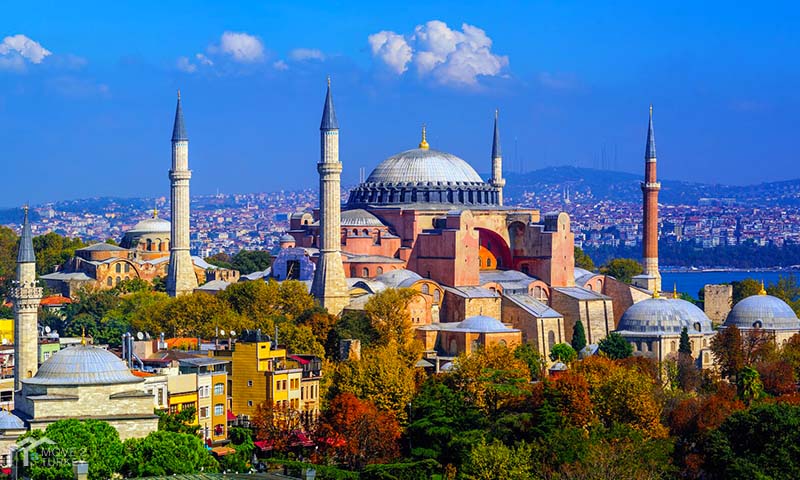
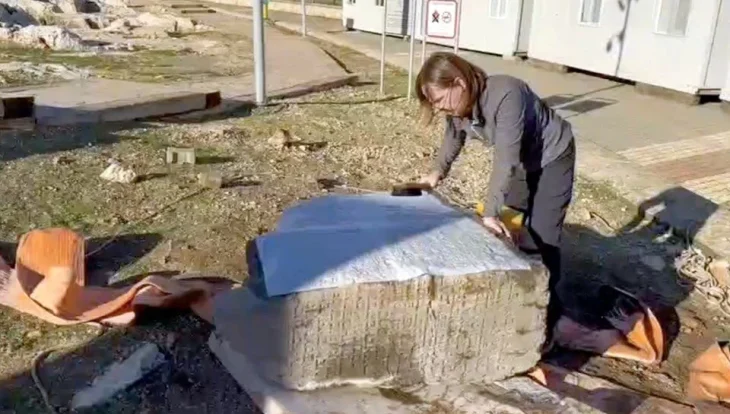
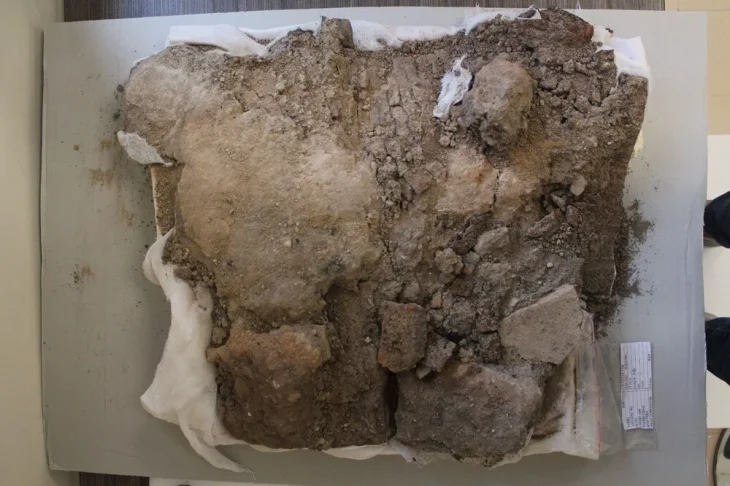
The Great Church was the name given to Hagia Sophia when it was initially constructed (Megale Ekklesia). However, the Church began to be called Sophia from the 5th century. Despite this, it continued to be popularly referred to as the Great Church. The name of the church was changed to “Hagia Sophia” after the conquest in 1453, and it is being used today.
From the views on where the name of the building came from; The idea that it was dedicated to a saint named Sophia is false. The church was dedicated to Theia Sophia, the second element of the Christian trinity, Holy Wisdom. The word Hagia Sophia, which was later named after, is composed of the words Aya (holy, saint) and Sophos (wisdom), meaning holy/divine wisdom.
Built Three Times
After Christianity was accepted as a legitimate faith by Constantine I (324-337), the construction of large churches began in different areas of the empire. The first building of Hagia Sophia was built on the first hill (Sarayburnu), in the form of a wooden basilica in the 4th century. Although this first structure is usually attributed to Konstantinos I (324-337), the church was completed in the time of his son Konstantinos (337-361), and the opening ceremony of the first structure of Hagia Sophia was held on February 15, 360.
This first building’s life did not last very long. On 20 June 404, the church was burned in the fire that broke out in the exile of the patriarch Ioannes Chrysostomos and the uprising that followed. II. Theodosius (408-450) had the building rebuilt with five naves and the church was reopened on 10 October 415.
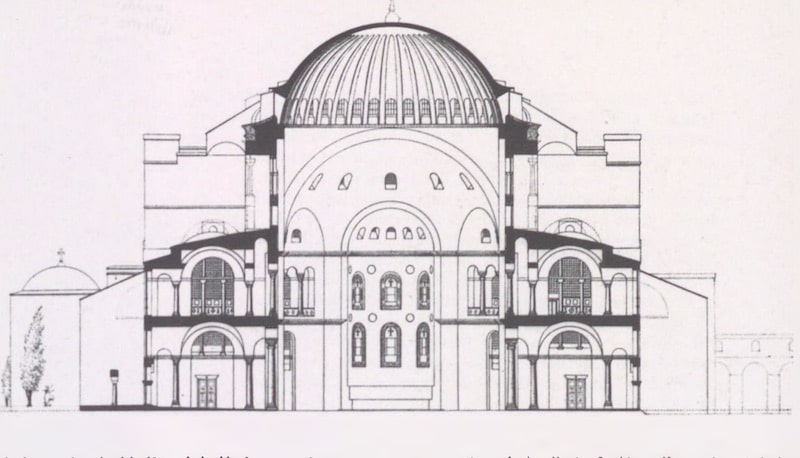
The second church was burned again in the Nika uprising, which broke out on the night of 13-14 January in 532, against Justinian (527-565) and his wife. On top of that, the emperor commissioned Anthemius of Tralles and Isidoros of Miletos to build a larger church from the groundbreaking and old buildings instead of restoring the church in accordance with its previous state. Prokopios (500-562?) wrote that the rebuilding of the church began on February 23. Hagia Sophia, which has survived to the present day, was also the structure that was rebuilt on this date. The construction of the structure lasted until 537. It is known that Justinian was directly interested in the building. Hagia Sophia was opened with a great ceremony on December 27, 537.
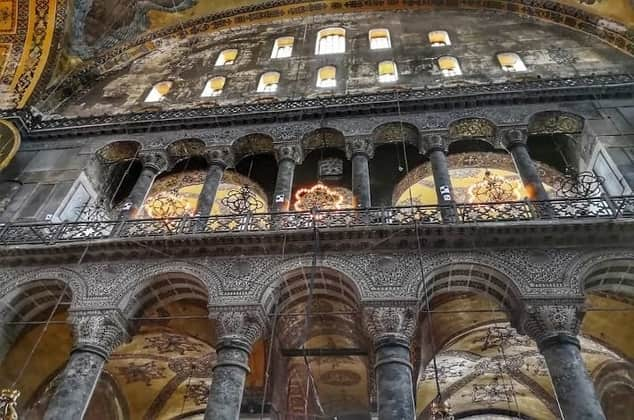

Columns and marbles were brought from ancient cities
Justinian requested materials from all over the empire for the rebuilding of the church, and he also collected the processed materials of the old buildings. Thereupon, eight large red porphyry columns were brought from Heliopolis in Egypt, from the Temple of Artemis in Western Anatolia Ephesos, from Kyzikos and Ba’lebek in Syria. In addition, marbles of different types and colors from different regions were moved here.
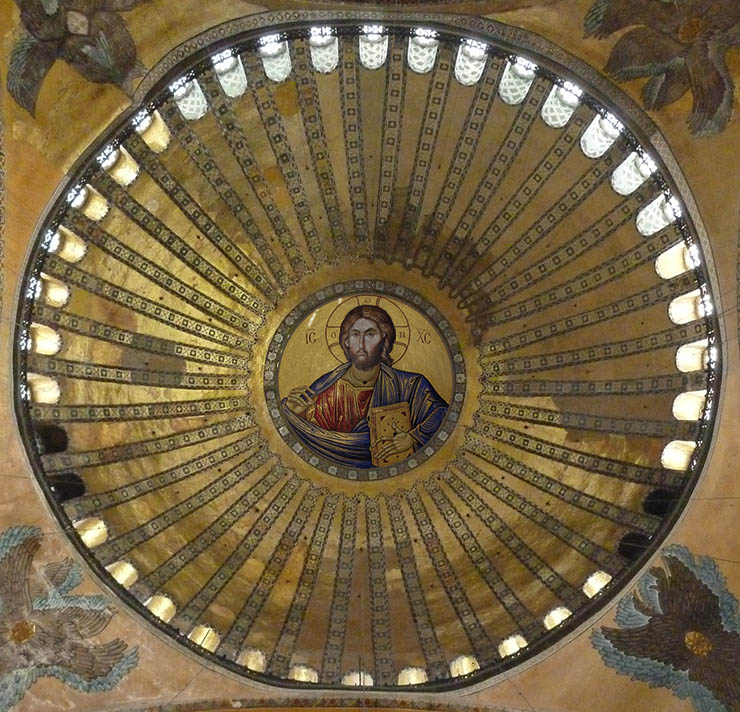

Dome
The most important innovation in the architecture of Hagia Sophia was its unusual size for a church, the size, and height of the dome dominating the middle space.
The height of the dome covering the main space is 55.60 meters from the ground, and its diameter is 31.87 in the north-south direction. meters, and 30.86 meters in the east-west direction. While the Hagia Sophia was being built, marble, stone, and brick were used by the architects in the construction of the building, and light and strong bricks specially produced from Rhodes soil were used to prevent the dome from collapsing easily in earthquakes.
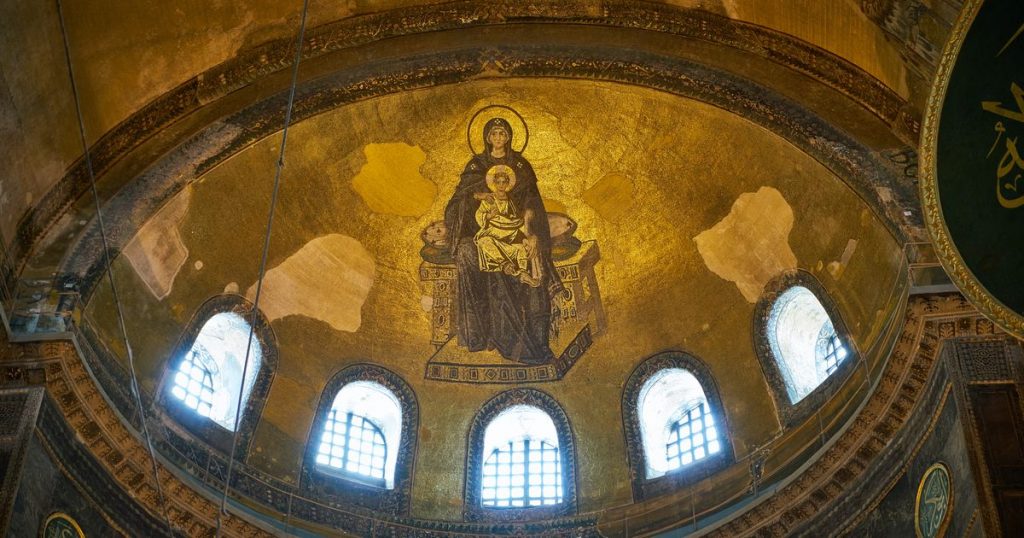

Apse Mosaic
It is thought that all the figured mosaics in the building were removed with the iconoclasm period. After the end of this period in 843, the first figured mosaic, the Apse Mosaic, was made in Hagia Sophia. In the mosaic; In the middle, the Virgin Mary is depicted sitting on a cushioned throne decorated with precious stones. She is holding the child Jesus in her arms.
On the right of the apse is the depiction of Gabriel, and on the left is the depiction of Michael. Although the depiction of Gabriel has survived to the present day, the sacred wing tip and part of the foot in the depiction of Michael have survived to the present day. The depiction of these two angels is thought to have been added to the apse in the second half of the 9th century.
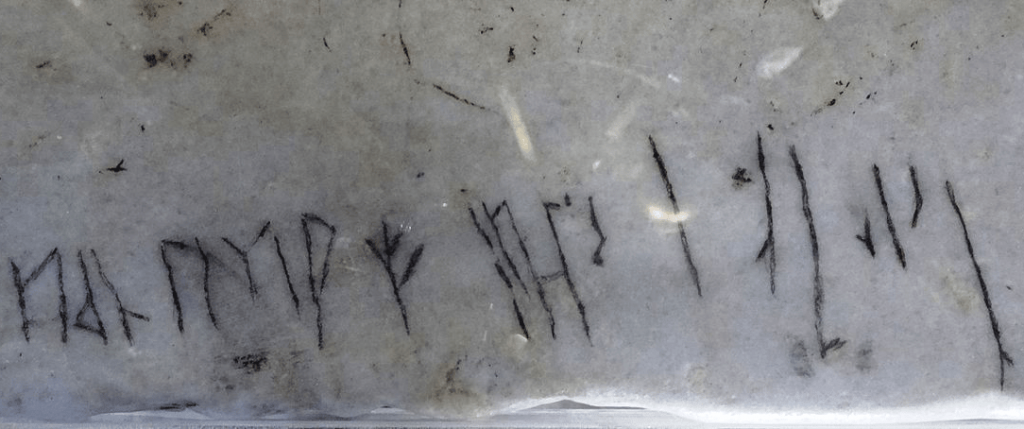

Viking Writing
In the middle of the south gallery, on the marble balustrades, there is a Viking inscription, apparently from the 9th century. In this article, “Halvdan was here.” he is writing. It is thought to have been written by a Viking soldier working as a mercenary in the army in Eastern Rome.
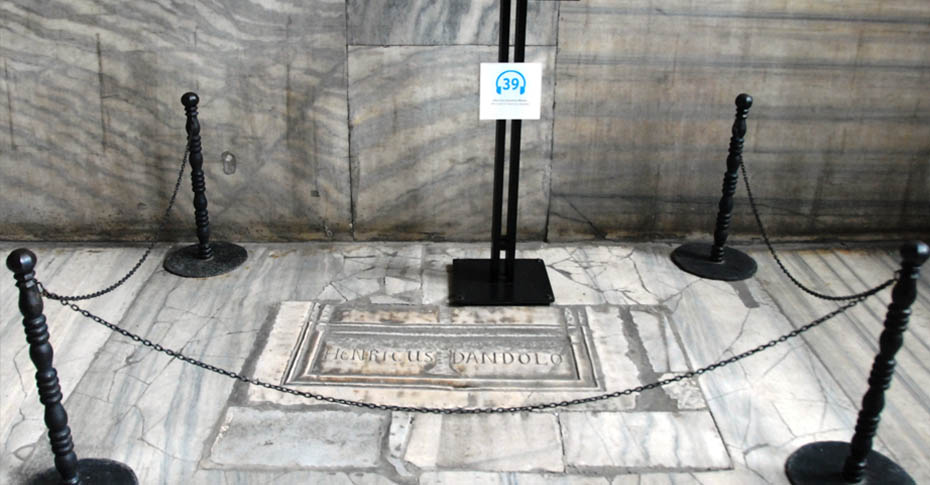

Tombstone of Commander Henricus Dandolo
The tombstone is located opposite the Deisis Mosaic, IV. It belongs to Commander Henricus Dandolu, who led the Crusade and died in Constantinople in 1205.
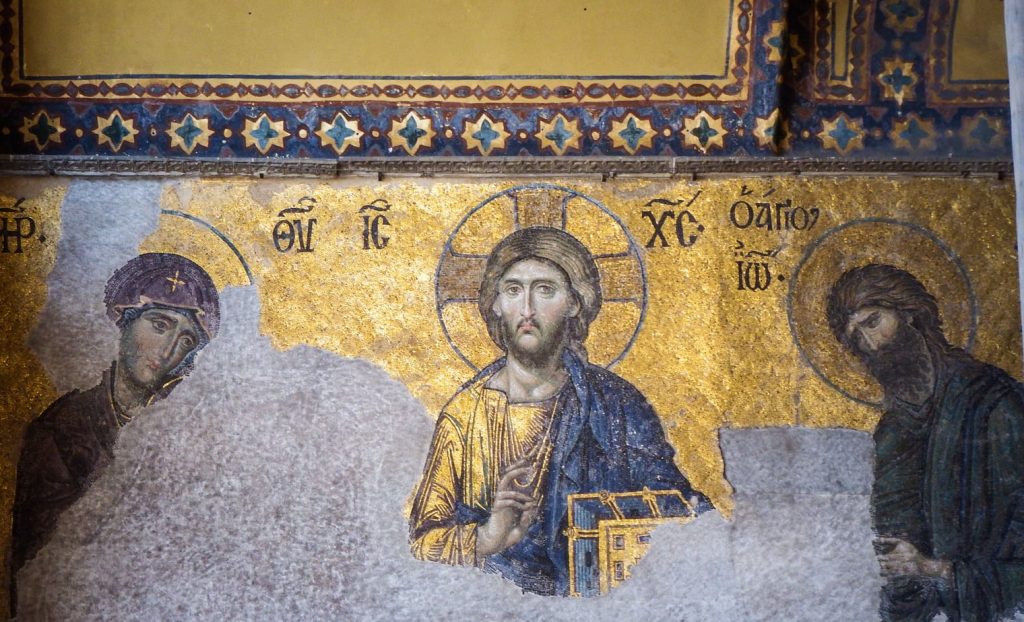

Deisis Composition
The Deisis Mosaic, located on the pediment of the door opening to the gallery in the parsonage, is one of the most famous mosaics of Hagia Sophia. Although there are different opinions about its dating, the mosaic, which is accepted to be made in the 13th century, is considered an important beginning in Eastern Roman Painting Art. In mosaic; In the middle of the scene, Ioannes Prodromos is depicted on the right of Jesus and Mary on the left. Mary and Ioannes Prodromos are depicted as pleading to Jesus for the forgiveness of humanity on the Day of Judgment. These three figures reflect the Hellenistic Period depiction art.
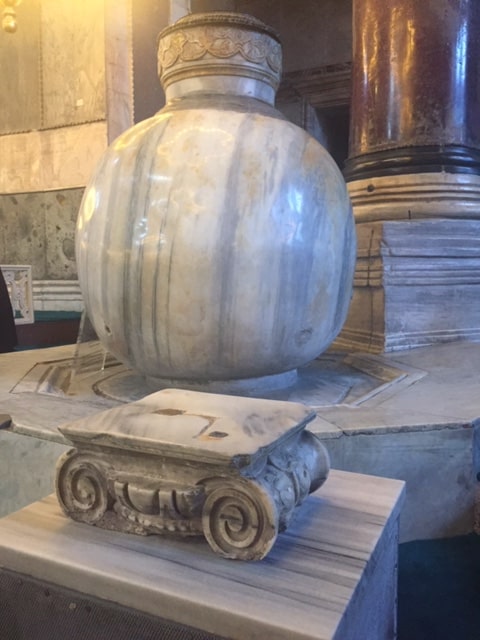

Marble Cubes
Two cubes from the Hellenistic Period, found in the ancient city of Pergamon and made of monolithic marble, belong to Sultan III. It was brought to Hagia Sophia during the reign of Murad II. There are taps at the bottom of the cubes. Sherbet was dispensed from these jars, which could hold 1250 liters of liquid, in oil lamps and Eid prayers.
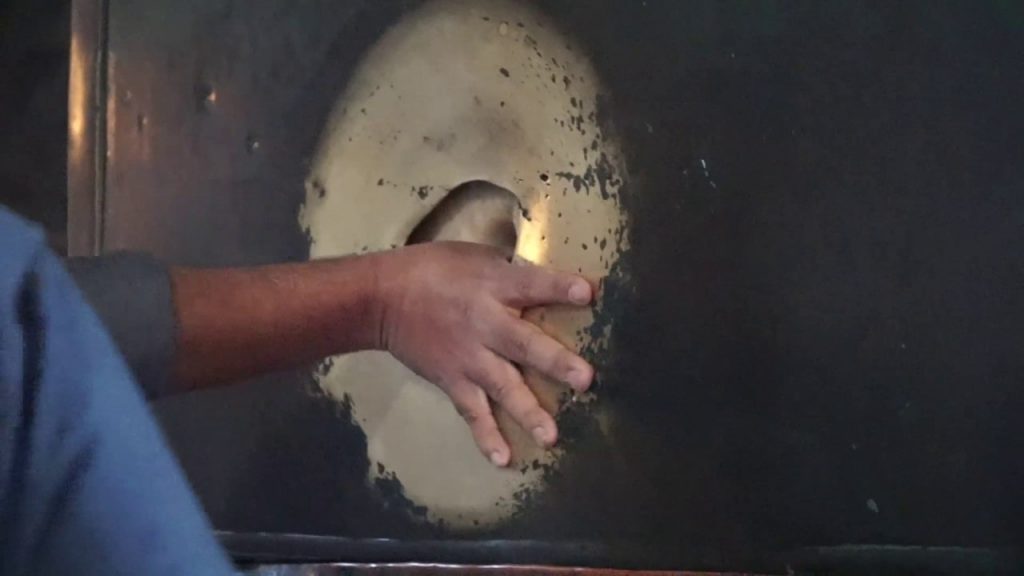

Wish Column
The column is known as the “wishing column” or the “perspiring column.”
The column is thought to feel wet to the touch, most likely due to moisture that collects on its surface. However, according to locals legends, its wetness is due to more mythical causes. According to the most common tale, the column has been emitting some kind of healing liquid since Saint Gregory the Miracle Worker arrived there in the year 1200. Some claim that it “cries” due to a sultan’s pity.
Source: Akgündüz, A., Öztürk, S. Ve Baş, Y. (2005). Üç Devirde Bir Mabed Ayasofya. Osmanlı Araştırmaları Vakfı
















