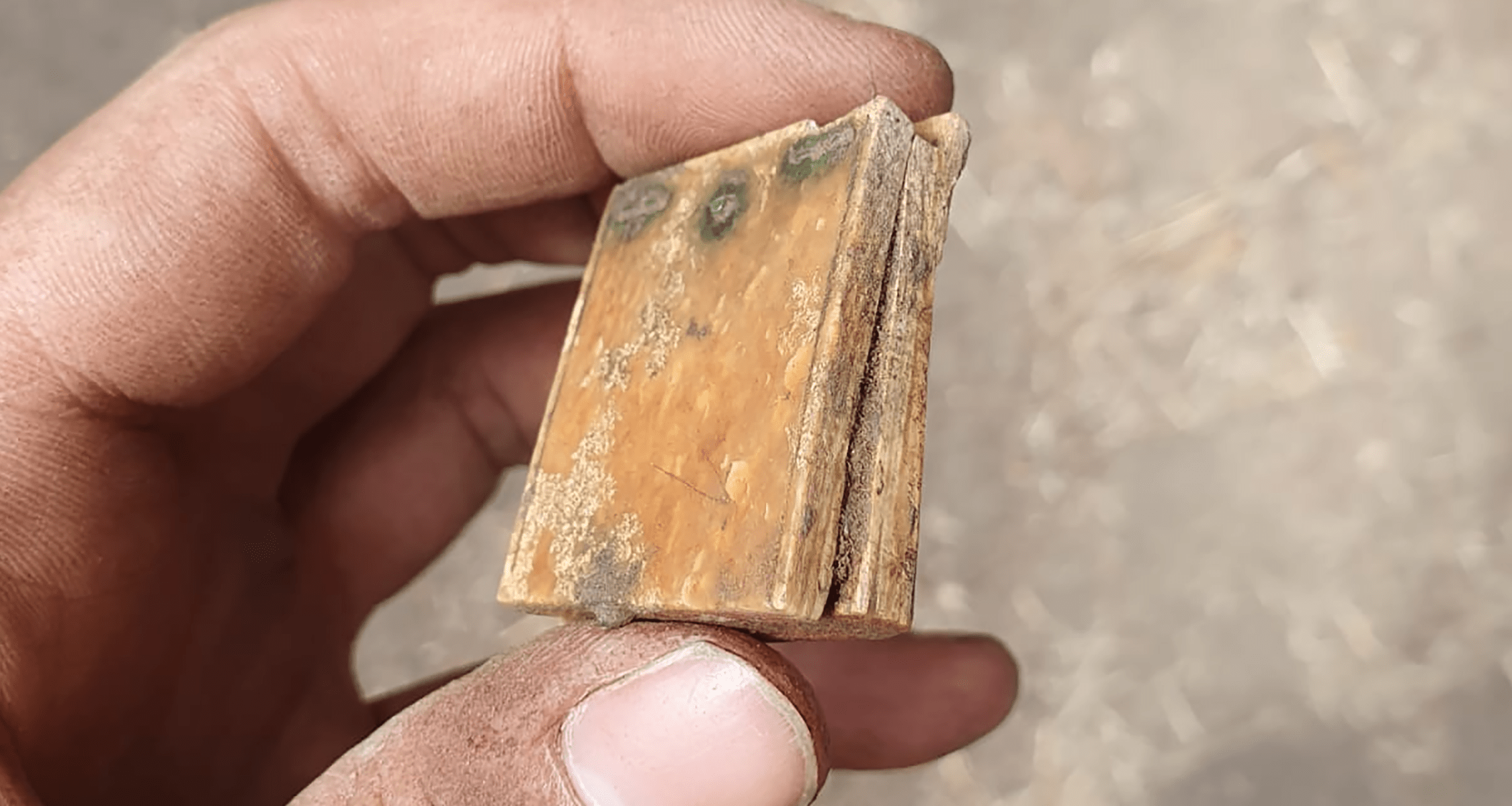
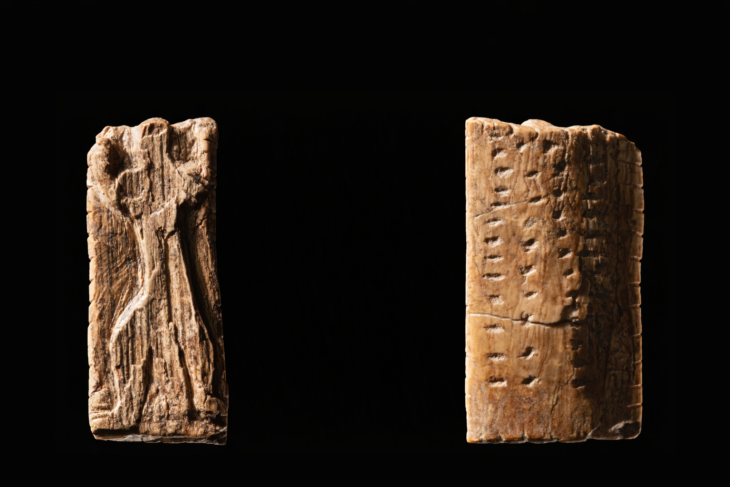
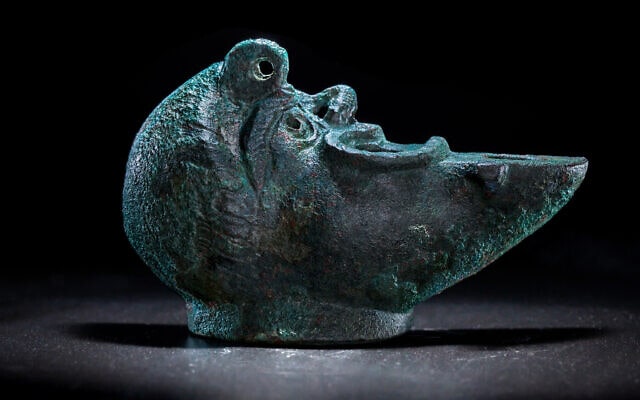
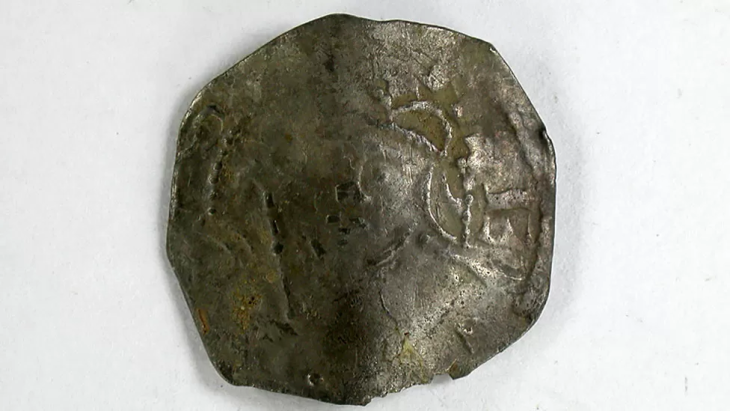
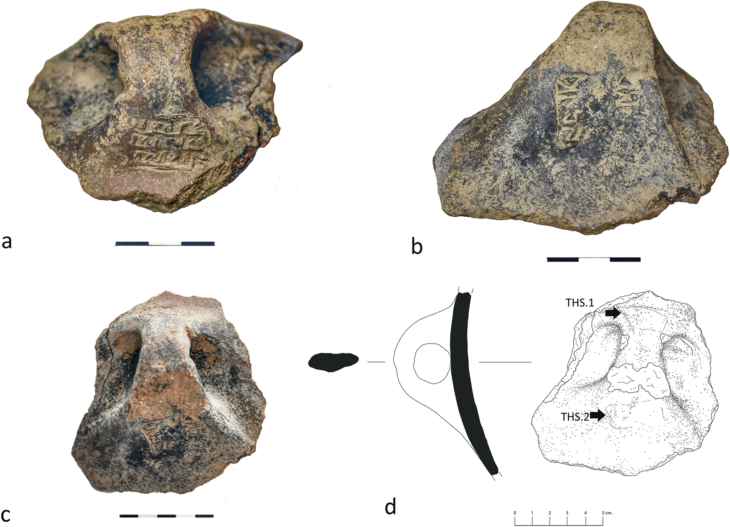
A rare Medieval sundial, which is approximately the size of a matchbox was discovered in the old town of Marburg, Germany.
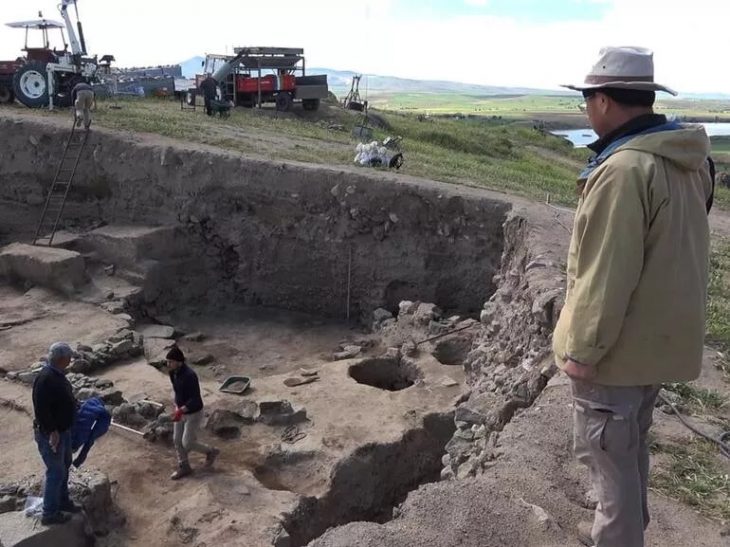
According to a statement from Marburg University, students were digging a church site in the town when they discovered the sundial. The sundial is constructed of bronze and wood.
The old clock, which is thought to be from the late medieval era, is thought to have belonged to the Brethren of the Common Life, a monastic order that was founded in the Netherlands in the late 14th century. It was a community established by Gerard Groote, a Dutch Catholic deacon. Eventually, the Brethren spread to the Netherlands, Germany, and Switzerland. They settled in the old monastery structure from 1527, situated in the upper part of Marburg.
“The sensational find provides a clear insight into the meeting of a high level of knowledge in astronomy and mathematics with specialized craftsmanship on the threshold from the Middle Ages to modern times,” explains the head of the educational excavation,” Professor Dr. Felix Teichner said in a press statement.
According to Professor Teichner, of the Department of History and Cultural Studies at the Philipps University of Marburg, it’s the first time an object like this has been found in Hesse, the German state, and not many such sundials are left.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeologists compared the unusual find with a similar one discovered by archaeologists in a Swiss ministry to identify the artifact. According to Teichner, they still don’t know why the sundial was discovered in the specific location.
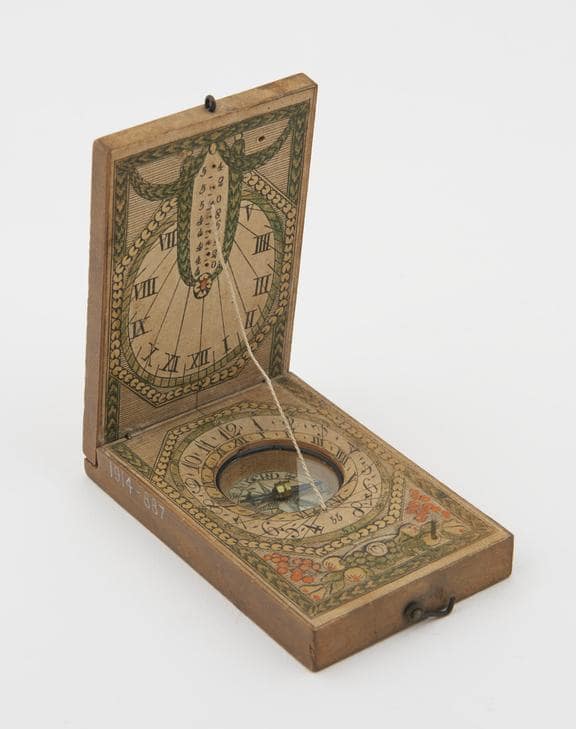

Ancient clocks called sundials tracked the sun’s position throughout the day to determine the time. They are made up of a flat plate and a gnomon, which, when the sun shines, casts a shadow on the plate. Sundials have been around since at least 1500 BCE.
When this specific sundial is opened, a hole that was intended to hold a stick for marking the sun’s shadow is visible.
Portable sundials have existed since ancient times, and by the 1600s, some Europeans were carrying pocket-sized sundials.
Excavations at the site are continuing, in the hopes of unearthing more rare finds.
Philipps University of Marburg
Cover Photo: Philipps University of Marburg