The long-held consensus that the more populated and “civilized” a society, the more complex their communication may be more nuanced than previously thought.
After systematically analyzing written and otherwise recorded evidence of shared information in prehispanic Mesoamerica over 3,000 years, two archaeologists say governance appears to be a more influential factor than society size in determining the complexity of computational communications.
They published their findings in a special theme issue of the Journal of Social Computing focused on the collective computational abilities of prehistoric societies.
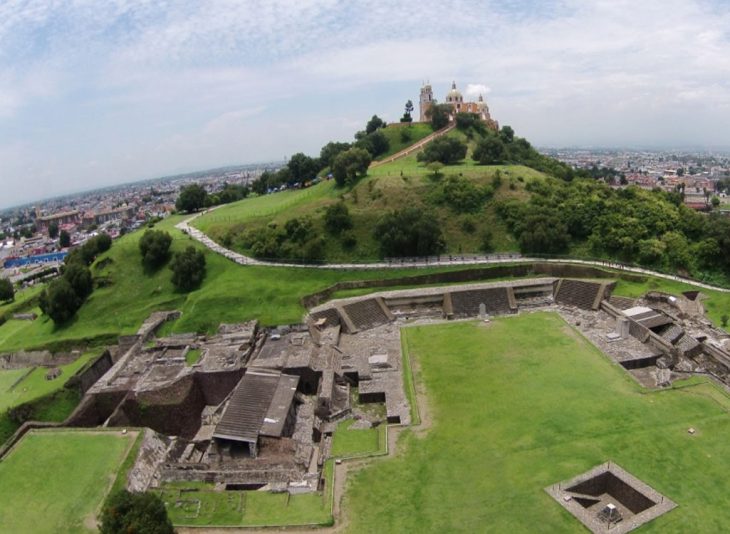
“Mesoamerica — much of today’s Mexico and Central America — is considered one of the few places in the world that saw pristine development of writing systems, without input from other scripts,” said paper author David M. Carballo, assistant provost for general education and associate professor of archaeology, anthropology, and Latin American studies at Boston University.
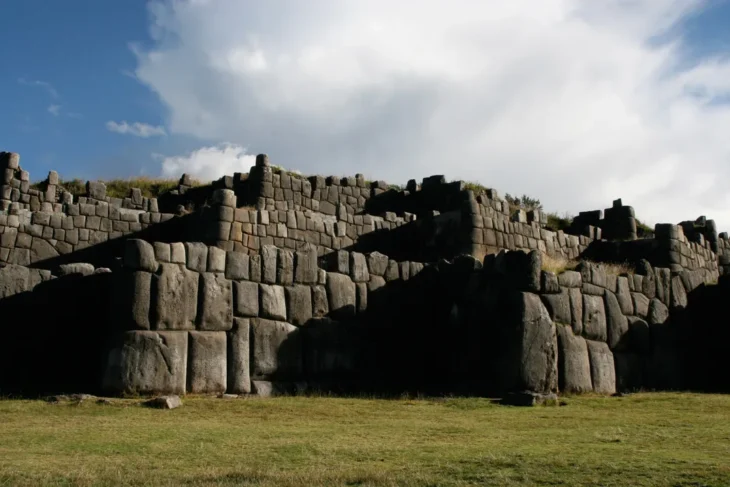
Mesoamerica’s relative geographic isolation from Eurasia from about 1500 BCE to 1520 CE, according to Carballo, makes it a unique case study in the contexts of how writing and other computational communications might evolve, or not, especially in neighboring cultural groups with different approaches. Carballo and Gary M. Feinman, MacArthur Curator of Mesoamerican, Central American and East Asian anthropology at the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago, examined the correlation between society size and 10 specific communication practices in 30 localities, then in six regional areas and finally in Mesoamerica as a whole.
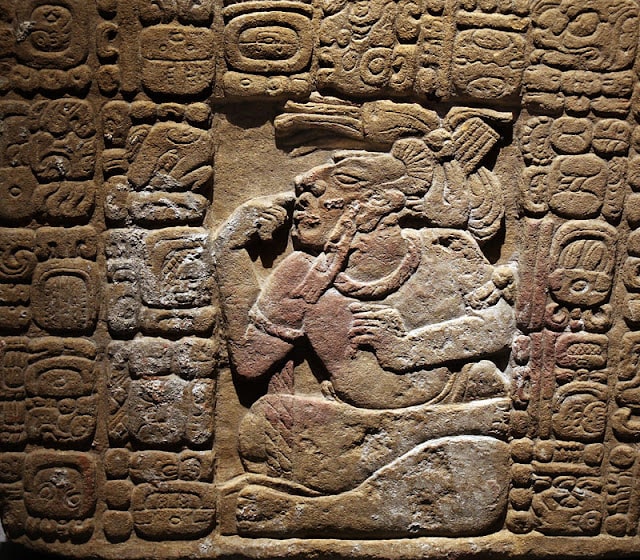

“The systematic analysis of 30 Mesoamerican population centers demonstrated that, while a correlation did exist between the presence and application of computational communication, including writing, and social complexity, viewed in terms of urban populations and area of political control, it was not a clean, linear relationship,” Feinman said. “Instead, another axis of sociopolitical organization — how people were organized, the nature of the relationships among political elite and between leaders and followers– had a direct effect on their communication and writing.”
Computational communications in areas ruled by autocratic rulers and kings was highly elaborate, but largely focused on extoling the ruler’s virtues to other elite or influential people since most people likely had low literacy rates. In areas governed by councils or other more “collective” means with distributed power arrangements, the computational communications were generally less elaborate, such as annual calendar systems related to agricultural, ritual, and market cycles. Those less elaborate approaches also made use of more symbolic narratives, so that the information could be understood across spoken languages regardless of literacy levels.
“This isn’t an issue of ‘oh, people aggregated and needed a way to communicate and the technology was magically developed and spread,’” Feinman said. “The process is much more variable, complicated, and linked to how people were organized and the resultant communications.”
The understanding deviates from more regular correlations determined by two other models, published in 2018 and 2020, respectively. As part of a Santa Fe Institute conference in late 2020, Feinman and Carballo assessed the two empirically based and cross-cultural models that outline the correlation on a global scale, but with different temporal relationships and smaller scalar units. The 2018 and 2020 publications used regional-scale empirical units from Seshat.
The 2018 model concluded a generally linear relationship between societal scale and advances in communications, while the 2020 model used a finer time scale and determined a punctuated, stepwise-correlation, wherein population grows, necessitating more advanced communications. The increase in size and complexity even out, before one jumps again, bringing the other with it.
Carballo cautioned that, despite the apparent discrepancy, the assessment of the more pristine Mesoamerica context does not invalidate the more global models.
“This work is highly interdisciplinary between high-level computational modelers and those studying the fine cultural details,” Carballo said. “It’s the forest and the trees. We can say to the modelers, these variables look a little simple, we need to understand how they correlate in the context of politics.”
Feinman echoed the sentiment.
“We’re seeing a pattern that technology is embedded in the cultural system, and that relationship may not hold everywhere,” Feinman said. “That doesn’t mean the model is completely wrong, in fact we find some support for the step-wise model; instead, it indicates that history is complicated. Demographic and spatial scale, though relevant, do not alone determine time/space diversity in media of computational communication.”
Carballo and Feinman plan to continue investigating how and why governance varied so greatly across Mesoamerica and its relationships to other aspects of life.
“Fifty years ago, most scholars believed that all premodern political units, especially outside of Europe, were governed despotically with direct administration of the economy,” Carballo said. “This model has now been shown to be completely off-base for many historical cases, and some Mesoamerican polities may be highly informative regarding how sustainable governance was maintained without great concentrations of wealth and power.”
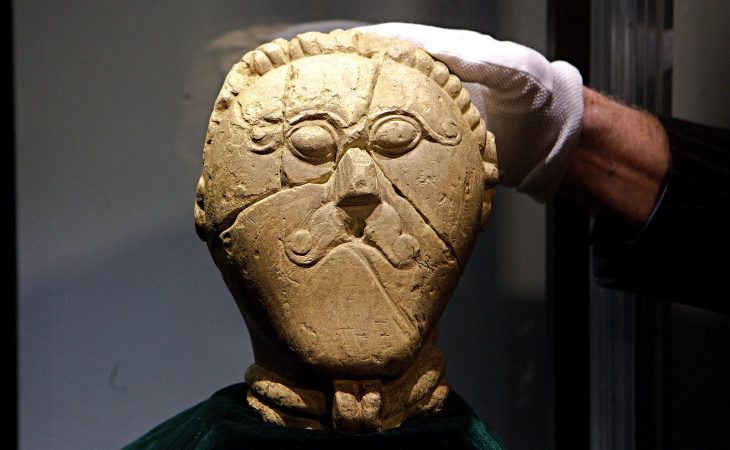
Cover Photo: Teotihuacan carved stone with glyph from plaza of the columns (photograph by david m. Carballo, illustrations by pedro cahuantzi hernández).