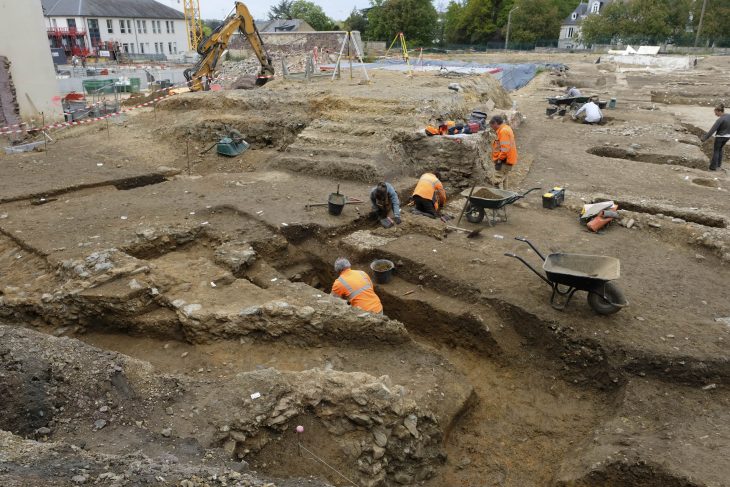
Archaeologists from the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archeology and Anthropology, working with an Iraqi excavation team, have unearthed a large stone monument depicting the goddess Ishtar in the ancient Assyrian city of Nimrud.
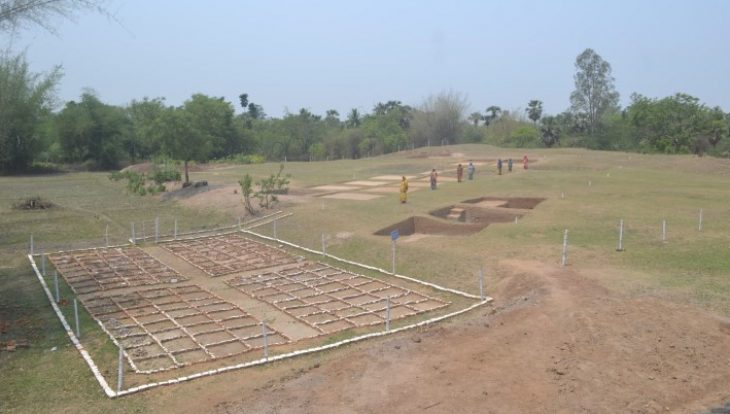
Archaeologists have uncovered more monumental finds in Nimrud, one of the heritage sites severely damaged by the so-called Islamic State (ISIS) in northern Iraq.
Among the new relics discovered at the site are those from a 3,000-year-old temple dedicated to Ishtar, the Mesopotamian goddess of love and war and the goddess with the earliest written evidence.
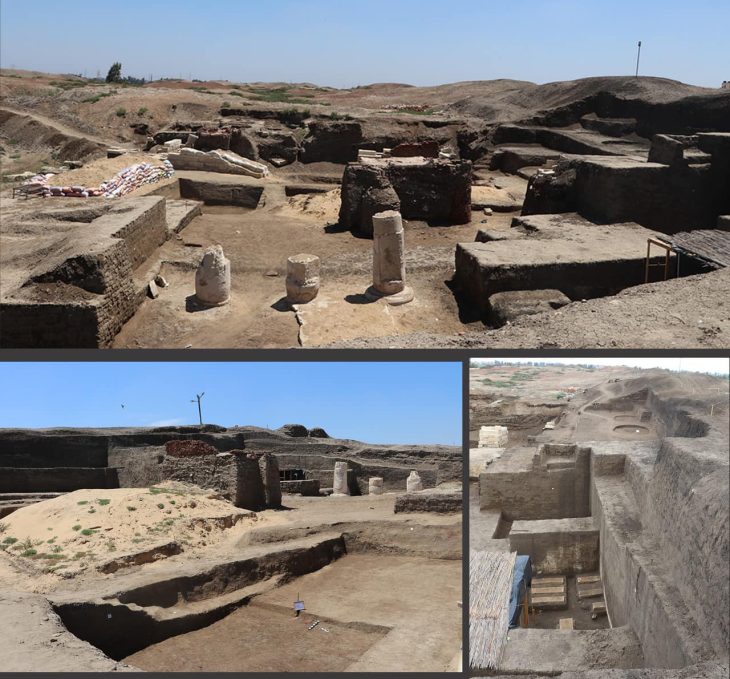
During earlier excavations in Nimrud, the same team revealed a 2,800-year-old palace belonging to an Assyrian king Adad-Nirari III, who reigned from 810–783 BCE.
This season, the team continued working inside the palace and expanded its efforts to include the Temple of Ishtar, which burned when Nimrud was sacked by an invading army in 612 BCE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
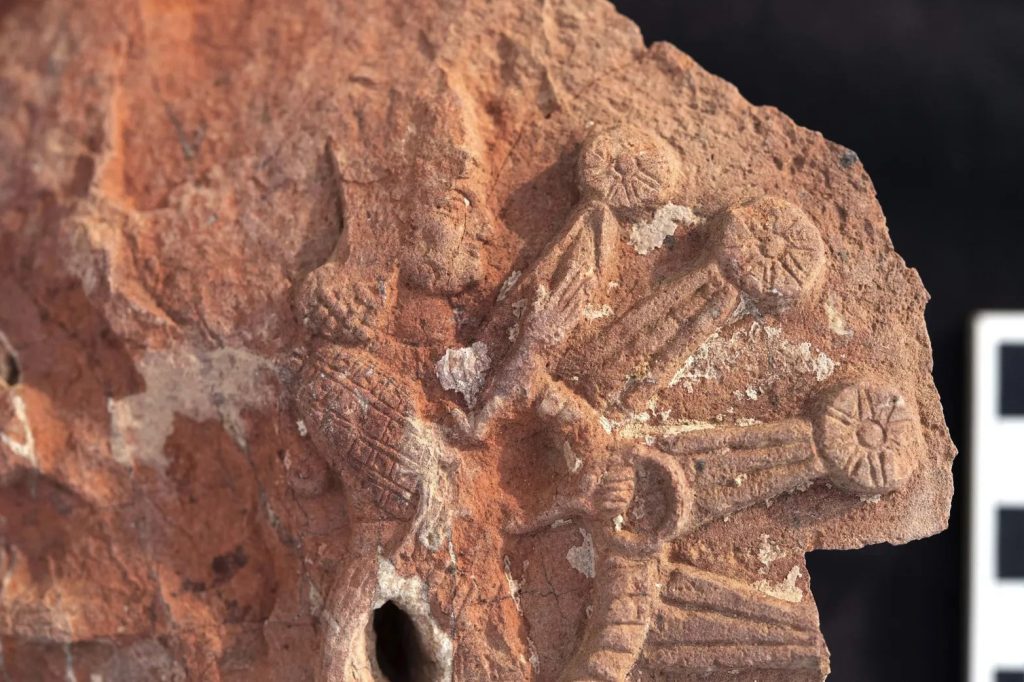

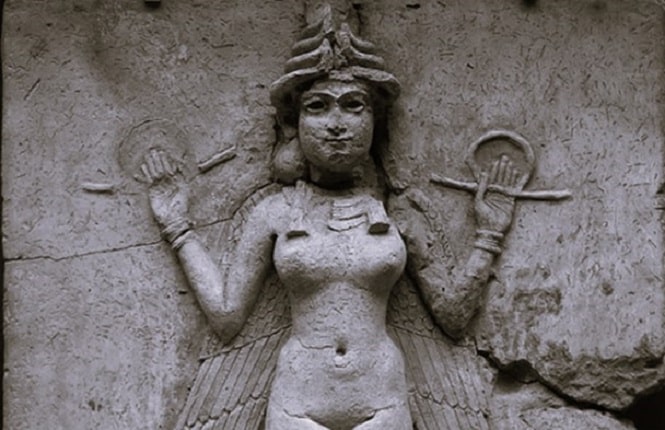
Chief among their finds were fragments of a large stone monument that depicts the goddess Ishtar inside a star symbol.
“Our greatest find this season was a spectacular fragment from the stone stele that shows the goddess Ishtar inside a star symbol. This is the first unequivocal depiction of the goddess as Ishtar Sharrrat-niphi, a divine aspect of the goddess associated with the rising of the planet Venus, the ‘morning star,’ to be found in this temple dedicated to her,” Dr. Michael Danti, Program Director of the Iraq Heritage Stabilization Program and archeologists at the University of Pennsylvania, said in a statement.
This season’s new discoveries largely focus on the splendor of Adad-Nirari III’s rule and ancient Nimrud’s affluence. Two enormous stone column bases that the archaeologists discovered suggest the palace was grandly decorated with exquisitely carved columns. Evidence of a sizable stone basin, which the researchers think may have served as a central heating system, was found inside the throne room.
In addition, they discovered scattered pieces of ostrich eggshell and ivory, both of which were rare and would have been extremely valuable in the early Bronze Age.