A missing link in crocodilian evolution and a tragic tale of human-driven extinction.
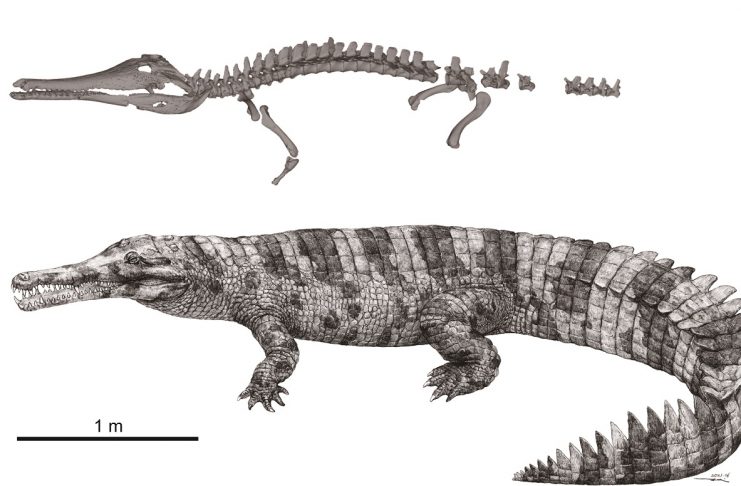
The partially fossilized remains of a giant extinct crocodilian that could have been ritualistically beheaded explain how modern crocodilian species may have evolved.
Discovered in southern China, the new species is estimated to have been 6 meters long and the top predator of its environment. Human migration into southern China and subsequent hunting might have driven it to extinction only a few hundred years ago. The discovery may impact knowledge of ancient Chinese civilization.
In the ninth century, during China’s Tang dynasty, the people of the Han River delta in the southern Chinese province of Guangdong had a crocodilian problem — though, depending on your perspective, you may prefer to say that the local crocodilians had a human problem. According to historical accounts, Han Yu, a government official and poet, tried warning the crocodilians and even sacrificed a pig and goat to implore them to leave the area. Unfortunately, the crocodilians, unable to recognize these threats, remained and, as new evidence suggests, met their ultimate fate.
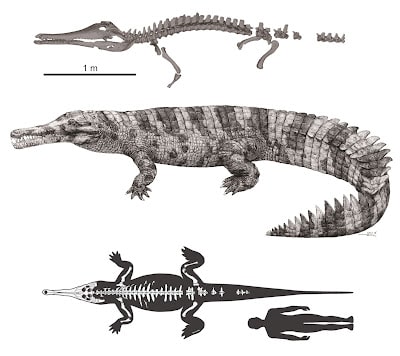
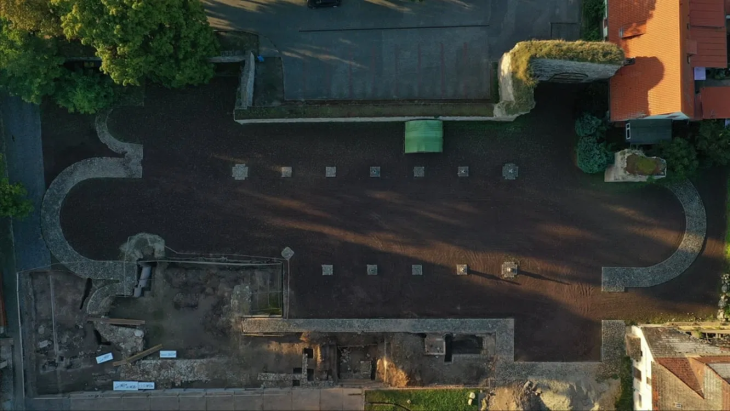
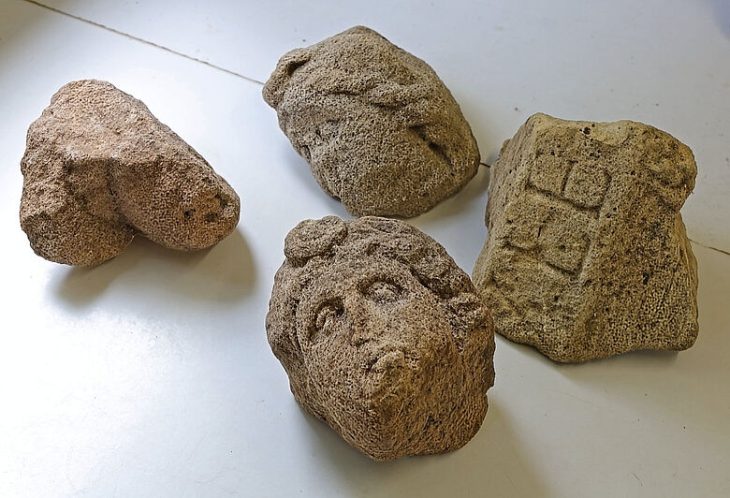
Twelve centuries later, Professor Minoru Yoneda from the University Museum at the University of Tokyo and research fellow Masaya Iijima from Nagoya University Museum in Japan, and Professor Jun Liu from Hefei University of Technology in China, found themselves studying two partially fossilized, or subfossil, individuals from a new species. The creatures were probably killed in the 14th and 10th centuries B.C., respectively, so were not the victims of Han Yu, but their existence does connect with that story, and so the researchers named this new species Hanyusuchus sinensis after him.
“I have studied modern crocodilians for years, but even though it’s extinct, Hanyusuchus sinensis is by far the most astonishing creature I’ve ever seen,” said Iijima. “Everyone is familiar with sharp-nosed crocodiles and blunt-nosed alligators, but may be less familiar with a third kind of modern crocodilian called gharials that have much longer and thinner skulls. Hanyusuchus sinensis is a type of gharials, but what’s exciting is how it also shares some important skull features with the rest of the crocodilians. This is significant as it could settle a decadeslong debate about how, when and in what way crocodilians evolved into the three families still roaming the Earth today.”
Any species considered a so-called missing link is always a significant find, but Hanyusuchus sinensis is important for other reasons too: chiefly, that it seems to have been driven to extinction by humankind. Both of the subfossil gharial specimens showed extensive evidence of vicious attacks and even beheading. The authors connected the fatal wounds with weapons of the period in question.
“Given the two specimens we have were killed by people, the species is no longer around, and given the historical evidence of systematic crocodilian purges in the region, the conclusion must be that humans are responsible for Hanyusuchus sinensis’ demise,” said Yoneda. “Crocodilians are top predators and play a pivotal role in the maintenance of their freshwater ecosystems. This historical crocodilian conflict serves as a warning to people in the present.”

Yoneda is interested in these creatures as he studies the emergence of ancient Chinese civilization around 4,000 years ago, and has encountered crocodilian bones in many archaeological sites, some of which might be culturally significant. These bones, found at sites in many areas of China, were thought to belong to the Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis), which only lived in the lower Yangtze River area in east central China. This may be evidence of a cultural influence from South to North China, but the new discovery could challenge this.
“I am not alone in thinking that the Chinese gharial, Hanyusuchus sinensis, might have left some marks themselves on ancient Chinese civilization,” said Yoneda. “Some Chinese characters and maybe even myths about dragons might have been influenced by this incredible reptile. It would be the only reptile in ancient China that feasted on humans.”
Members of the team are actively exploring other aspects of this discovery as well. The subfossils are recent enough that some soft tissue is preserved. This means that genetic material can hopefully be extracted to help paint a more accurate picture of how Hanyusuchus sinensis fits into the crocodilian branch of the tree of life.
Image Credit : Masaya Iijima and Hikaru Amemiya