inscriptions of the Parthian Empire period, but their analysis will tell us much clearer things. It will enable us to give a clear date with carbon analysis. Aramaic inscriptions are very important for Anatolian archeology. For the first time, Aramaic inscriptions were found on an architectural wall in the Eastern Anatolia Region. Another important point is that this place “Has a grid plan. When we make a rough calculation, it shows us that between 7 thousand and 14 thousand people lived on this hill alone. It is a very important site for archeology.”