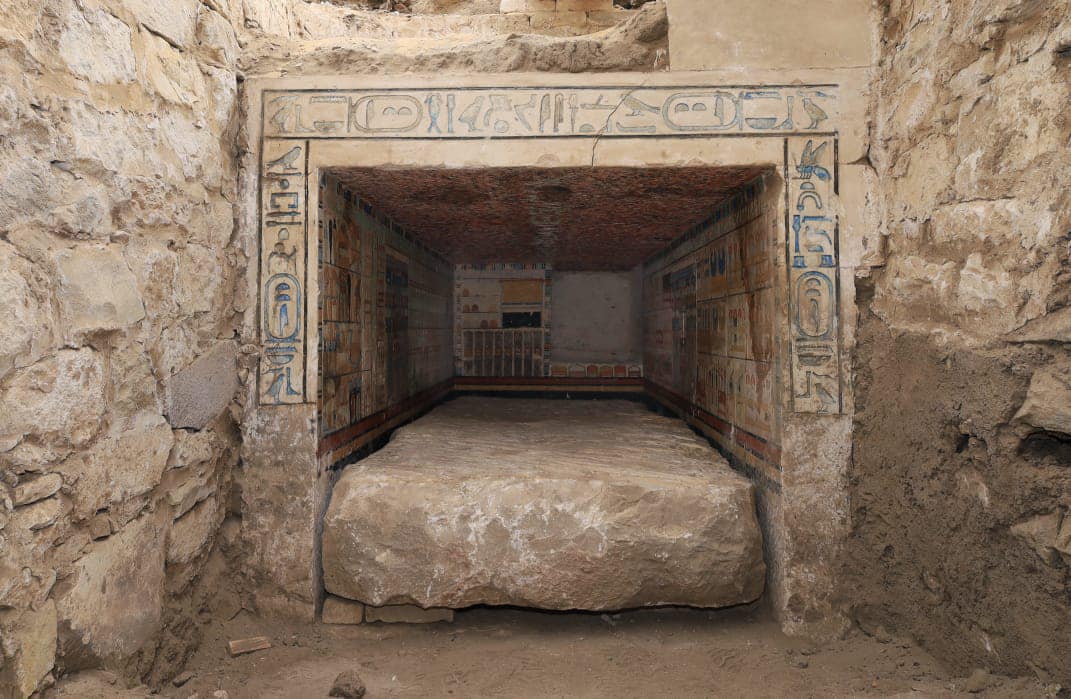
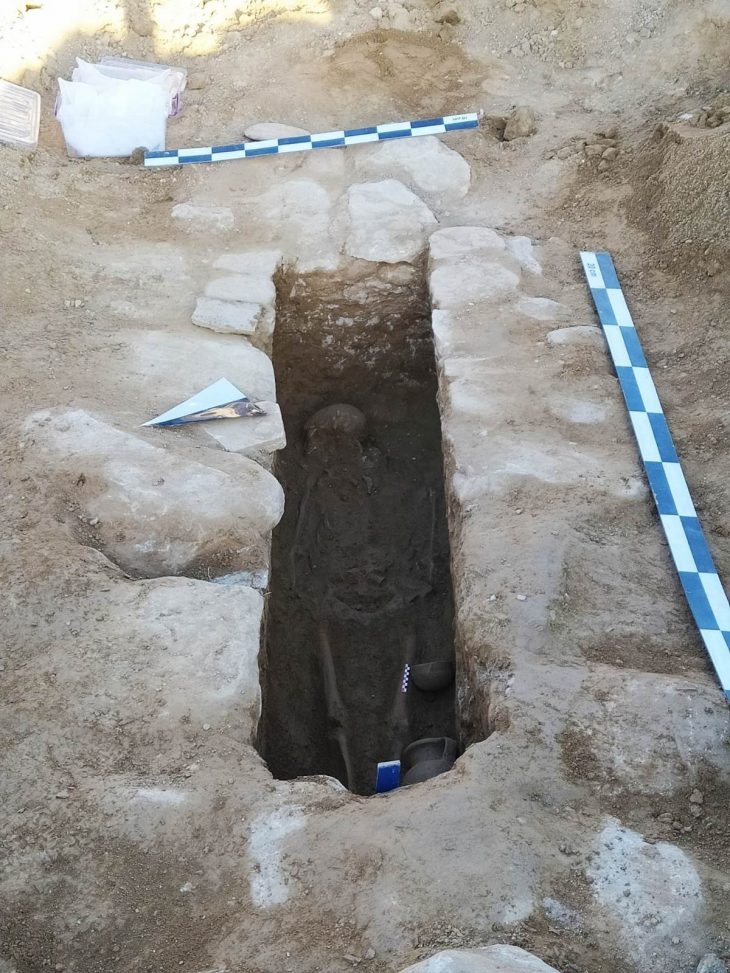
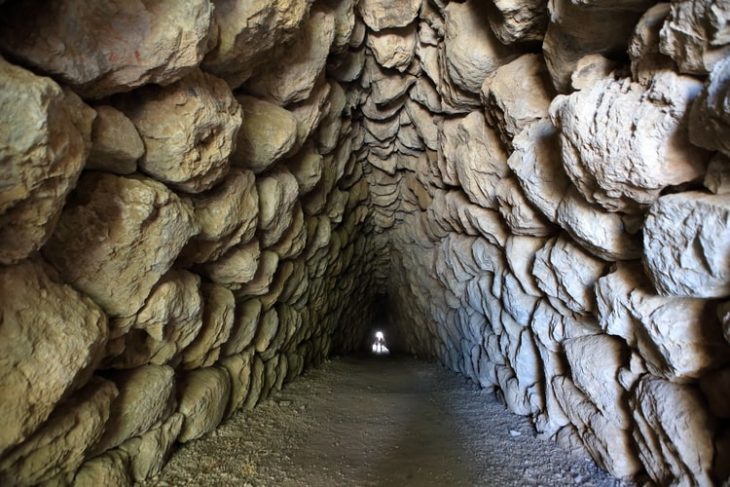
In the southern region of the Saqqara archaeological site, a joint French-Swiss archaeological team made an important discovery uncovering the mastaba tomb of the royal physician Teti Neb Fu from the Old Kingdom, according to a statement by the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities.
This tomb, unearthed in the southern region of the archaeological site of Saqqara, known to contain the tombs of high-ranking officials from the Egyptian Old Kingdom, shows that medicine and magic were once equally revered, and expertise in both earned a long-dead physician to the pharaohs a place of honor among the ancient world’s most esteemed.
Dating back over 4,000 years to the reign of King Pepi II, this important find features exquisite carvings and vibrant artwork, including a painted false door and elaborate scenes depicting funeral offerings.
The sarcophagus found inside the tomb was also inscribed with the name of its occupant and his titles, according to the post. Because of the burial location in Saqqara, researchers knew he was important, but Teti Neb Fu’s official titles named him as the chief palace physician.
Teti Neb Fu, who held prestigious titles such as Chief Palace Physician, Chief Dentist, and Director of Medicinal Plants, also had a unique role as a “Magician” of the Goddess Serket, specializing in the treatment of venomous bites.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Additionally, he was known as the “Great Physician of Teeth” and “Director of Medicinal Plants”, suggesting that he led research and practical applications in the fields of dentistry and the use of therapeutic herbs.
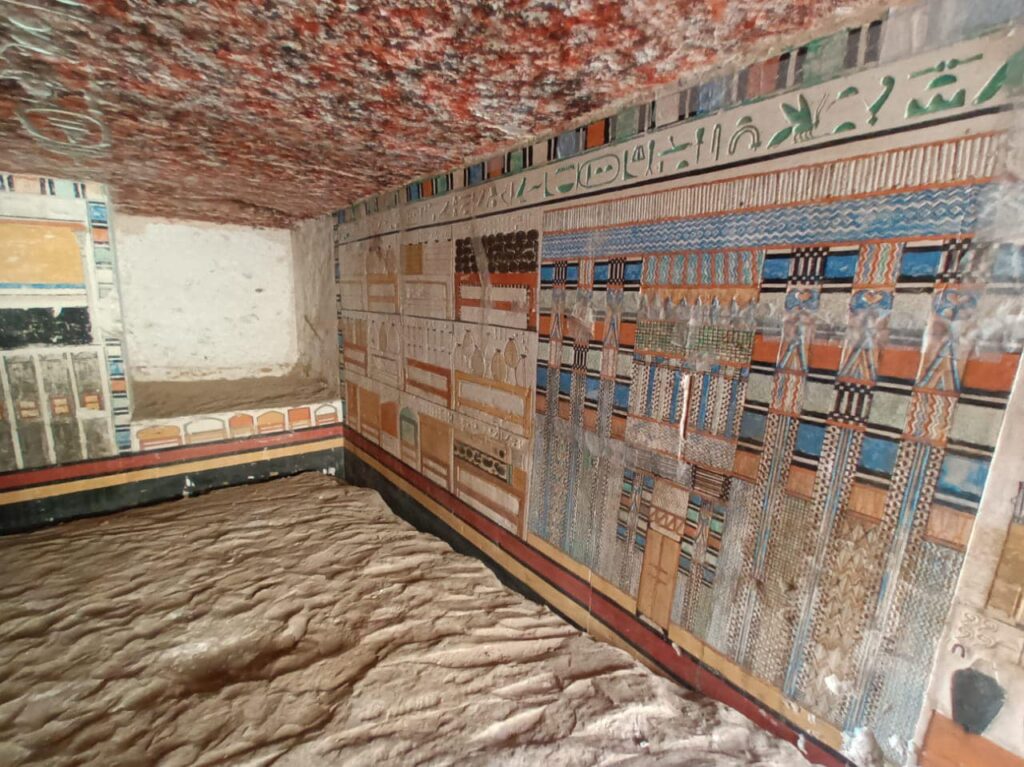
Even though it may have been looted in the past, the mastaba still has many of its ornamental features. The director of the archaeological mission, Dr. Philippe Collombert, said the walls are decorated with remarkable reliefs and inscriptions, including a complex frieze that displays the owner’s name and titles.
Among the most remarkable elements is the red-painted ceiling, which is intended to resemble granite blocks, a material commonly found in imposing buildings. The titles and name of the doctor are also written in the middle of the ceiling. An additional noteworthy discovery within the mastaba is a stone sarcophagus, which has hieroglyphic decorations inside that offer more information about Teti Neb Fu and his accomplishments.
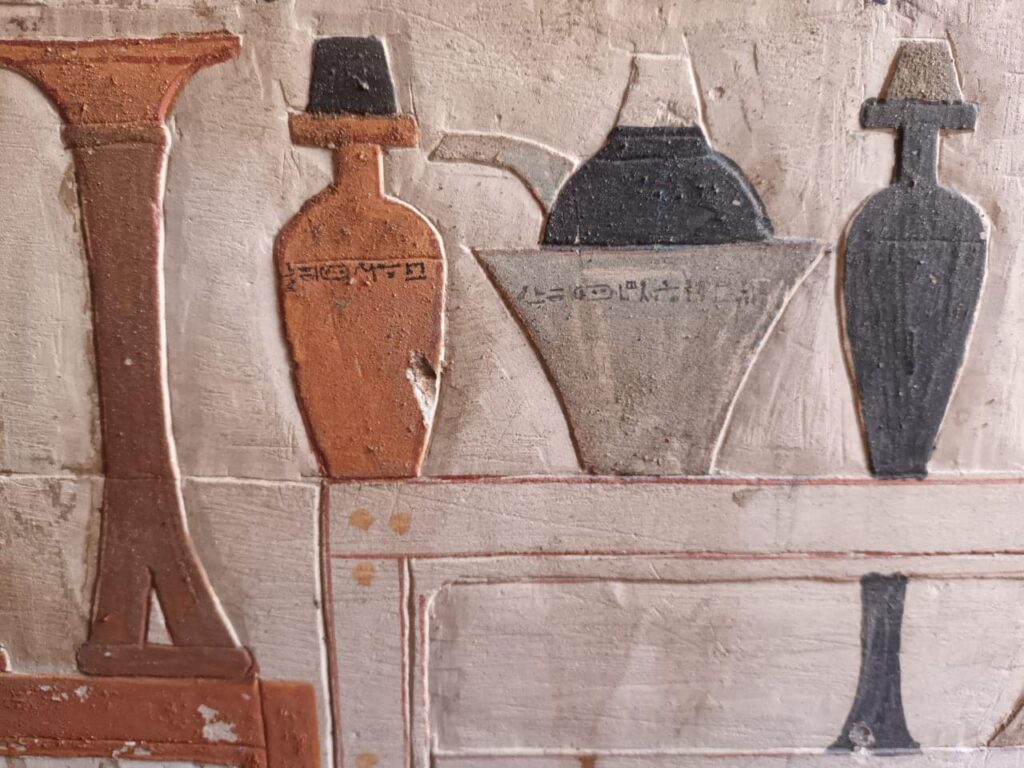

Mohamed Ismail Khaled, secretary-general of Egypt’s Supreme Council of Antiquities, emphasized the importance of this discovery, stating that the texts and drawings on the tomb’s walls unveil new insights into the daily life of the Old Kingdom.
This discovery strengthens Saqqara’s position as one of Egypt’s most important historical sites and contributes to its rich archaeological legacy.
Excavations in this area of Saqarra began in 2022, to unearth the graves of state employees for King Pepi who are buried near him and his wives, officials said.
Egypt Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image Credit: Official Facebook page of the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities