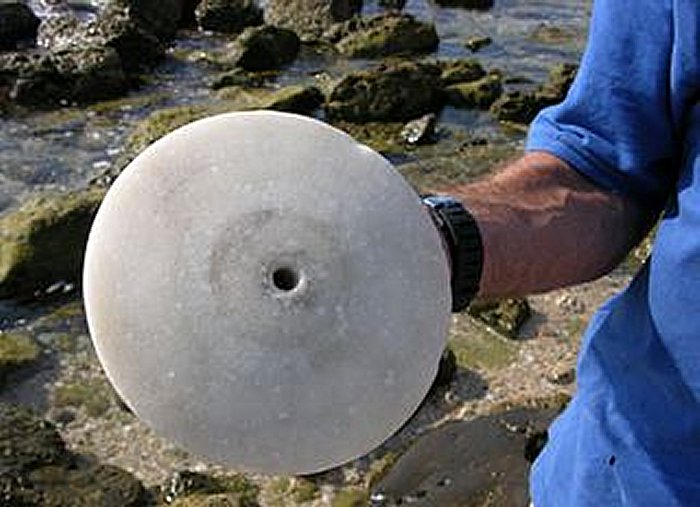
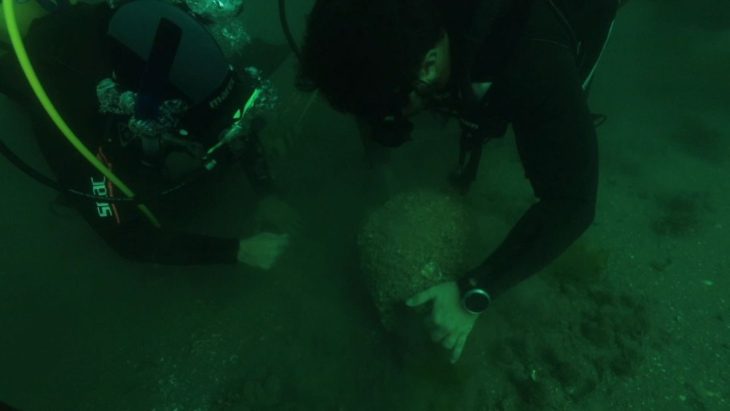
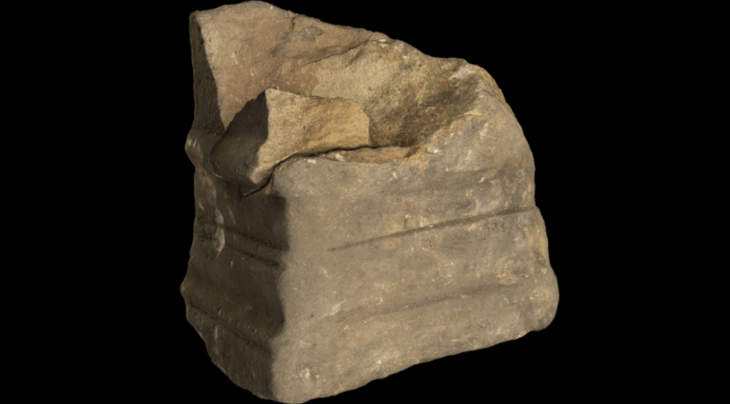
A rare 2,500-year-old marble disc designed to protect ancient ships and ward off the evil eye was discovered by a lifeguard diving at sea and turned over to the Israel Antiquities Authority.
The Israel Antiquities Authority announced from social media on July 18 that the object the lifeguard turned over was a 2,500-year-old, eye-shaped marble disc that was attached to ships to ward off the evil eye.
Experts say the relic, found during a dive by lifeguard David Shalom at the Yavne-Yam archaeological site near Palmachim Beach, dates back to the 5th to 4th centuries BC.
Yaakov Sharvit, Director of the Marine Archaeology Unit at the Israel Antiquities Authority, explains: “From drawings on pottery, mosaics, and ancient coins, as well as from historical sources from the 5th century BCE, we learn that this design was common on ships’ bows and served to protect against the evil eye and envy, aided navigation, and acted as a pair of eyes looking ahead and warning of danger. This decoration is still common today on modern ships in Portugal, Malta, Greece, and the far east.”
The large white marble disc, 20 cm in diameter, is flat on one side and curved on the other, and it has a central cavity with traces of paint appearing as two circles around the center. It is identified as an eye motif, in Greek “ophtalmoi,” and such discs adorned the bows of ancient warships and merchant’s vessels. Lead or bronze nails attached the center of the disc to the ship’s hull. Archaeologists have turned up a wealth of artifacts in the same area.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Although this artifact was once common and one would expect to find many similar artifacts, it is, in fact, rare. So far, only four similar ancient items have been discovered in the Mediterranean: two from the wreck of an ancient merchant ship found at the Tektaş Burnu site off the western coast of Turkey, between the islands of Samos and Kios, dating to 440–425 BCE, and two on the Mediterranean coast of Israel—one from the Carmel Beach and the other, just discovered, on the Yavneh-Yam coast.
In water surveys conducted by the Marine Archaeology Unit of the Israel Antiquities Authority since the 1980s, finds from shipwrecked ships testifying to extensive commercial activity at the site were discovered.
Cover Photo: Israel Antiquities Authority