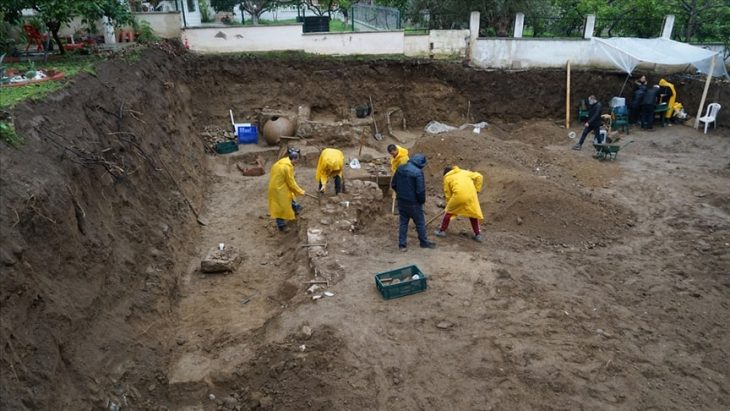
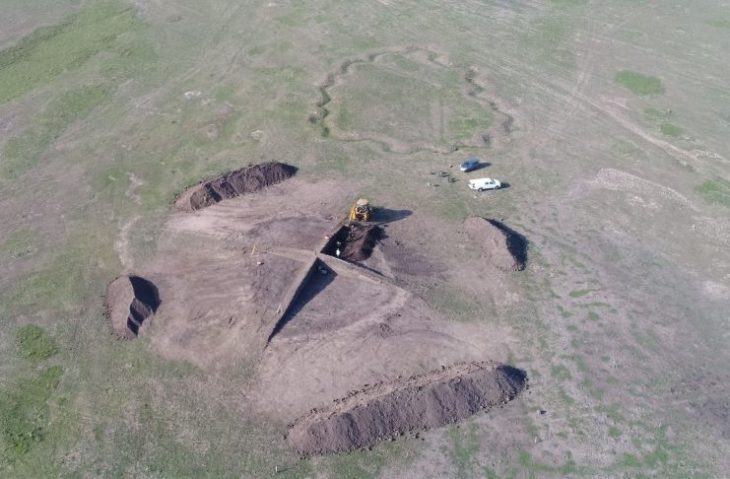
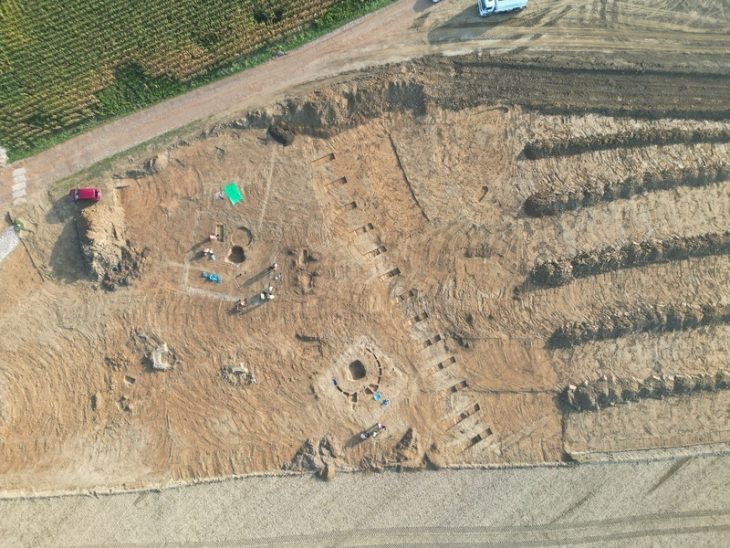
The Malta Superintendence of Cultural Heritage announced on Friday that trenching works by the Water Services Corporation had uncovered an ancient quarry that most likely originated during the classical era.
The area, which has a high incidence of known archaeological sites recorded, was being monitored by an approved archaeologist of the Superintendence of Cultural Heritage.
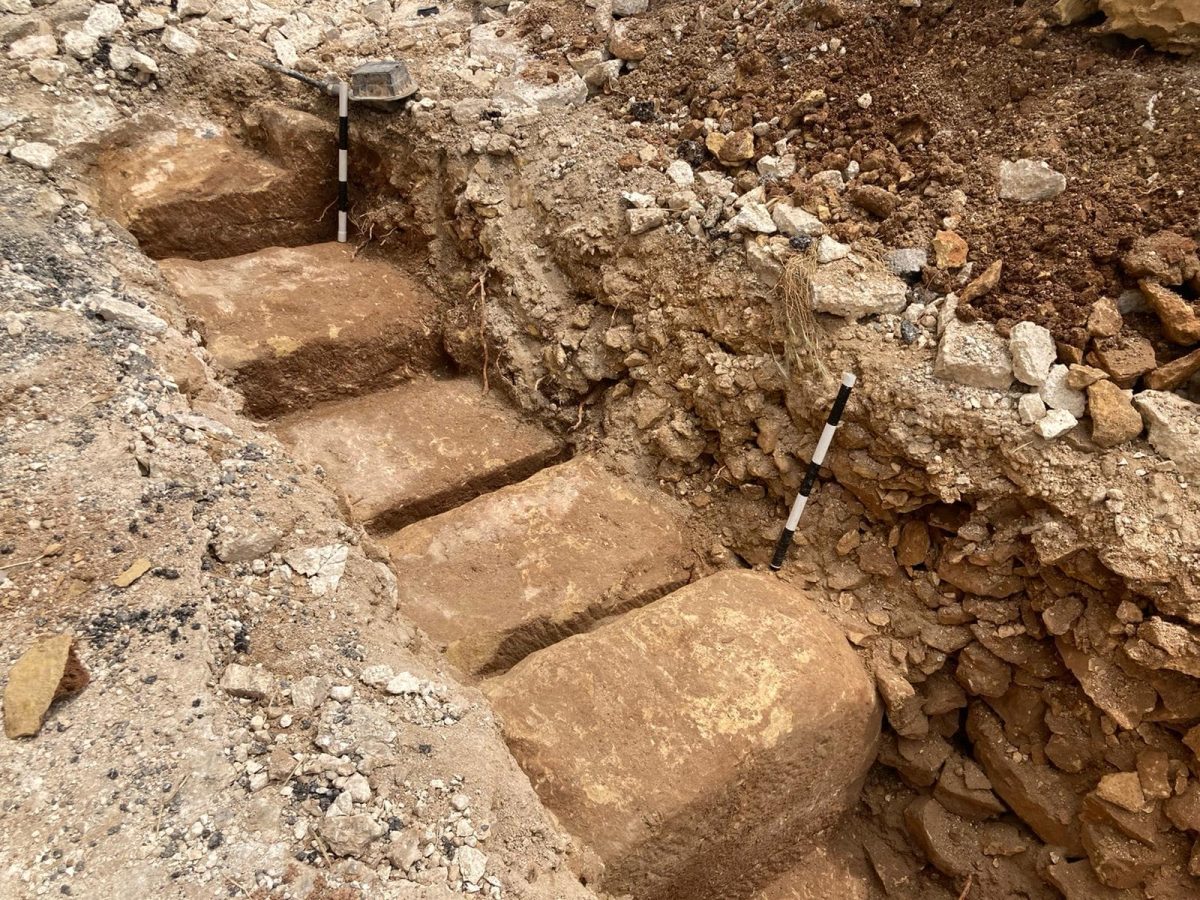
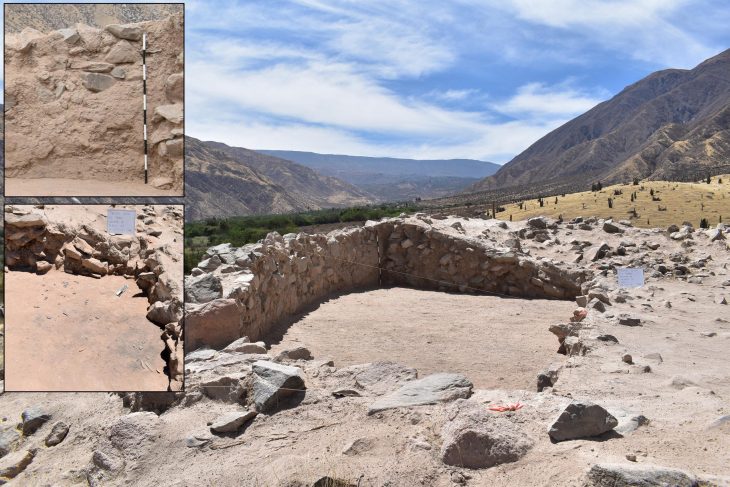
According to a statement issued on Friday, the archaeological monitor immediately notified the Superintendence of a potential discovery when rock-cut surfaces with visible tool marks were discovered during the works.
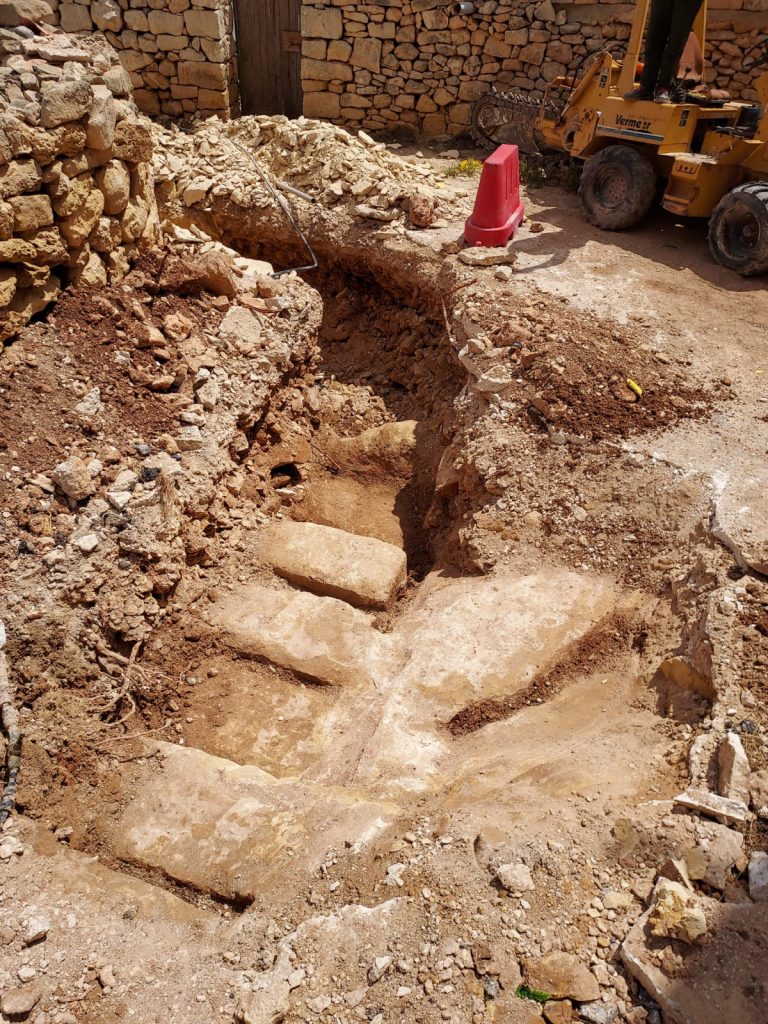

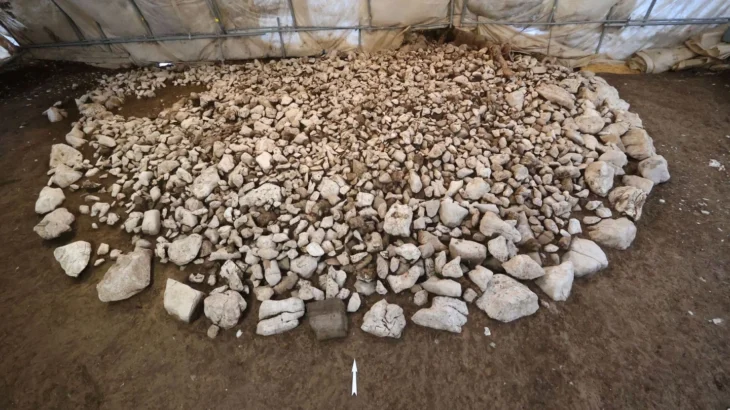
The Superintendence then issued instructions for the proper investigation of this feature, which turned out to be an ancient quarry with large ashlars (large rectangular stone block) hewn out of the rock, yet to be detached from the bedrock.
According to the statement, while no associated material has been discovered, and so an accurate date could not be attributed, based on the ashlars and the typology of the quarry, the discovery could be safely attributed to a classical period date.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The classical period is typically associated with ancient Greece and ancient Rome.
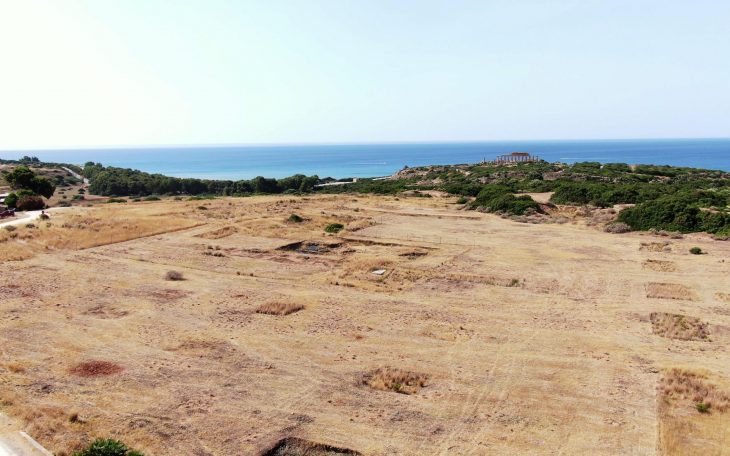
The discovery was made not far from Tas-Silġ, home to a multi-period archaeological complex with remains dating back roughly 4,000 years.
Activity on the Tas-Silġ started in the prehistoric Tarxien phase (3,150-2,500 BC) when a number of megalithic temples were constructed on the site. The Phoenician – Punic period saw adaptations of the temple to fit newly emerging ritual needs but the sacred character and function of the site was maintained. The site at one point served as a Phoenician and Punic temple to the goddess Astarte and during the Roman era was converted into a temple dedicated to the goddess Juno.
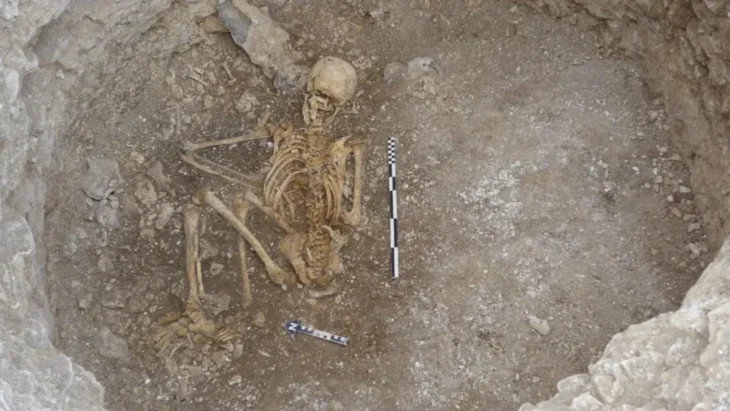
Heritage Malta announced in 2021 the discovery of a new neolithic structure at Tas-Silġ.
Cover Photo: Superintendence of Cultural Heritage