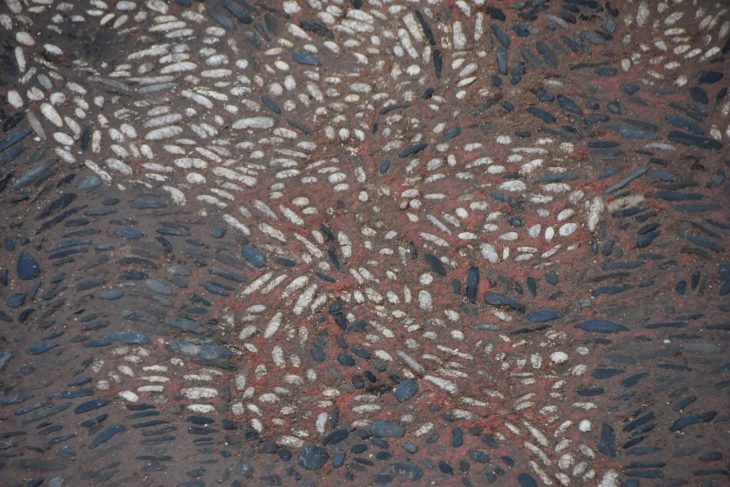
According to a press release from the Petrozavodsk State University a unique tomb was discovered on the western shore of Lake Onega.
Archaeologists from Petrozavodsk State University, while exploring the ancient sites of the Copperstone Age in the territory of the Russian Republic of Karelia, found a tomb containing numerous amber jewelry and flint items.
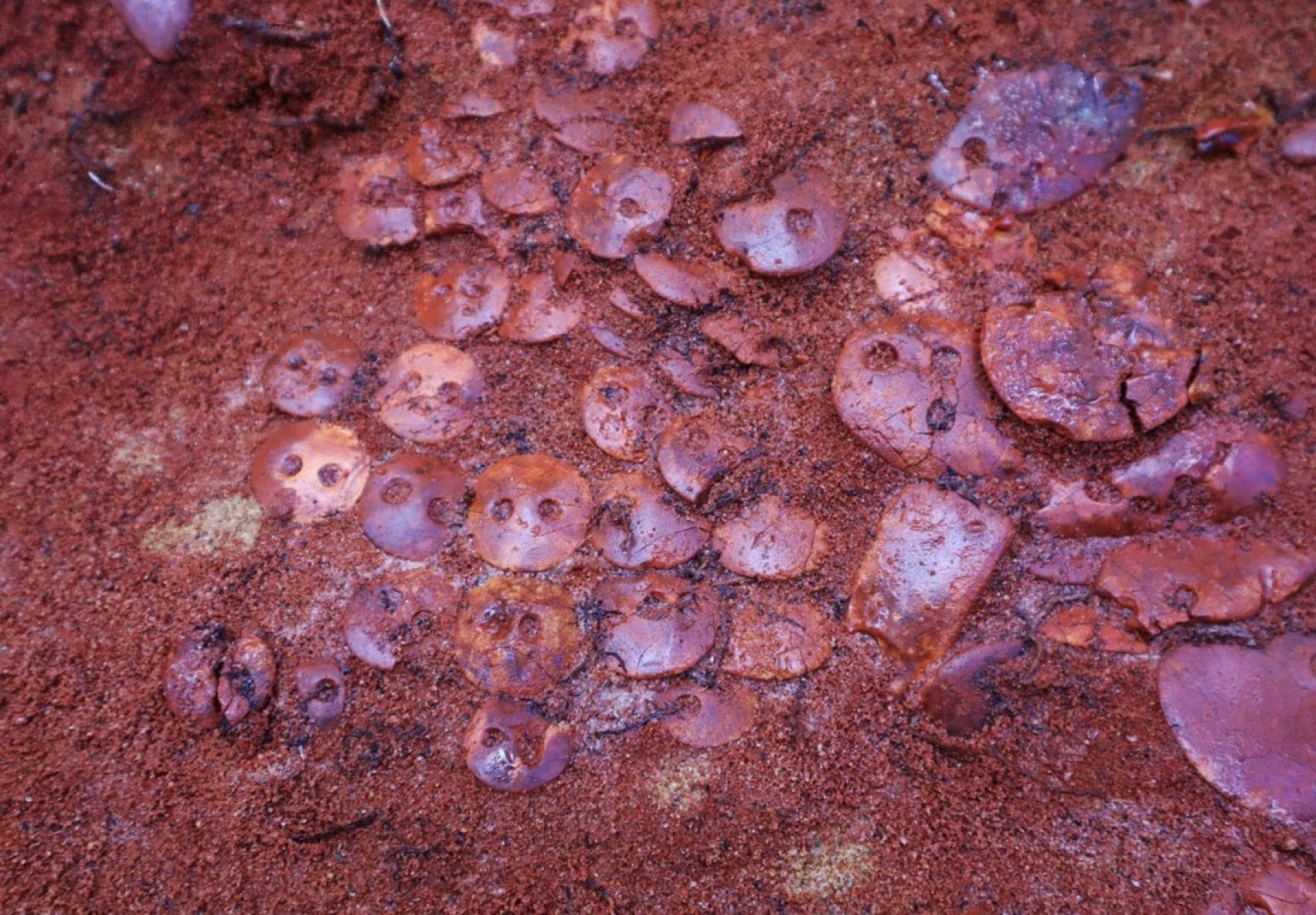
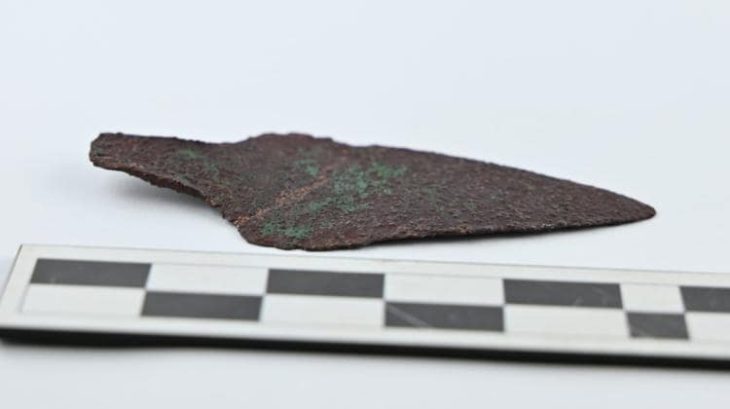
The researchers discovered a high-status individual’s burial in a tiny oval pit bordered with red ochre. They uncovered 140 pieces of amber jewelry (examples of which had previously only been found in the Eastern Baltic) while cleaning the burial, which included buttons, pendants, and numerous flint objects.
Associate Professor Alexander Zhulnikov, head of the archaeological excavation said the amber buttons were “arranged in rows face down and sewn into a leather cover covering the deceased.”
According to Zhulnikov, tombs with so many amber ornaments were not found either in Karelia or in the neighboring north-western regions. Two rows of amber ornaments were placed on the edge of the tomb.
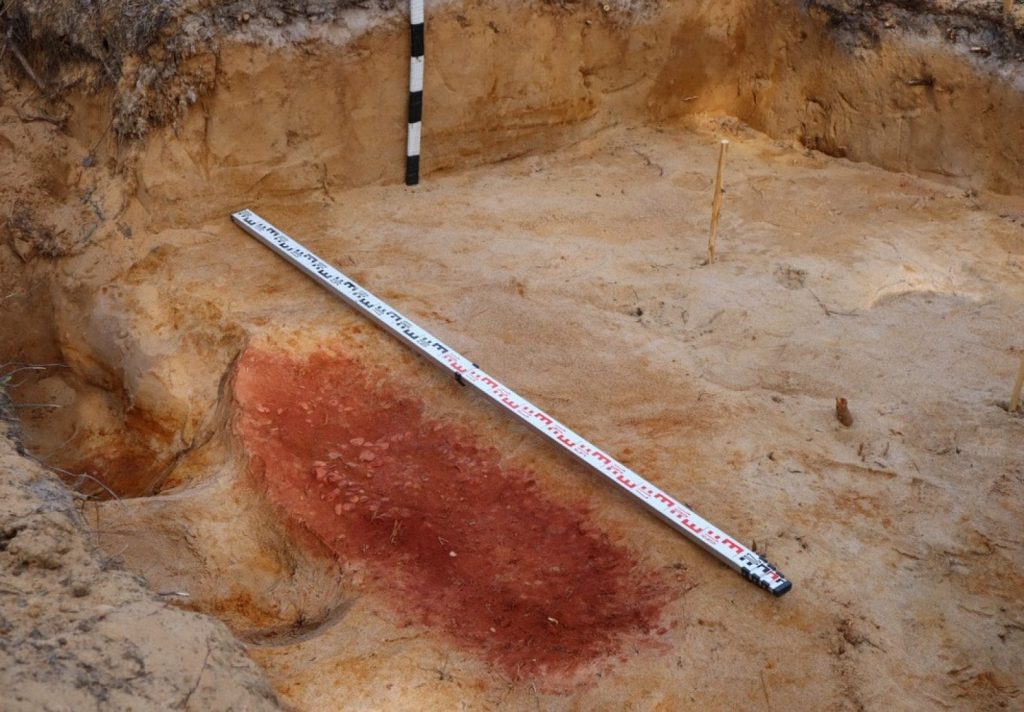

Archaeologists have proposed that the burial dates from approximately 3400 BC during the Chalcolithic or Copper Age by analyzing the similarity with amber ornaments from sites in the Eastern Baltic.
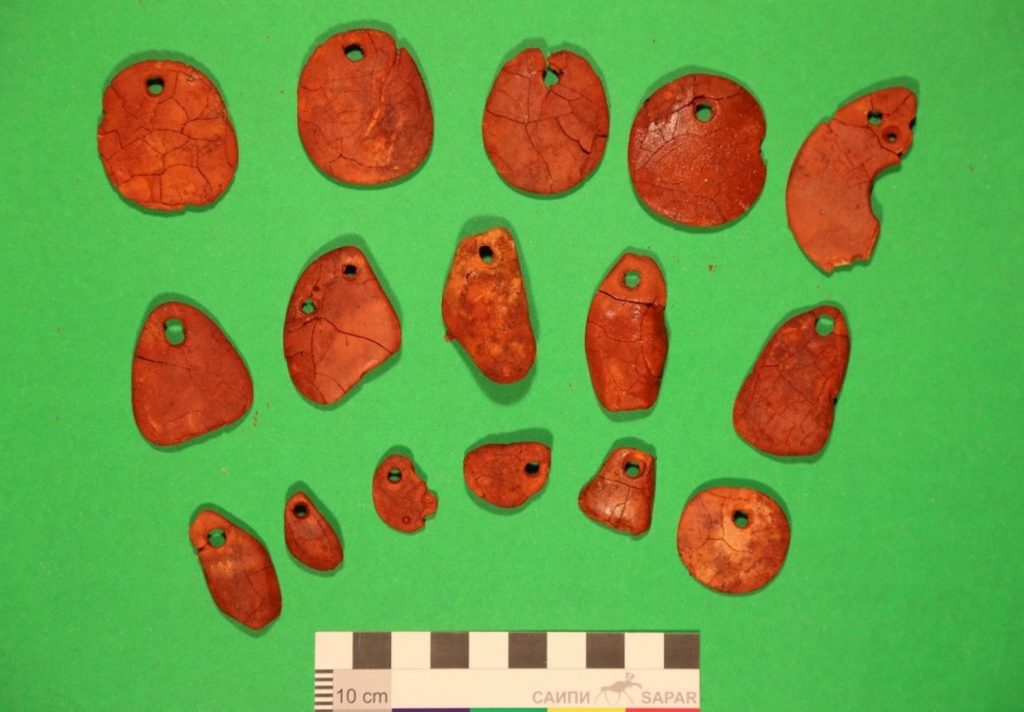

The deceased may have been a merchant from the Eastern Baltic States who came to the western side of Lake Onega to obtain axes in exchange for amber, according to the experts. The Baltic region is home to the largest known deposit of amber, called Baltic amber or succinite.
The “amber” tomb, discovered by the expedition of the University of Petrozavodsk, testifies to the strong ties of the ancient population of Karelia with the tribes living on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea.
Over Photo: Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation