Iranian researchers say the Iranian plateau served as a migration route between East and West during the Pleistocene period, which began about 2.6 million years ago and lasted until about 11,700 years ago.
A new study reinforces a hypothesis that the Iranian plateau was like a bridge between East and West during the Pleistocene epoch.
Iranian researchers Mohsen Zeidi, Cyrus Barfi, and Shahram Zare concluded in an article published in the International Scientific Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science (IRJMETS) in April 2021 that the Iranian plateau acted as a human migratory pathway during the Pleistocene.
“Increasing Paleolithic finds in this region and neighboring countries (Pakistan and Afghanistan) reinforces the hypothesis that the Iranian Plateau has been used as a human migratory pathway in the Pleistocene linking East and West.”
“The results of the archaeological survey we presented here emphasized the great potential and the importance of south-eastern Iran in general and southern margins of Lut Desert in particular, for the understanding of the Pleistocene culture history of this region,” stated the authors of the research.
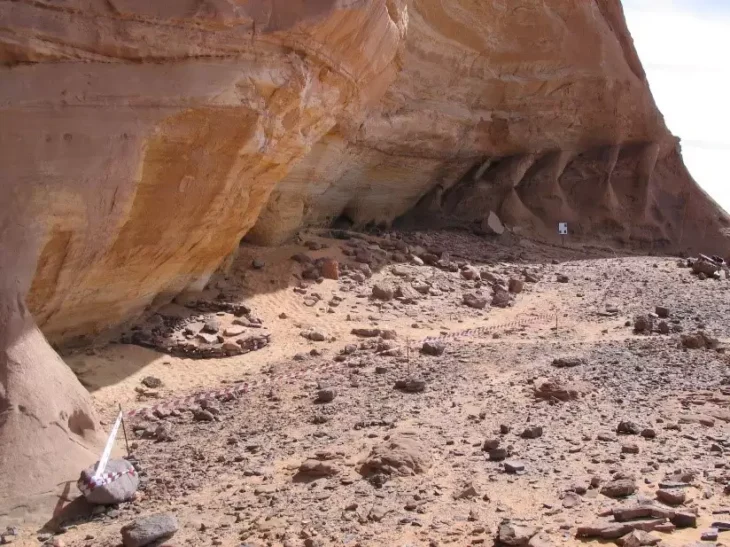
The survey was carried out in parts of Kerman province’s Fahraj-Rigan district, with the belief that new Paleolithic localities hold great potential for understanding the complexities of Pleistocene hominin populations in south-eastern Iran.
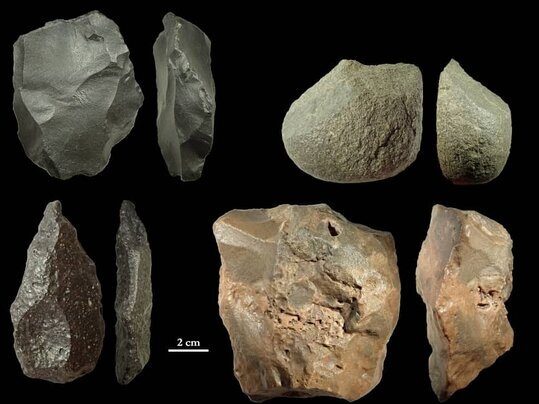
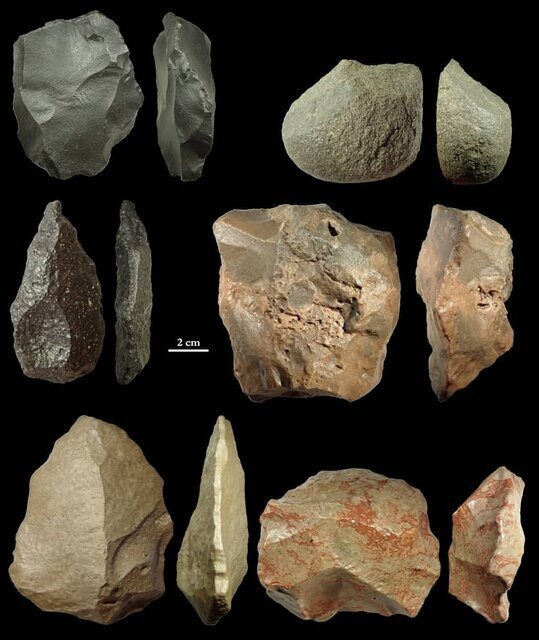
During the summer of 2020, one of the authors collected a collection of surface stone tools as part of a Paleolithic survey in the Fahraj-Rigan region on the southern edges of the Lut Desert, and as a result, 12 new Paleolithic localities were identified.

The surveyed field, which has a semi-arid to the arid climate, has a mean elevation of 700 meters above sea level and is bounded by volcanic mountains to the northwest, south, west, and east. The area between these mountains has been covered by Quaternary alluvial sedimentary deposits. Many of the sites were discovered along low-height hills of Quaternary river terraces or on flat alluvial plains.
Part of the volcanic band of south-eastern Iran, which is mostly made up of igneous rock formations, was also included in the survey region. According to the authors, different forms of igneous rocks have been used for the construction of chipped stone objects as a result of the geology of the area, with the exception of a few examples.
The abundance and relatively large scale of the available raw material blocks in the area indicate quick access to primary and secondary raw material sources, according to the researchers. The two common types of stone objects obtained are core-tool/core-chopper and Levallois core and flakes. Between the captured fragments are a big unifacial point and a highly retouched flake.
The researchers found that all of the stone objects they analyzed had a normal post-depositional surface modification called gloss patina, which produced smoothness, pronounced luster, and a reduction in surface topography. This patination is thought to be characteristic of desert environments. However, striking platform, core removals, bulb of percussion and, flake negative removals are obviously visible on many stone artifacts.
“Overall, based on preliminary techno-typological observations of the stone artifacts, direct percussion using Levallois technique mainly applied for making cores and stone tools. Therefore, it is possible to propose both Lower and especially Middle Paleolithic dates at least for five localities. However, these are the first Lower and Middle Paleolithic finds reported from the systematic survey of southern margins of Lut Desert and make this area an important and very promising area for further Paleolithic investigations,” the study revealed.
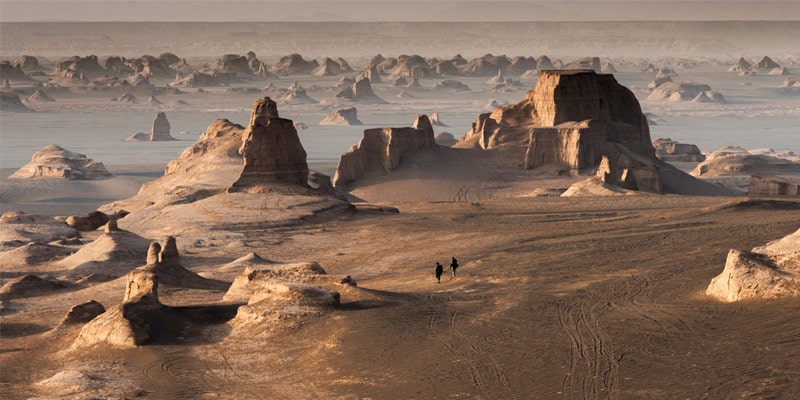

“Our knowledge about the Paleolithic of Iran is still little,” the authors say although, Iran in general and south-eastern Iran, in particular, has been considered as one of the major hominin dispersal corridors during the Pleistocene connecting East and West.
The research looked at areas of the Lut Desert (Dasht-e Lut), which is situated in the country’s southeast and is one of the country’s main high-aridity desert basins. The provinces of Kerman and Sistan-Baluchestan are home to this vast salt desert.
Due to its harsh environment and remote location in the region, this area was archaeologically unknown for a long time. The first visit to the regions of Sistan-Baluchestan and Kerman was made in the 1930s by prehistoric archaeologist-explorer Marc Aurel Stein, who explored south-eastern Iran and reported several late prehistoric and historic sites.
Based on field observations, the surveyed areas seem to be largely undisturbed by natural and modern human activities, and our preliminary findings indicate that surface scatters of stone tools and debitage are typically found in vast areas along drainages and seasonal rivers terraces where water bodies were likely attractive to Pleistocene hominins. However, documenting the full extent of the localities and their lithic scatter needs further intensive survey.
Source: Tehran Times