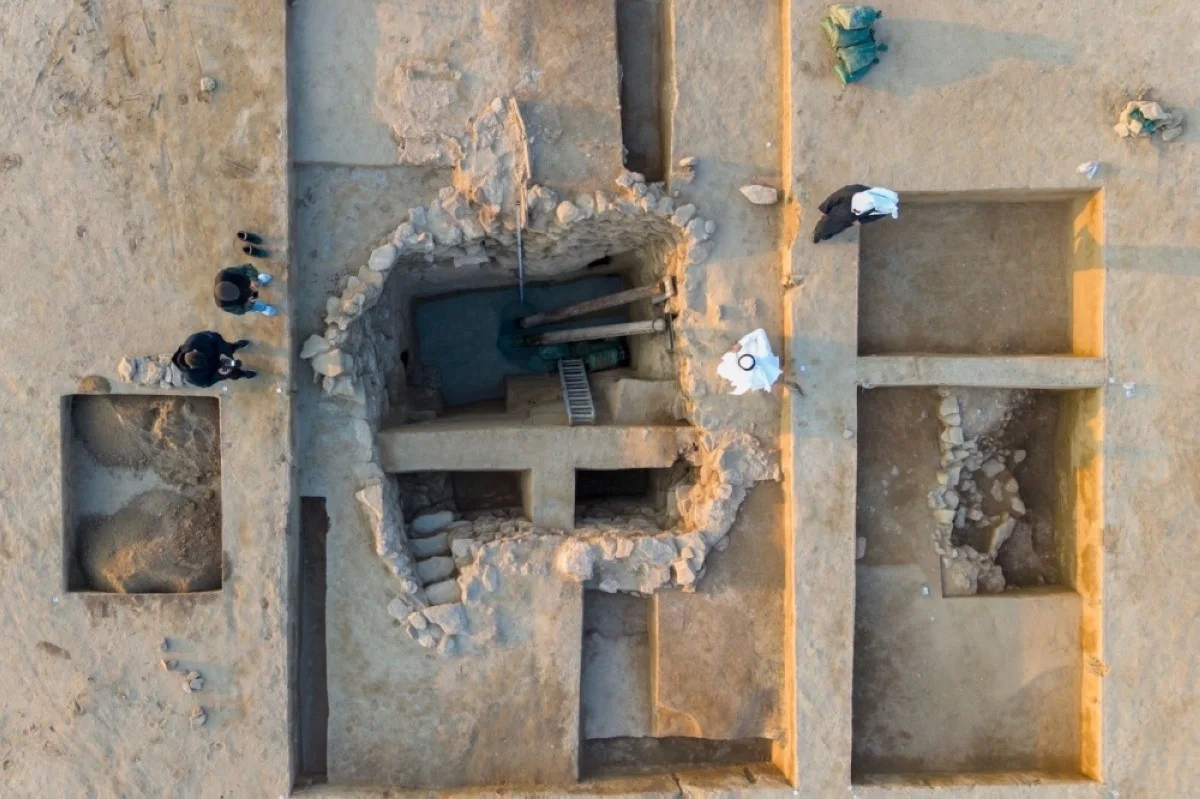
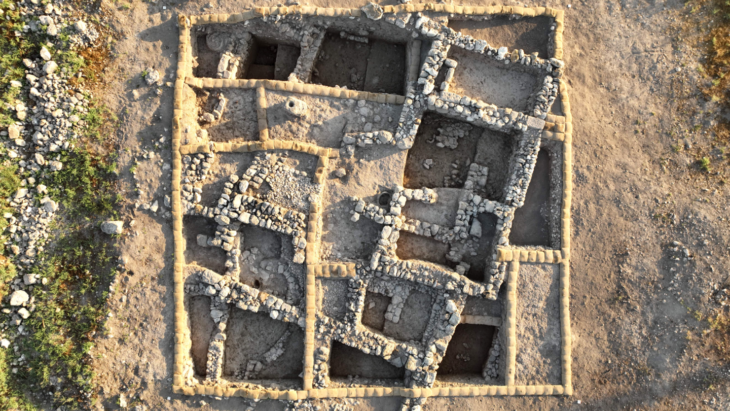
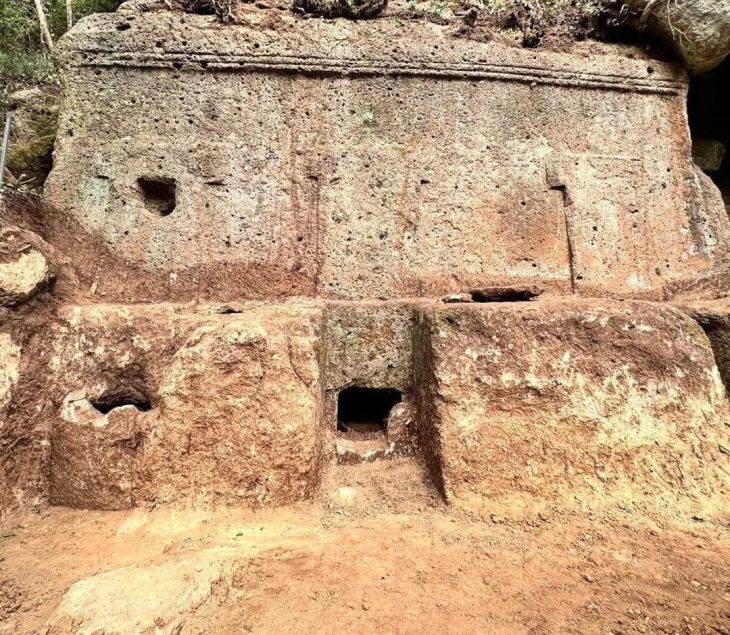
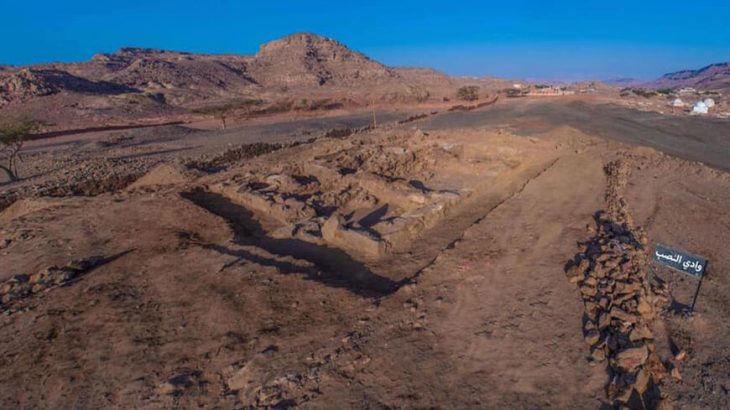
An ancient well, dating back to the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods, has been discovered on Failaka Island, providing valuable insights into the region’s past. This impressive well, notable for its large size and abundant water supply, was found within the courtyard of a substantial residence from the 7th and 8th centuries AD.
The discovery was announced by the National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL), with insights provided by Mohammad bin Redha, the Acting Assistant Secretary General for Antiquities and Museums. In a statement to KUNA, bin Redha elaborated on the significance of the find, highlighting not only the well itself but also the surrounding archaeological features that contribute to our understanding of the island’s rich history during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods.
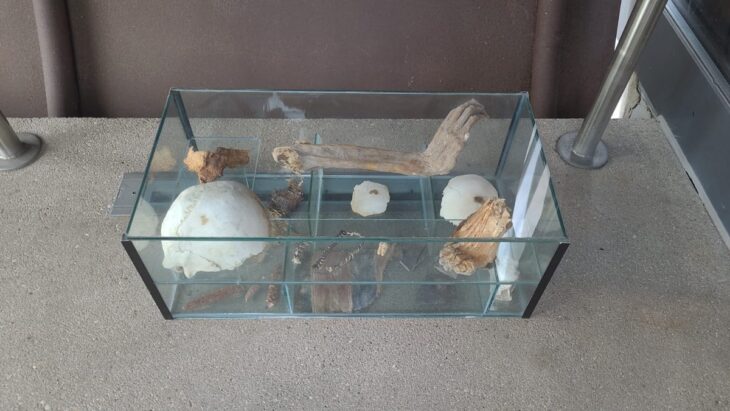
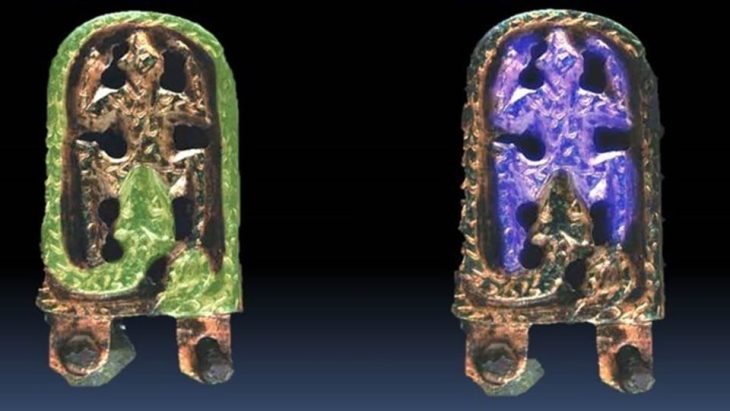
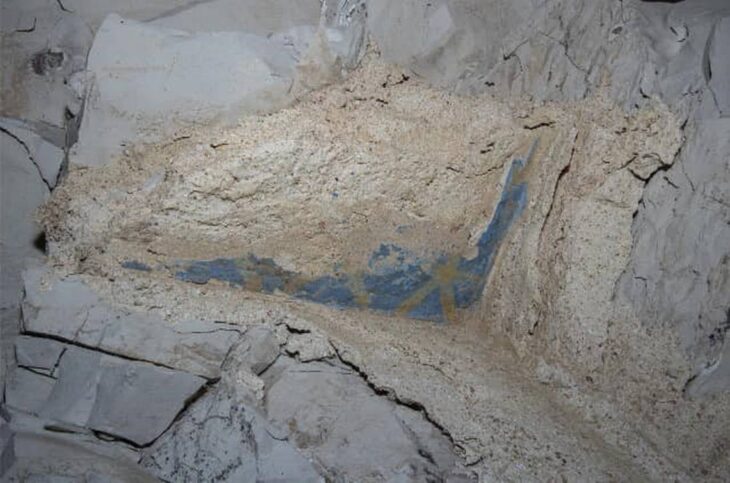
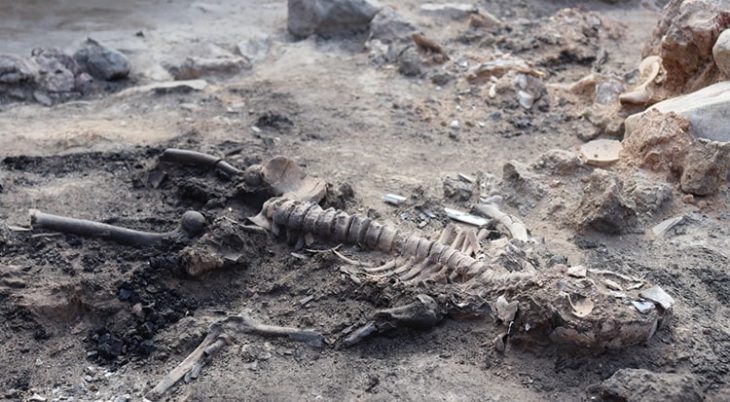
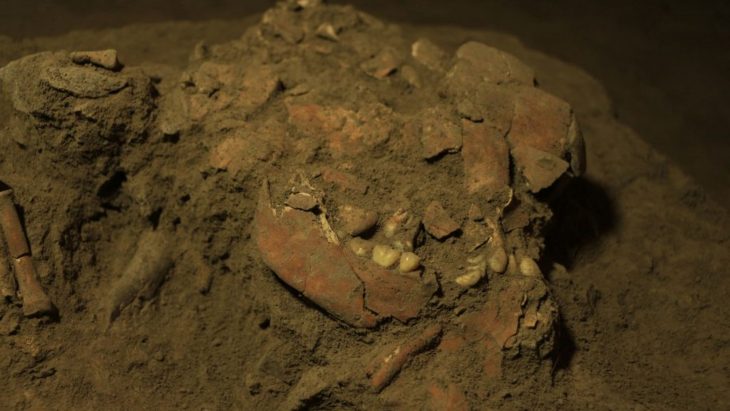
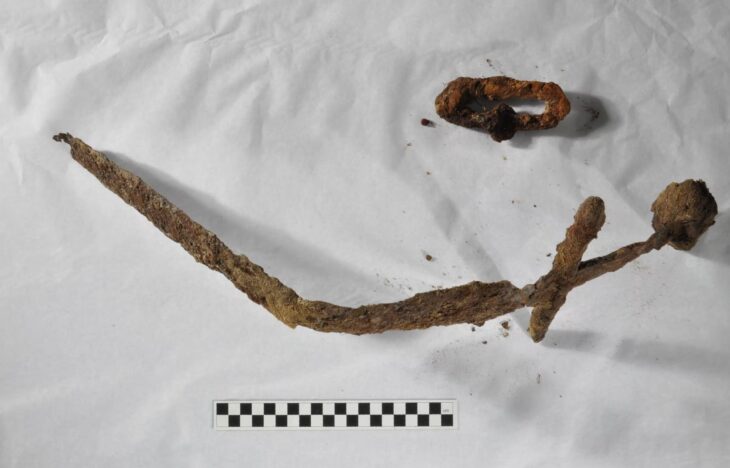
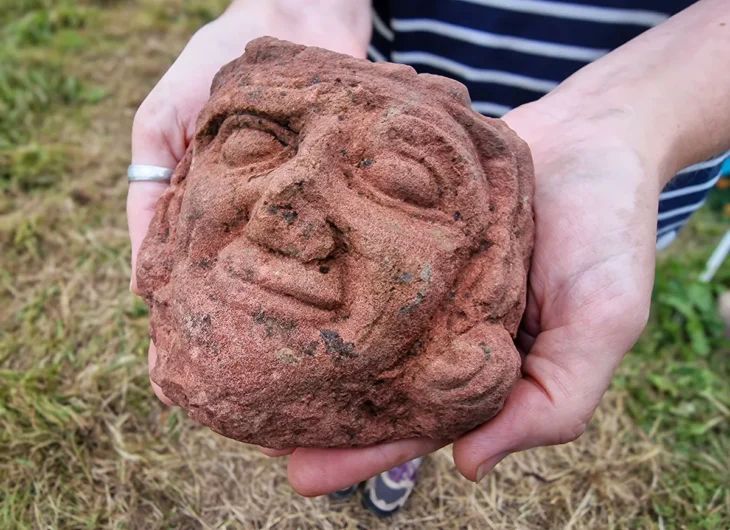
In an interview with KUNA, bin Redha shared that the excavation also uncovered the rock foundations of a nearby structure, remnants of a significant wall that once enclosed the courtyard, and fragments of pottery estimated to be around 1,300 to 1,400 years old. This excavation is part of a larger project led by a Kuwaiti-Slovakian archaeological team, which began its work in 2019 in the Al-Qusour area, known for its rich historical context.
Dr. Hassan Ashkanani, a Professor of Archaeology and Anthropology at Kuwait University, described this discovery as one of the most significant archaeological finds on Failaka Island. He noted that the well and the associated artifacts provide essential insights into the cultural and economic activities that took place on the island during the transition from the Christian period to early Islam. Among the extraordinary discoveries were over five kilograms of precious stones, including rubies and purple amethyst, indicating a vibrant trade network that existed on the island 1,400 years ago.
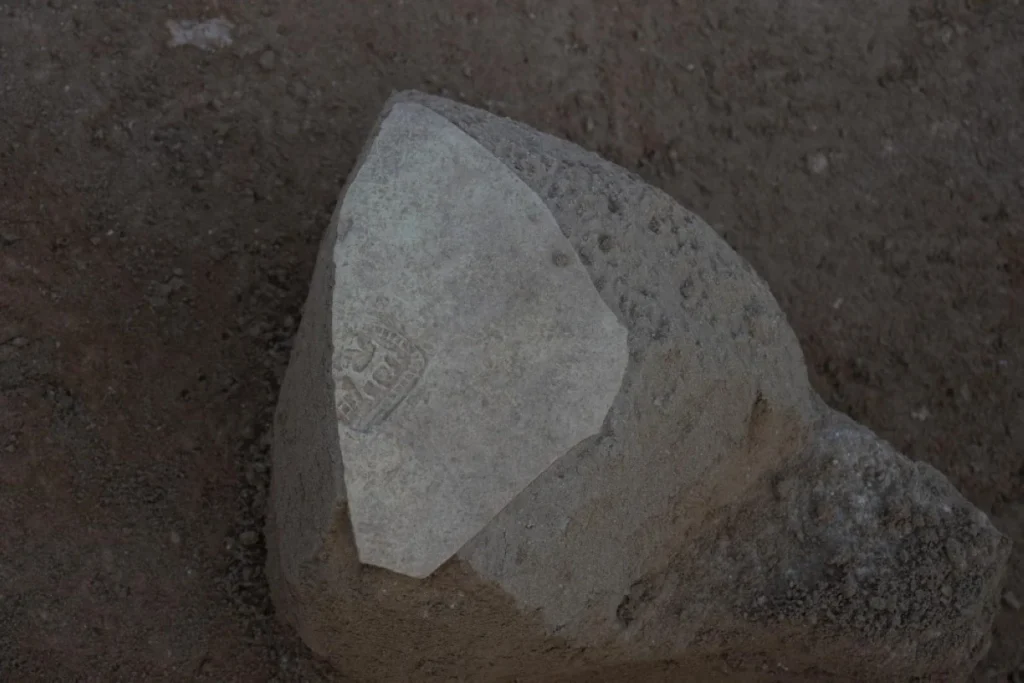

Furthermore, Dr. Matej Rutkay, the leader of the Slovak mission, announced plans for the excavation team to focus on the northern section of the Al-Qusour settlement in the upcoming 2025 season. This area has previously revealed evidence of a courtyard and a large house, thought to belong to a prominent figure of that time. The newly discovered site measures 38 meters in length and 34 meters in width, while the house itself covers an area of 97 square meters. The well, measuring 4.5 meters by 4 meters, is located next to an ancient water channel, showcasing the advanced infrastructure of the settlement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Al-Qusour site is recognized as one of the most significant and expansive archaeological locations on Failaka Island, stretching approximately two kilometers from east to west and extending one kilometer inland to the south. Previous excavations have uncovered the foundations of churches, residential structures made from limestone and mud bricks, as well as gypsum artifacts, pottery, and precious stones from various historical periods.
Failaka Island continues to be a focal point for archaeological research, offering invaluable insights into Kuwait’s rich cultural heritage and its historical role in the region.
Cover Image Credit: Aerial photo of the discovered water well and the stairs leading to the bottom. Credit: KUNA