Research at the Rašaška (or Račeša) site, located in the eastern part of Croatia, revealed a grave with an unusual burial practice. In a layer beneath the church floor, an interesting grave marked as 157 was discovered along the southern wall.
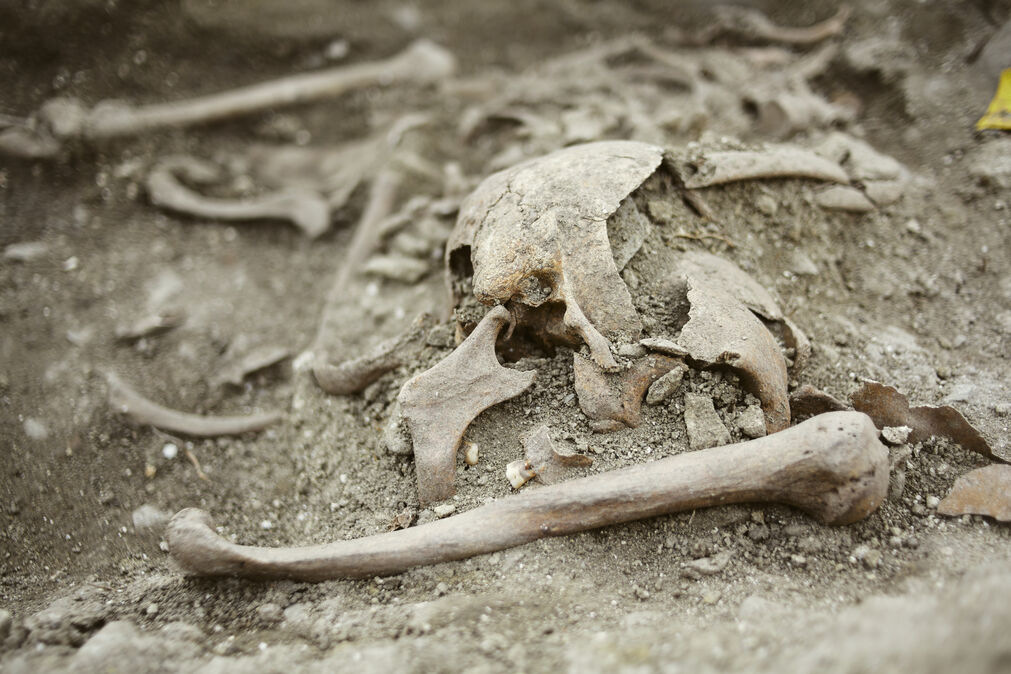
The remains of the deceased were intentionally displaced, and two stones were found at the head and feet. This discovery may indicate a ‘vampire‘ burial, as confirmed by the anthropological analysis of the skeleton.
Researchers have revealed that the discovery of an unusual “vampire” burial in Croatia highlights the persistence of such beliefs in Eastern medieval Europe.
In an email to Live Science, Nataša Šarkić, an independent archaeologist who studied the find, stated, “We know that in many Slavic countries, belief in evil spirits persisted even after the adoption of Christianity. The belief in vampires has been quite widespread, for sure.”
The scientific paper was published in the proceedings of the scientific conference, “Military Orders and Their Heritage.” The paper sheds light on possible reasons for post-mortem interventions, suggesting that the burial may reflect the social status of the deceased or a fear of vampirism.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
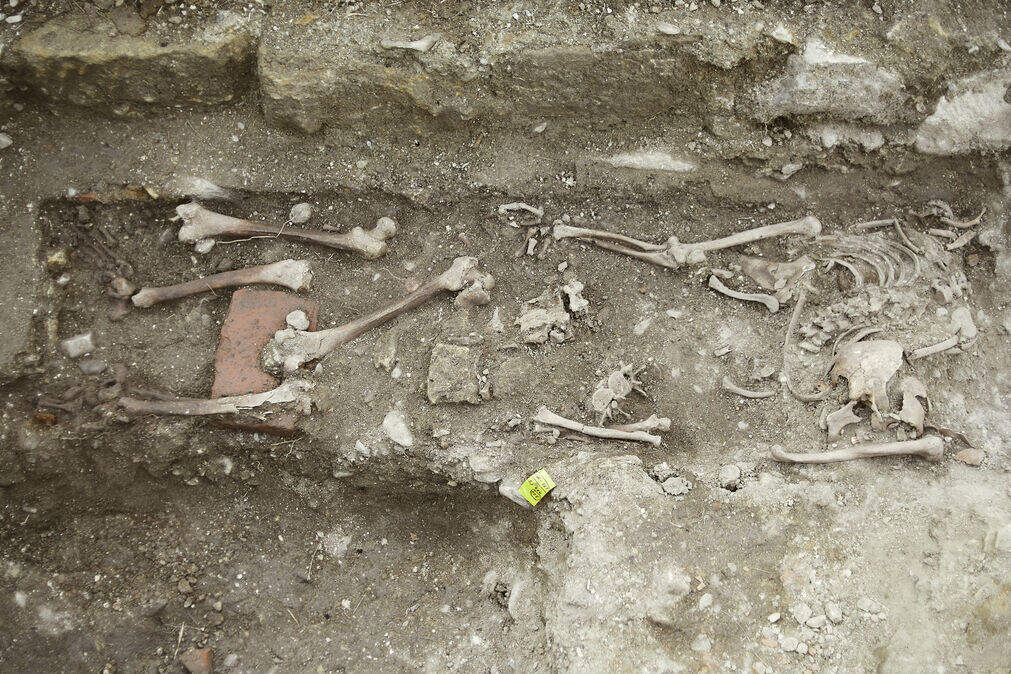

The studies of the skeleton determined that the body had been male; and it seemed it was deliberately twisted after death, so that his torso was facing down while other body parts were facing up.
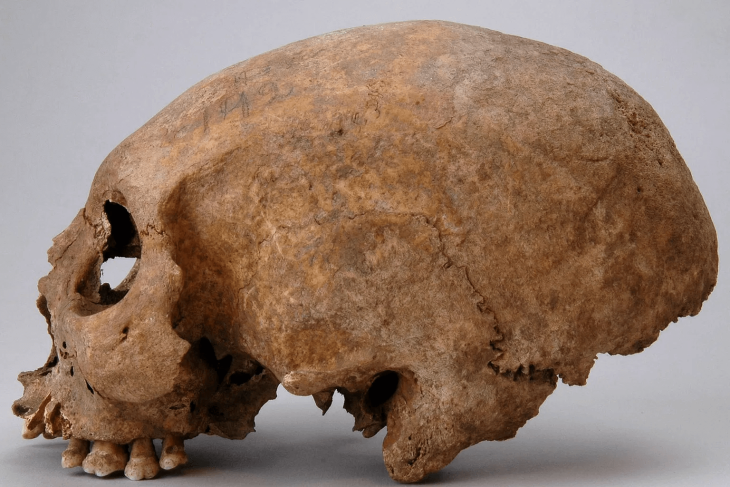
The focal point of the study was Grave 157, where researchers initially observed large stones that appeared to have fallen from a nearby wall. However, their analysis uncovered a startling revelation: the skeleton had been decapitated, with the skull positioned separately from the other bones. Further examination of the remains confirmed that the body was male and indicated that it had been deliberately twisted after death, resulting in the torso facing downward while the other body parts were oriented upward.
Anthropological analysis revealed that the individual was a man aged 40-50 years, with signs of heavy physical labor on the spinal vertebrae and lower limbs. Healed injuries on the skeleton indicated that the man had experienced a violent life, and the latest analysis revealed that he had ultimately died from injuries to his skull.
The unusual burial suggests that the individual may have been regarded as a “deviant social person” during his lifetime, leading to suspicions that he could rise again after death, according to the researchers.
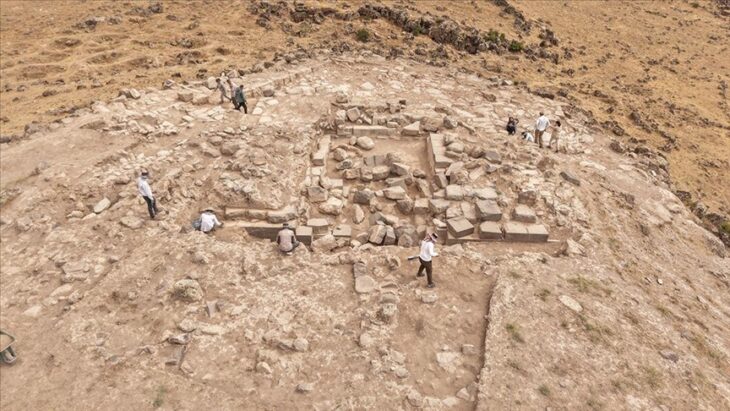
The archaeological site of Račeša was discovered in 2011 during systematic field research of the larger settlement of Bobare. “Račeša’s estate originally belonged to the Templars, then to the Order of the Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, and finally to the local nobility, according to historical sources from the 13th to the 16th century,” the paper states.
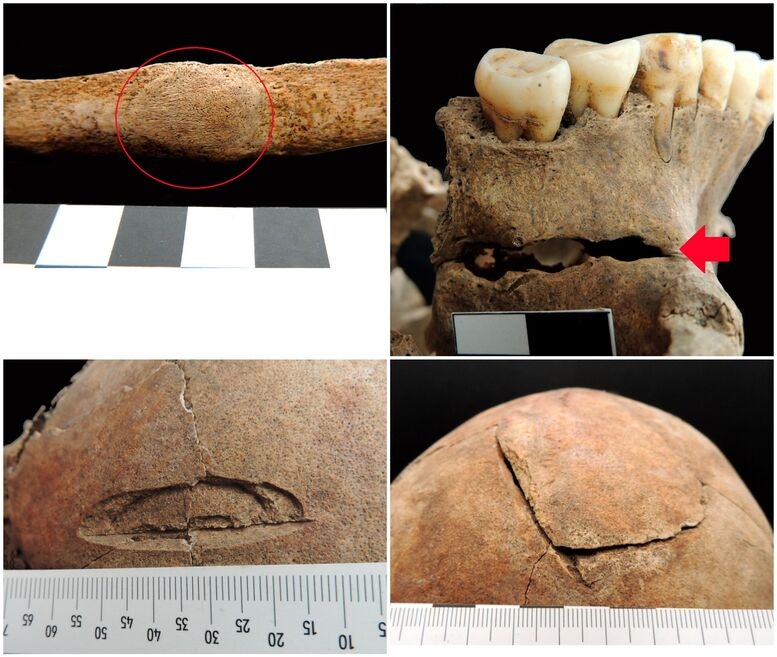

Based on the location and terrain configuration, everything indicates that this was a fortress, but research suggests the presence of a sacred object. From 2012 to 2023, archaeological investigations uncovered an architectural complex that includes 181 skeletal burials and a significant number of dislocated bones.
Typically, the deceased were positioned on their backs in an east-west orientation, with their arms crossed over their hips, lying on their stomachs, or extended alongside their bodies. Only small fragments of personal jewelry were discovered in several graves. C14 analysis showed that most graves date back to the 15th-16th century.
Cover Image Credit: Milica Nikolić