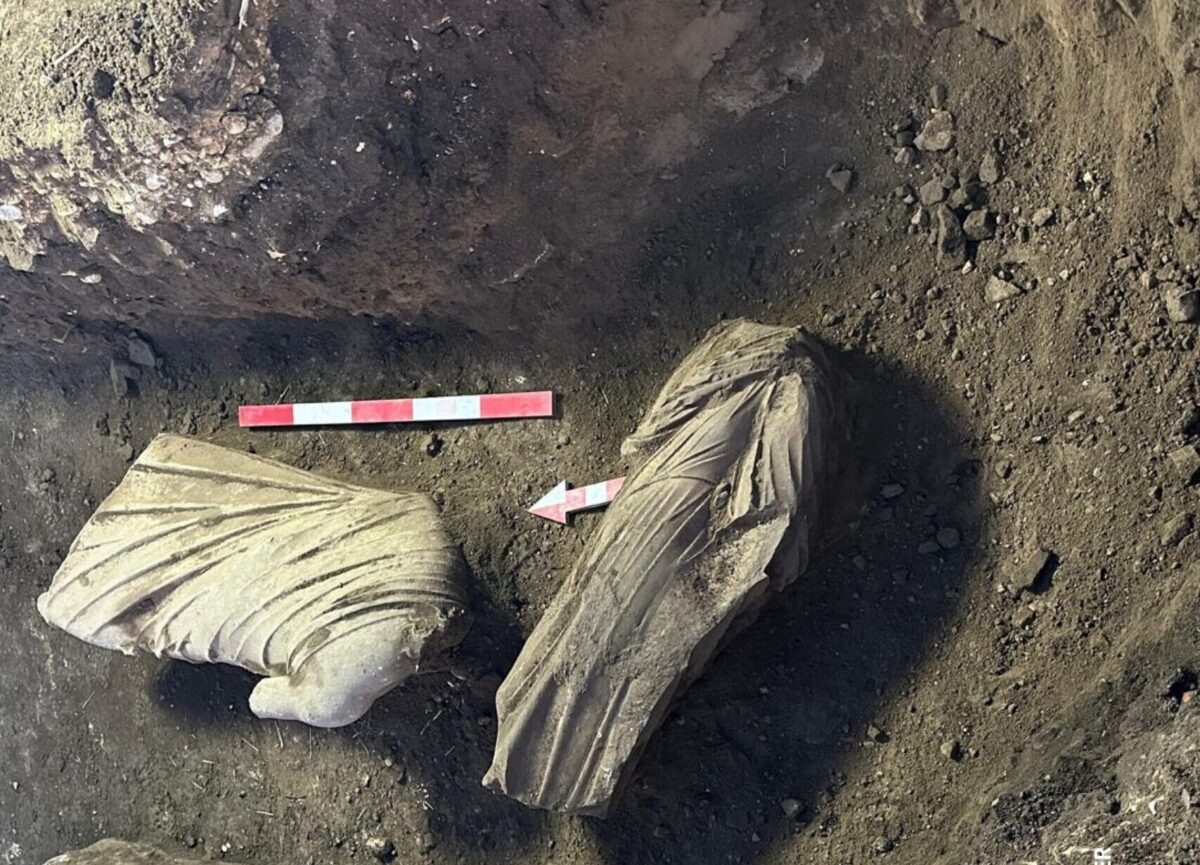
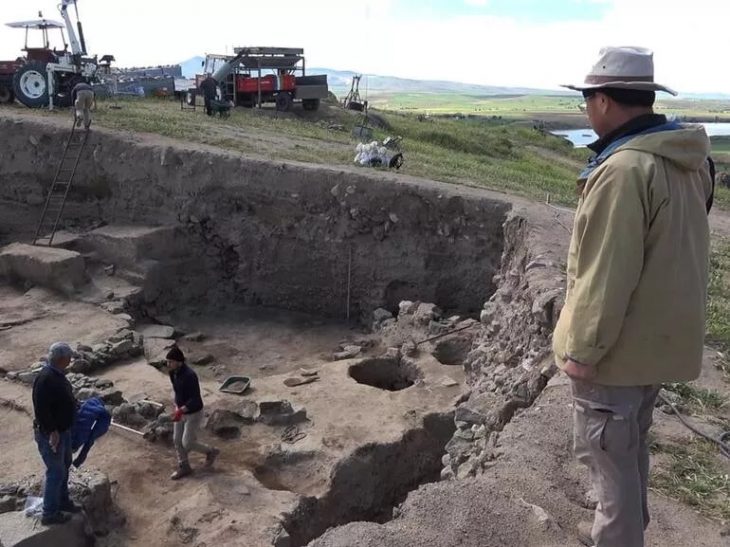
During the excavations in the ancient city of Perge in Antalya, one of the most organized Roman cities of Anatolia, five different statues were unearthed.
Perge is an ancient city located in the Antalya province of modern-day Turkey, approximately 15 kilometers east of the city of Antalya. Founded in the Hellenistic period, around the 3rd century BC, Perge became an important center of commerce and culture in the region. The city was initially settled by the Pamphylian people and later came under Roman control in the 1st century BC. The ancient city has been on the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List since 2009.
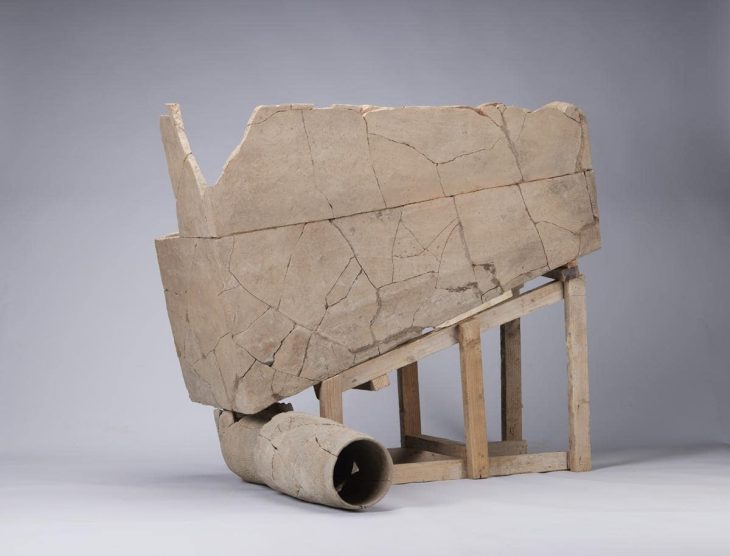
Recent excavations in the ancient city of Perge have unveiled remarkable statues that shed light on the region’s artistic heritage. Among the discoveries is a statue of Aphrodite, approximately 2 meters tall, depicted sitting on a dolphin alongside the god of love, Eros. Initial examinations suggest that this statue is a replica dating back to the 2nd century AD during the Roman Imperial Period.
Adjacent to the Aphrodite statue, another significant find is a 1.87-meter tall statue of a clothed woman standing upright. Preliminary assessments indicate that this statue exhibits characteristics from the Severan Period. Additionally, within the same area, another clothed female statue with similar features was discovered in two separate pieces.
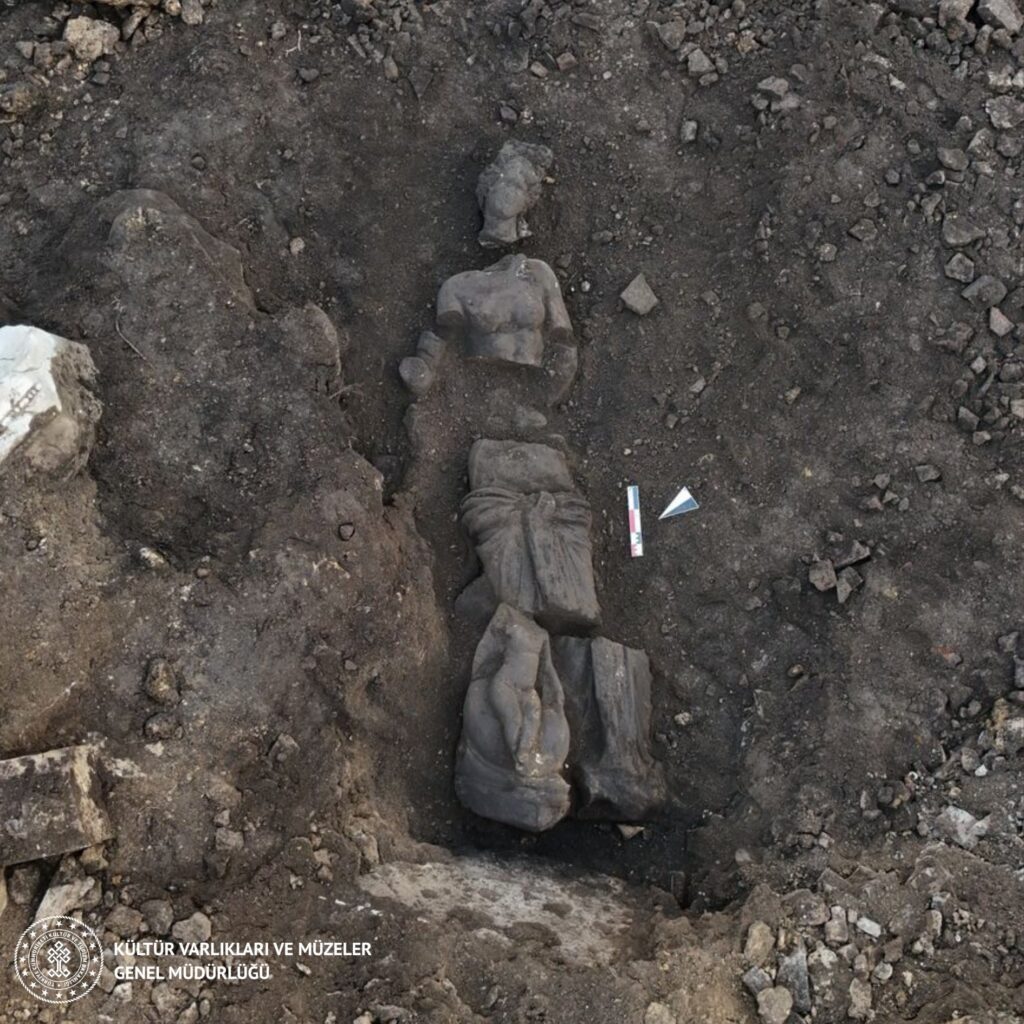

During the excavation works on the Eastern Street of the city, a clothed female statue and a clothed male statue were found side by side, marking them as the other two notable artifacts. These discoveries provide new insights into Perge’s sculptural tradition and contribute to our understanding of the social structure and artistic production processes of the time.
Roman Imperial art, flourishing from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD, is characterized by its grand scale, realism, and a blend of influences from earlier Greek and Etruscan traditions. This period saw the emergence of monumental architecture, intricate sculptures, and detailed frescoes that celebrated the power and achievements of the Roman Empire. Artists focused on portraying human figures with a high degree of realism, often emphasizing individual features and expressions.
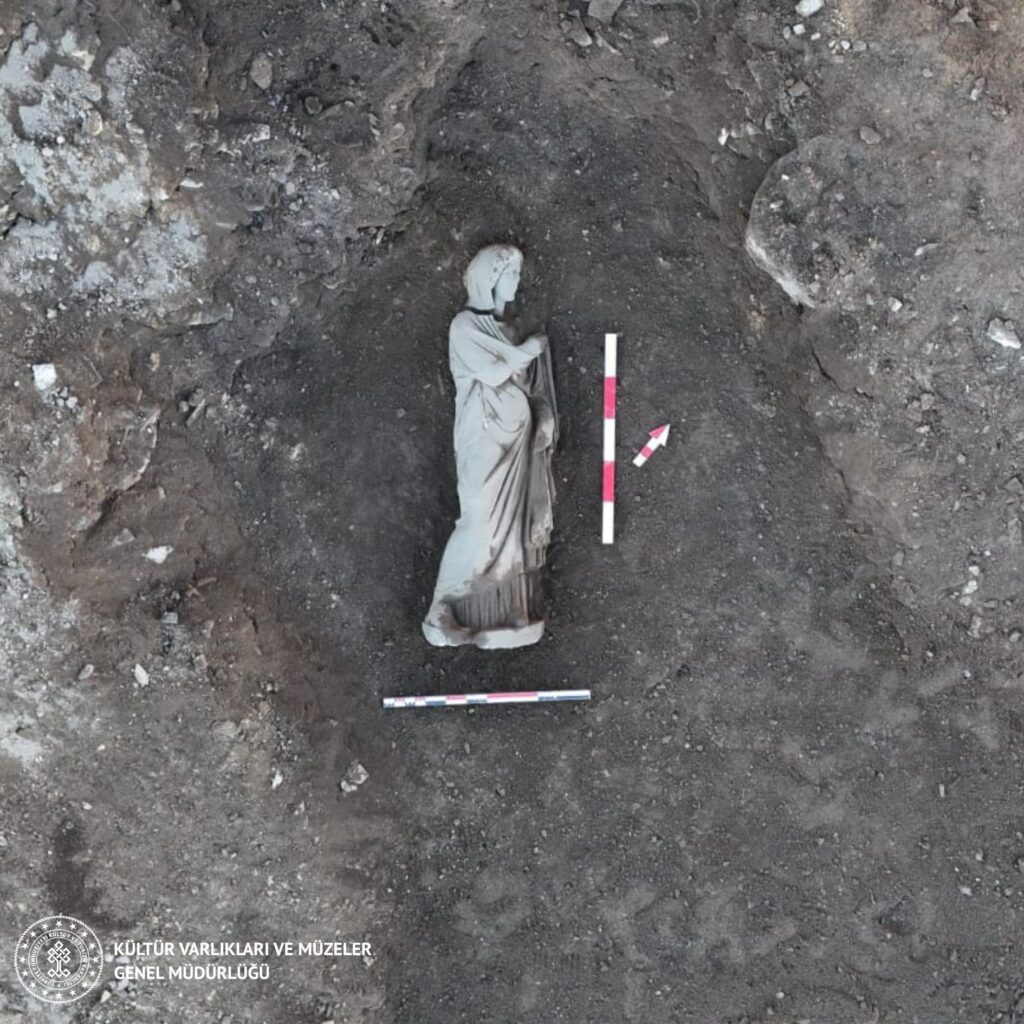

The ancient city of Perge, located in modern-day Türkiye, serves as a significant example of Roman Imperial art. Renowned for its well-preserved ruins, Perge showcases a rich artistic heritage that reflects the cultural and social dynamics of the time. The city is home to numerous sculptures, including depictions of gods, goddesses, and everyday life, which highlight the artistic techniques and styles prevalent during the Roman era. The recent discoveries of statues, such as those of Aphrodite and other figures, further illustrate the city’s role as a center of artistic production and its connection to the broader trends of Roman Imperial art.
Through these artifacts, we gain valuable insights into the aesthetic values, religious beliefs, and social structures of the Roman Empire, as well as the unique contributions of Perge to this rich artistic tradition.
The excavations in Perge are being conducted as part of the ‘Heritage to the Future Project,’ aimed at preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of the region.
Türkiye Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums
Cover Image Credit: Türkiye Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums