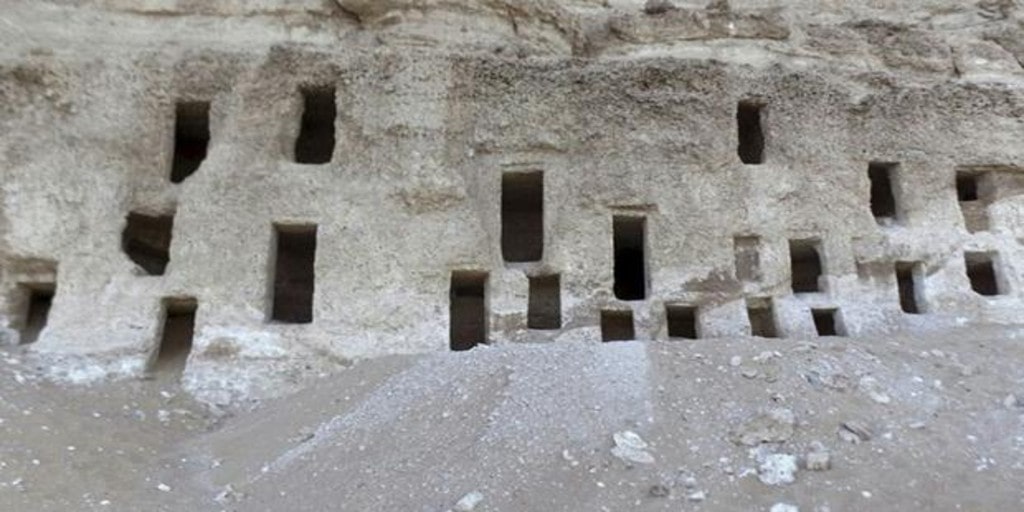
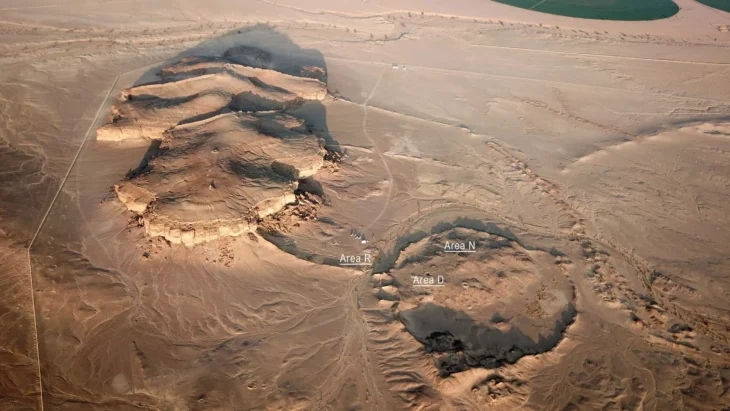
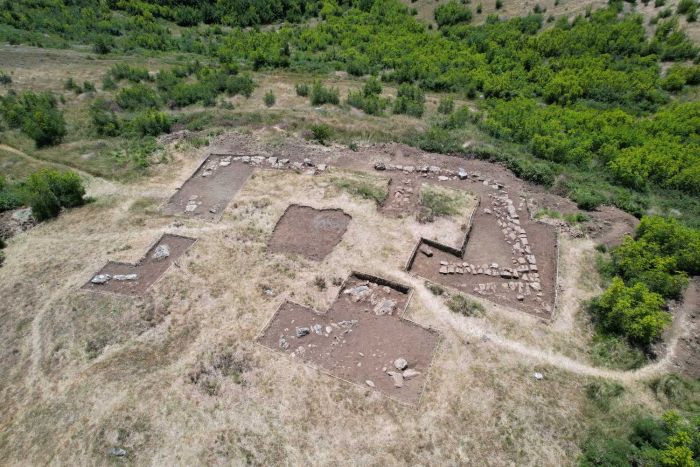
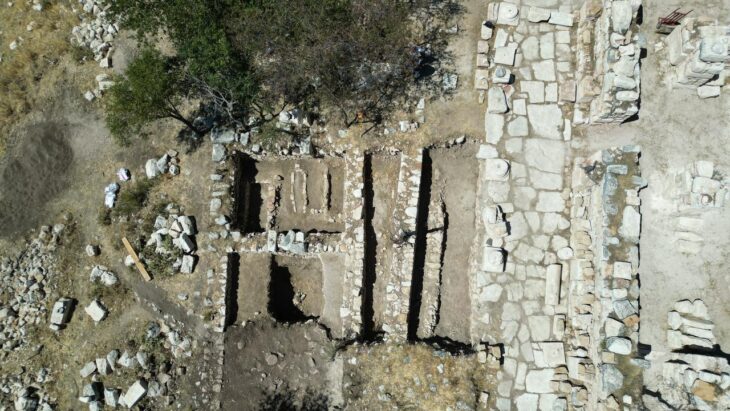
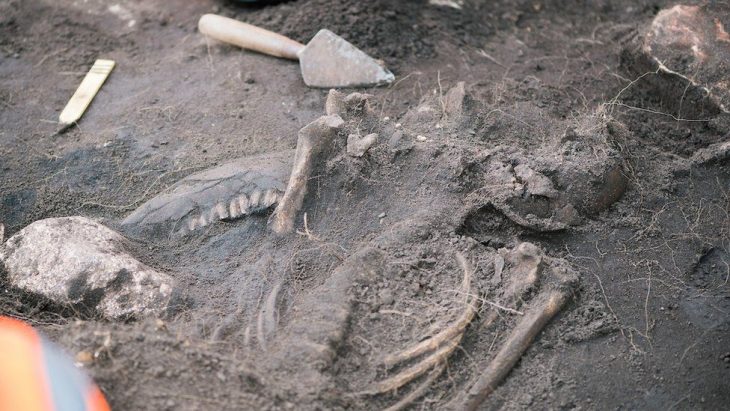
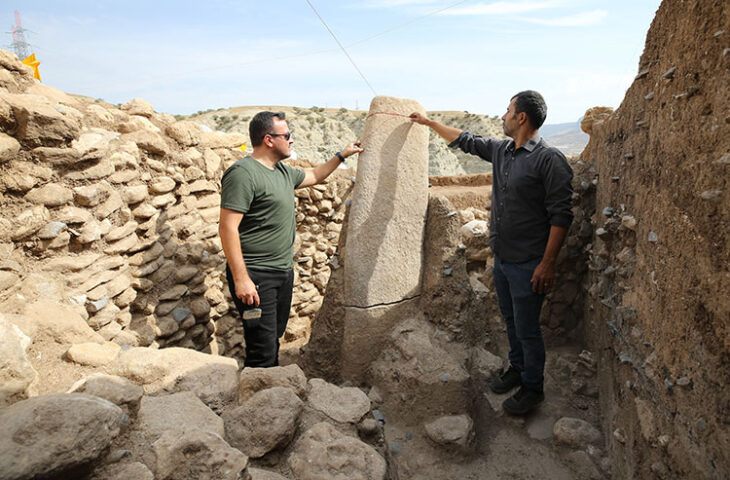
A series of rock tombs carved into the slope of a mountain have been discovered in the Al-Hamidiyah necropolis on the west bank of the Nile in southern Egypt.
Mostafa Waziri, secretary-general of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, said that the tombs have different architectural styles and are dug at several levels in the mountain. They include tombs with one or several burial shafts and some have slope corridors that end with burial shafts. These tombs extend to periods of time ranging from the end of the Old Kingdom to the end of the Ptolemaic period.
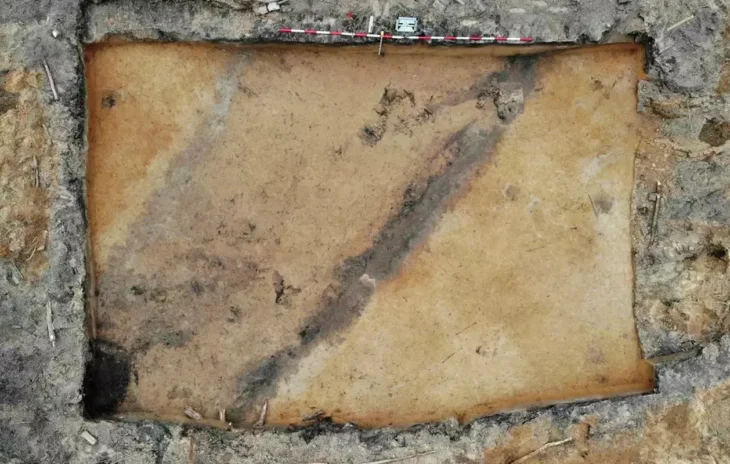
He pointed out that among the discovered tombs is a sloping tomb from the end of the Old Kingdom that consists of a false door and an entrance leading to a gallery with a burial shaft in the southeast, which was reused in later times.
These tombs were discovered by chance during the documentation and archaeological record studies in the necropolis.

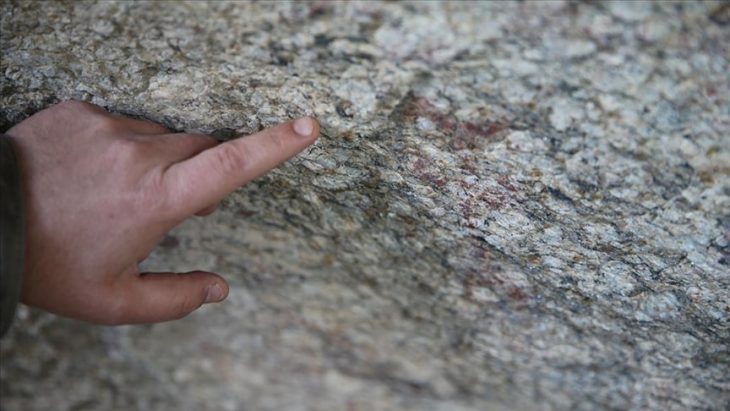
The ruins of hieroglyphic text and scenes showing the tomb owner performing rituals and people making offerings to the dead are engraved on the false entrance.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
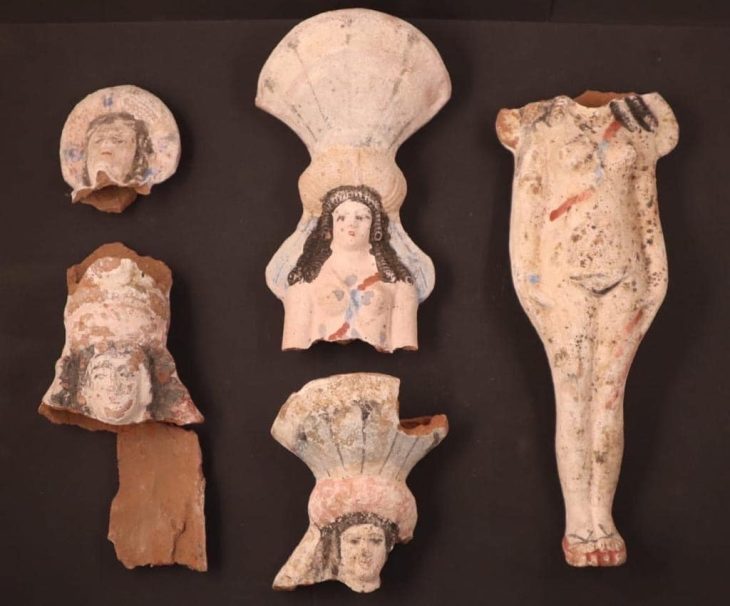
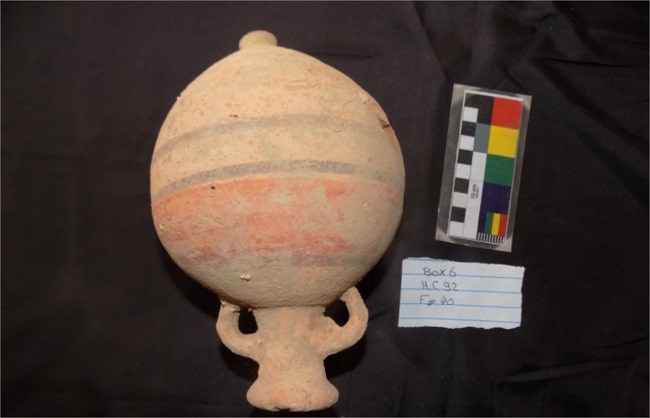
Mohamed Abdel-Badiaa, head of the Central Department of Upper Egypt Antiquities, said that the excavation work in the necropolis also resulted in the discovery of many pottery vessels, some of which were used within daily life and others for funerary purposes as miniature symbolic deposits which are known as “votive miniatures”.
Small size bowls with remnants of yellowish paint on the exterior were discovered, as well as many small-sized alabaster and pottery vessels, the remains of a circular metal mirror, human and animal bones, and several pottery fragments representing Late Period amphorae. There were also inscriptions on limestone that may be funerary plates to tomb owners dating back to the end of the Sixth Dynasty.
Within the framework of the project, more than 300 cemeteries in the area were documented. It stretches from Nag Al-Sheikhs in the south to Al-Kharandariyah in the north.
People buried here are thought to have been elites in the nearby administrative center of Akhmim. It is expected that more graves will be uncovered before the project is completed.
Source: Ahram Online