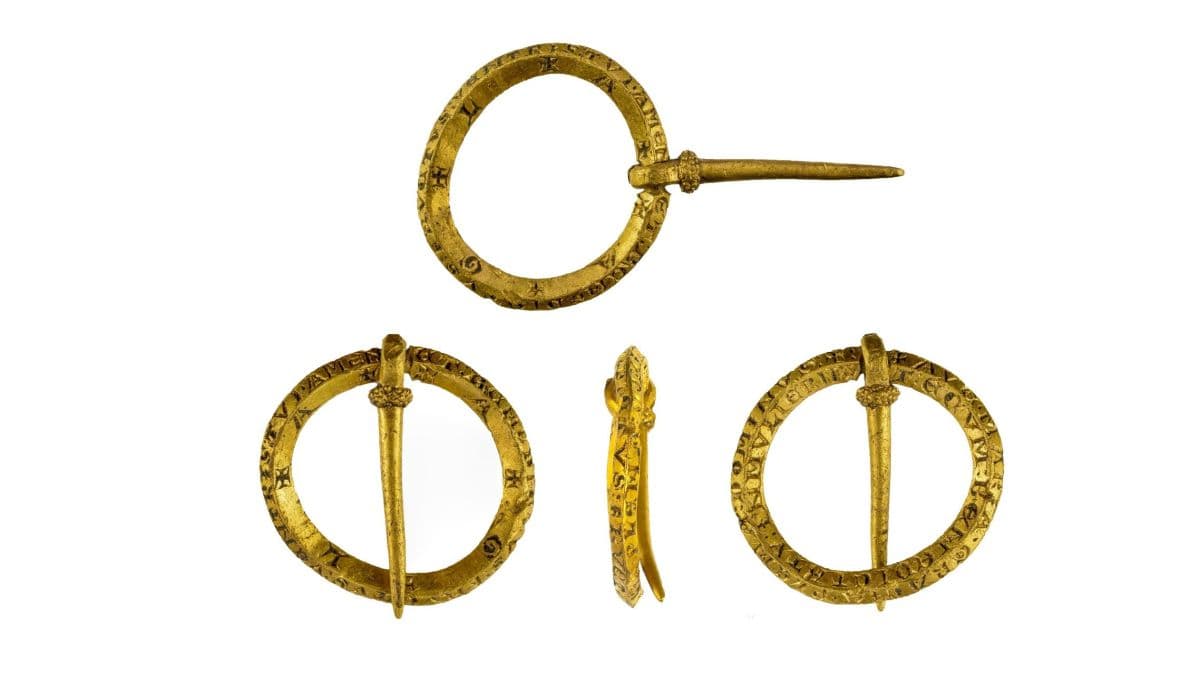
A Medieval gold annular brooch with prayerful inscriptions has been discovered in the parish of Manningford in Wiltshire, in the U.K.
A medieval gold brooch with a series of Latin and Hebrew inscriptions may have mixed religion and magic in an attempt to give its user protection against illness or supernatural events.
It was dated between 1150 and 1350 A.D. and is inscribed with a Latin prayer as well as the initials of a Hebrew phrase said to have amuletic characteristics. While this type and age of inscribed brooch have been previously been discovered, this one is unique on the archaeological record because the inscription is complete, without errors (common in an age when artisans were not literate), is engraved on four sides, and includes both the prayer and the amuletic initials.
A complete Medieval gold inscribed annular brooch, dating to c. AD 1150-1400. The brooch has a slightly sub-circular frame, with a lozengiform cross-section. The frame is beveled on either side, giving four surfaces, each inscribed with part of Christian devotional prayer. The letters are inscribed in Lombardic text, with the use of cross potent to divide some of the text. Each part of the inscription reads clockwise from the pin constriction.
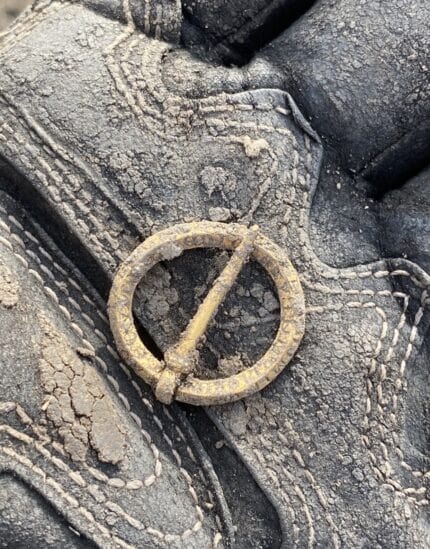

The inscription on three of the surfaces is the Hail Mary which all together read: + AVE. MARIA. GRACIA. PLENA: DOMINVS: + T: ECVM: BENEDICTATV: INMULIERIBV ET: BENEDI(CT)VS: FRVCTVS: VENTRIS: TVI. AMEN. (Meaning “HAIL MARY FULL OF GRACE THE LORD/ IS WITH THEE/ BLESSED ART THOU AMONGST WOMEN/ AND BLESSED IS THE FRUIT OF THY WOMB. AMEN.”) The S at the end of “MULIERIBV” is missing, not an error, but a deliberate choice because the pin attachment was in the way.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The fourth surface, the reverse inner angle, reads: + A + G + L + A +, the initials of the Hebrew phrase “Atha Gebir Leilam Adonai. (Meaning “Thou art mighty forever, O Lord.”) The AGLA initials were used in the Middle Ages as words of power to protect against illness, particularly fever, and nefarious supernatural forces.
The brooch was discovered by metal detectorist William Nordhoff in March of last year in a freshly plowed field in Pewsey Vale.
At a coroner’s inquest last month, it was proclaimed treasure. The next step is valuation, after which a local museum, in this case, likely the Salisbury and South Wiltshire Museum, will have the opportunity to acquire the brooch for the assessed market value.