Researchers think they have discovered the earliest evidence for intestinal parasites in the UK.
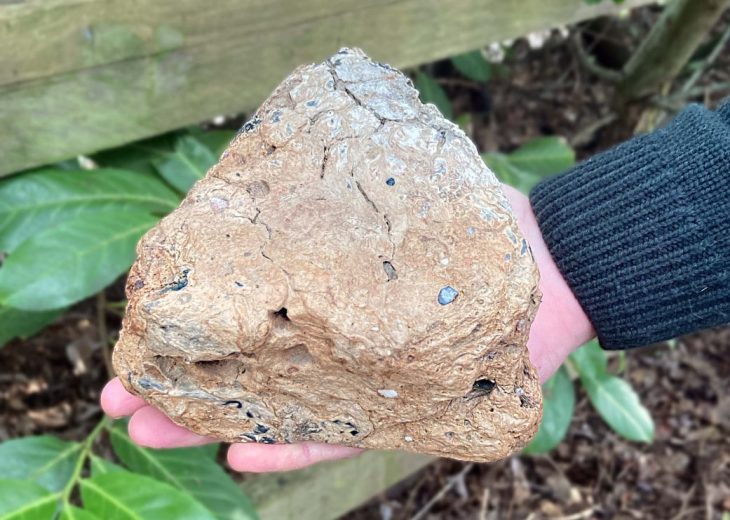
Ancient poop found at the site of a prehistoric village near Stonehenge revealed that the settlement’s inhabitants may have dined on badly cooked cow offal.
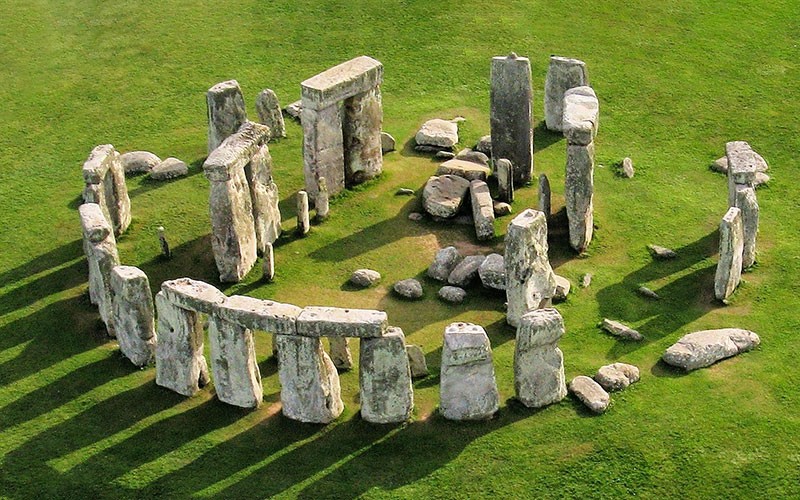
The bizarre find at Durrington Walls, just 2.8km from the ancient stones in Wiltshire, dates from 2,500 BC when much of Stonehenge was constructed and experts think the site housed the people who built Stonehenge.
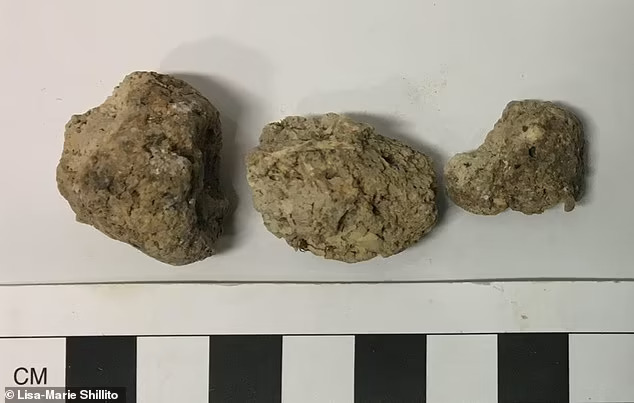
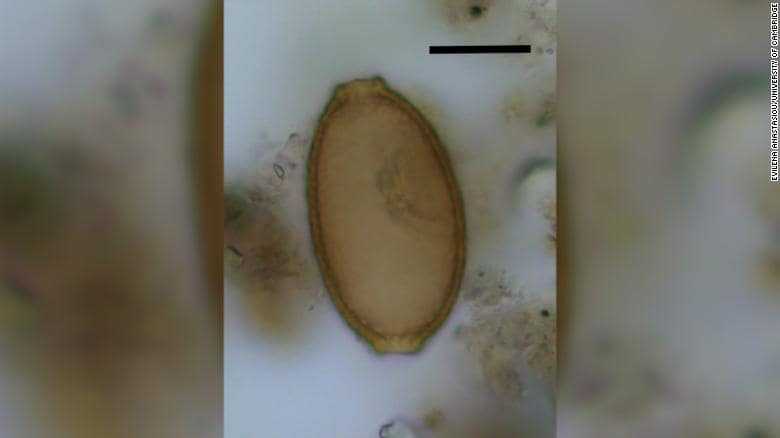
A team of archaeologists led by the University of Cambridge investigated 19 pieces of ancient faeces, or ‘coprolite’, found at the site and preserved for more than 4,500 years. And an analysis of the feces found has uncovered evidence of the eggs of parasitic worms.
As reported in the journal Parasitology, at least five out of these 19 ancient poops (one from a human and four from dogs) contained parasite eggs. At least four, including the human poop, featured the eggs of a capillariid parasite worm, which likely made their way into the intestines of people after they ate the raw or undercooked organs from an infected animal. Archaeologists suggest the inhabitants feasted on the internal organs of cattle and fed leftovers to their dogs.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researchers suggest this is the earliest evidence for intestinal parasites in the UK where the host species that produced the faeces has also been identified.

‘This is the first time intestinal parasites have been recovered from Neolithic Britain, and to find them in the environment of Stonehenge is really something,’ said study lead author Dr. Piers Mitchell, from Cambridge’s Department of Archaeology.
“As capillariid worms can infect cattle and other ruminants, it seems that cows may have been the most likely source of the parasite eggs,” Dr. Piers Mitchell, lead study author from Cambridge’s Department of Archaeology, said in a statement.
However, bones dug up from the trash heap suggested that cattle weren’t the most commonly consumed animal. Some 90% of the 38,000 bones unearthed were from pigs and 10% from cattle.
One piece of the poop belonging to a dog contained the eggs of fish tapeworm, indicating it had become infected by eating raw freshwater fish. However, no other evidence of fish consumption, such as bones, has been found at the site.
Durrington Walls was most likely not simply a permanent home to the Stonehenge builders. The team argues that it was the site of big winter feasts for the groups of people who trekked down to the south of England seasonally, most likely in winter, to visit and build upon the monument. However, there is little evidence to suggest that people lived or ate at Stonehenge itself.
“Durrington Walls was occupied on a largely seasonal basis, mainly in winter periods. The dog probably arrived already infected with the parasite,” said study co-author Dr. Piers Mitchell, a medical doctor and senior research associate and director of the Ancient Parasites Laboratory at the University of Cambridge’s department of archaeology, in a news release.
Prof Mike Parker Pearson, from UCL’s Institute of Archaeology, who excavated Durrington Walls between 2005 and 2007, added: “This new evidence tells us something new about the people who came here for winter feasts during the construction of Stonehenge.
“Pork and beef were spit-roasted or boiled in clay pots but it looks as if the offal wasn’t always so well cooked.
The findings are published in the journal Parasitology.