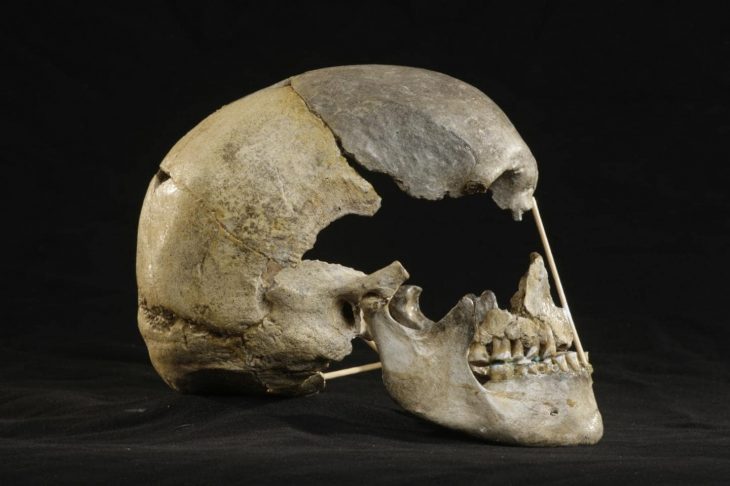
Archaeologists have recently unearthed a massive stockpile of weapons near Hedensted, Denmark, buried 1,500 years ago by an ancient chief. In addition to many weapons and unique chainmail, fragments of a Roman helmet from the 4th century have also been found.
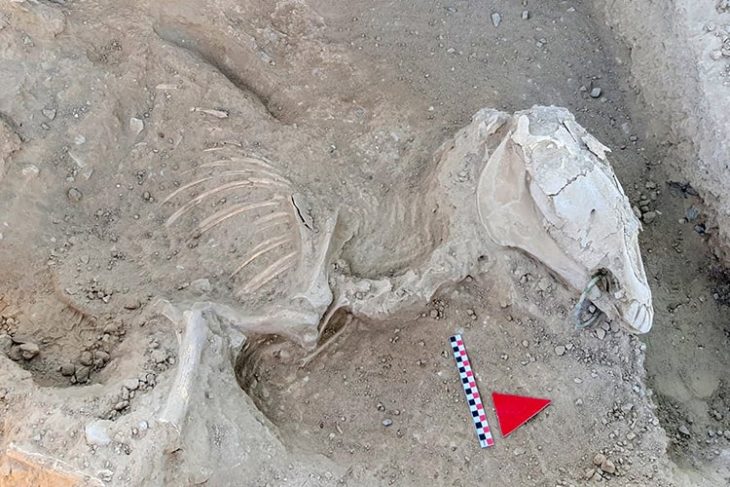
During recent archaeological excavations at Løsning Søndermark in Hedensted, Denmark, a significant discovery has been made that sheds light on the region’s Iron Age history, dating back 1,500 to 2,000 years. Archaeologists unearthed a burial site containing an extensive array of weapons, sufficient to equip a small army, alongside a remarkable chainmail shirt and other valuable artifacts. This find suggests that the site belonged to a powerful chieftain, and the manner of the burial indicates that these war implements may have been offered to higher powers.
The excavation was prompted by the Danish Road Directorate’s ongoing project to expand the motorway to three lanes, leading to the unearthing of these extraordinary artifacts just northwest of Hedensted, situated between Vejle and Horsens.
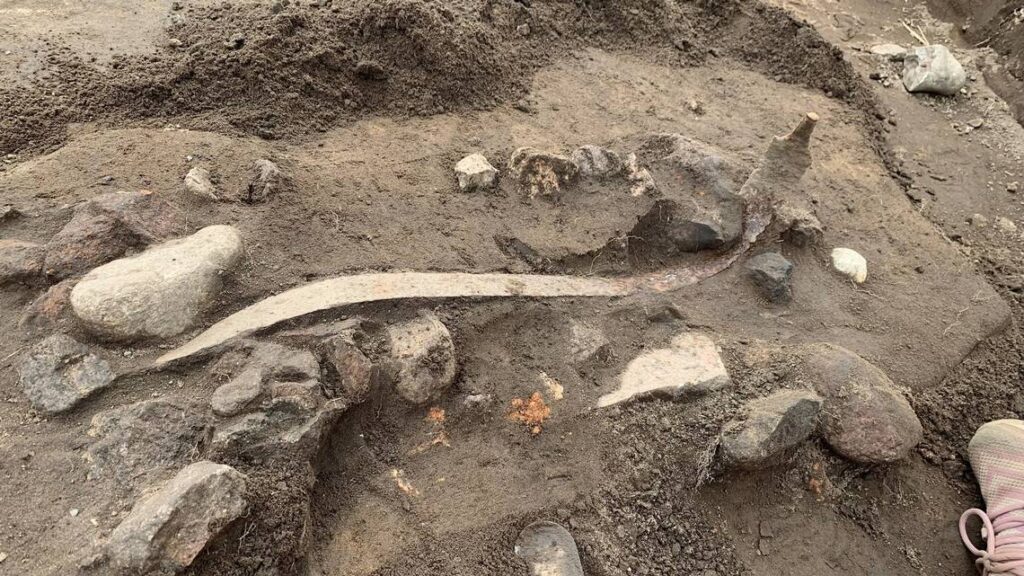

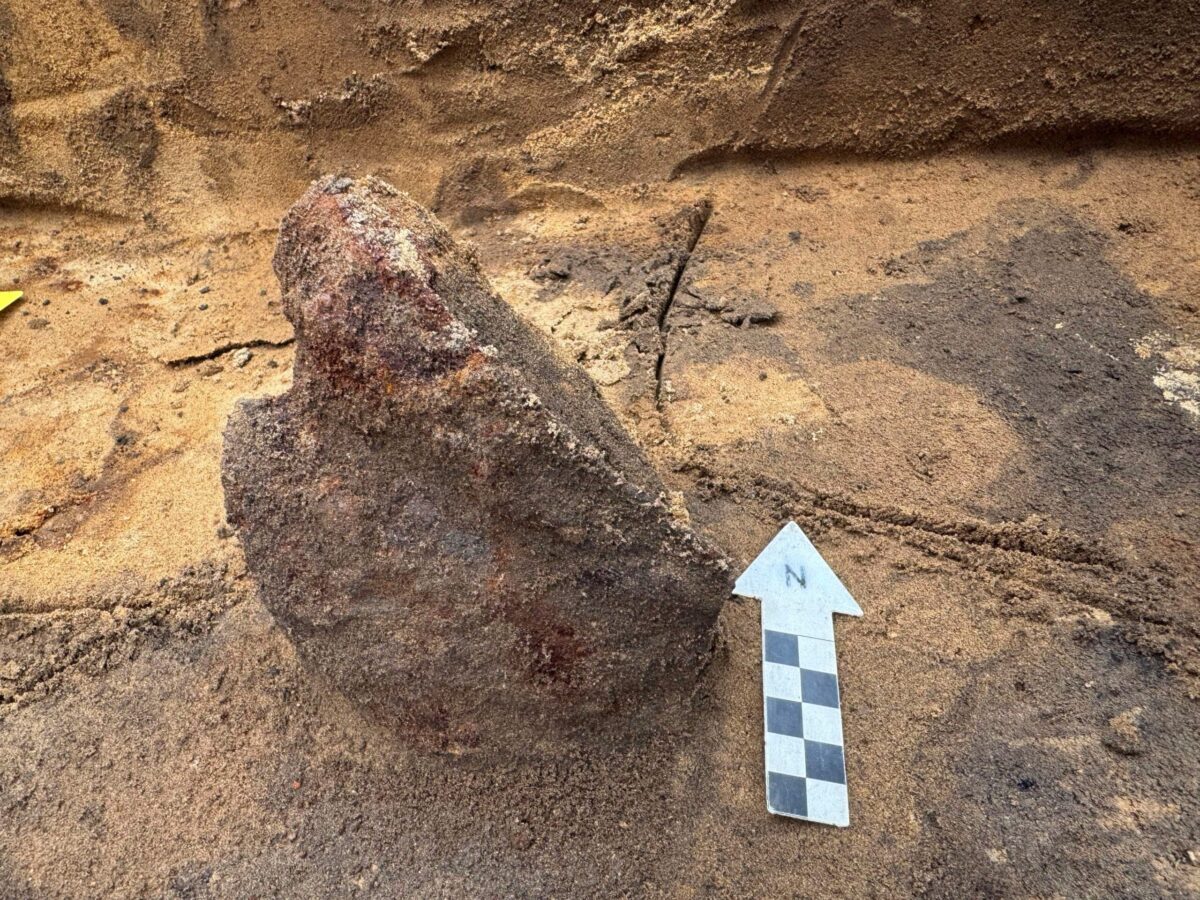
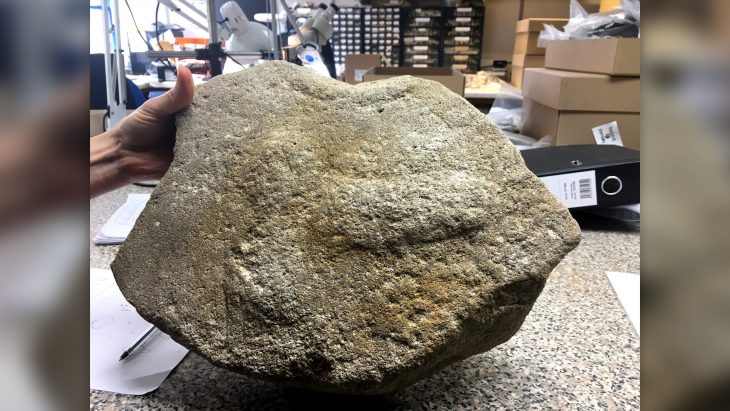
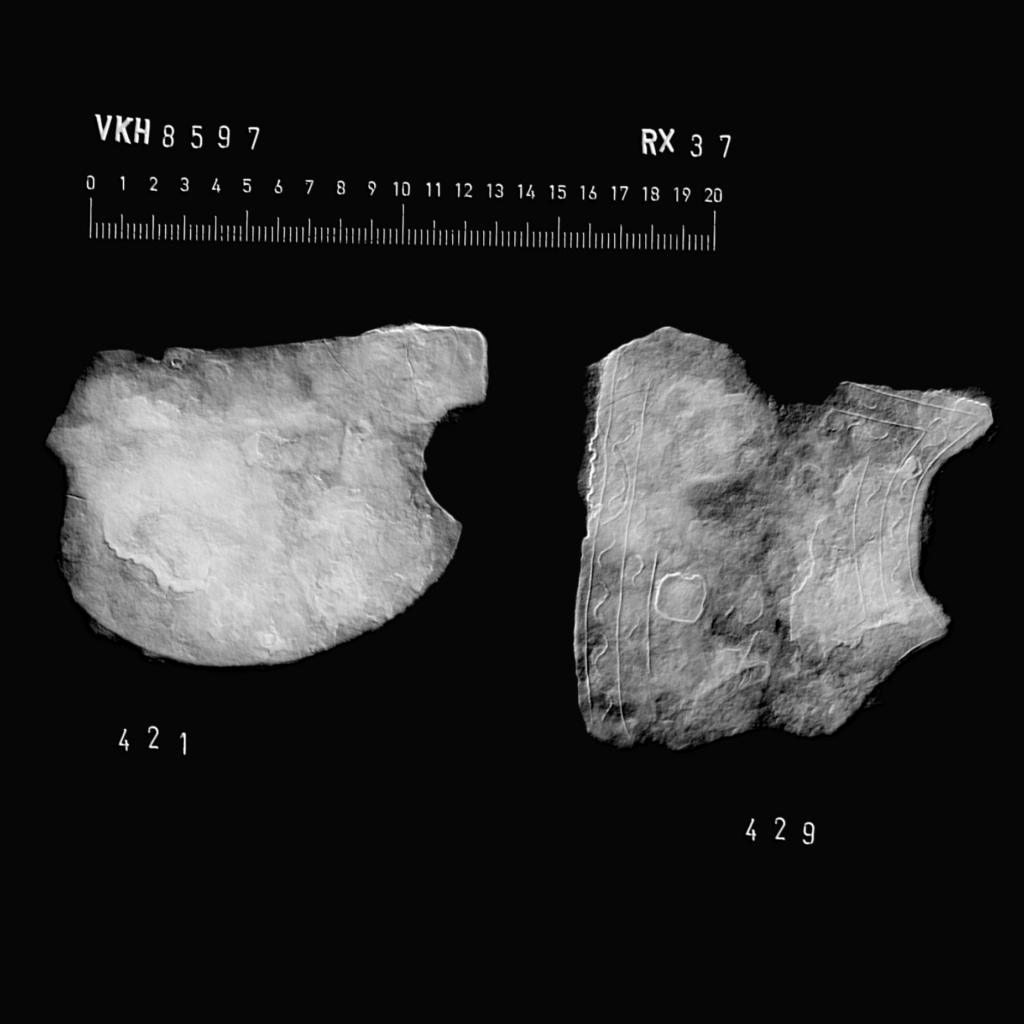
In addition to the extensive weapon deposits, archaeologists have discovered two unusual iron plates, each approximately the size of a human palm. Initially, the origins of these plates were uncertain. However, through the application of X-ray imaging technology, conservators and archaeologists were able to penetrate the thick layers of rust that obscured the objects.
The imaging results revealed an extraordinary and rare discovery: the remnants of a Roman helmet. The two plates identified consist of a neck guard and a intricately decorated cheek guard, which are components of a crest helmet—a type commonly utilized during the 4th century within the Roman Empire.
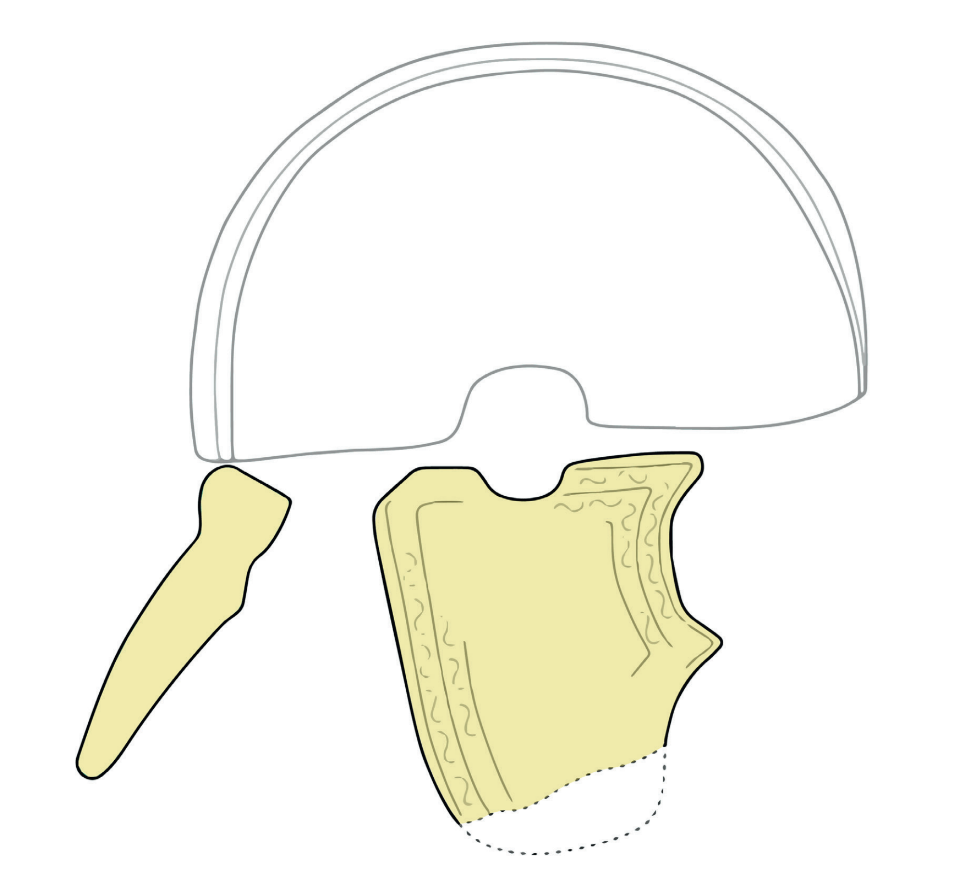
Finds of Roman helmets from the Iron Age are exceptionally uncommon in southern Scandinavia, and this particular discovery lacks direct parallels within the region. The few comparable artifacts have been located at Thorsbjerg Moor in Schleswig, as well as in southern Sweden and Gotland, with no similar finds recorded in Denmark itself.
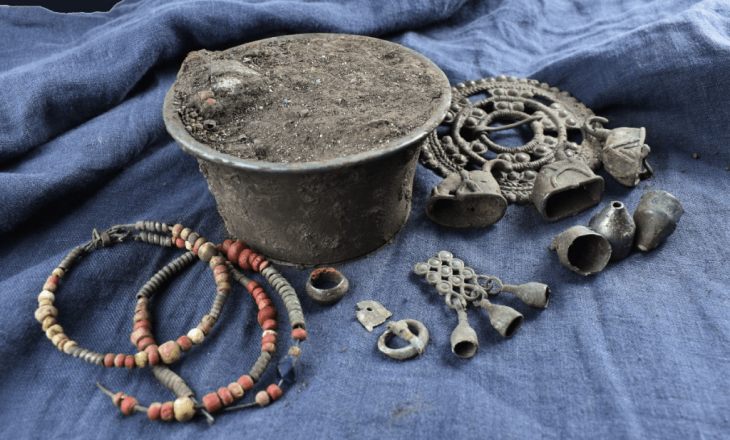
In addition, a chainmail shirt was discovered at Løsning Søndermark. Only a very small number of chainmail shirts from the Iron Age have been found in the southern Scandinavian region. Notably, the chainmail unearthed at Løsning Søndermark is particularly remarkable as it is the first instance found in association with a settlement, rather than being recovered from a burial site or bog.
The production of chainmail required specialized expertise, access to resources, and a considerable, sustained effort. Consequently, these expensive pieces of armor were owned exclusively by the highest echelons of the warrior elite in society, underscoring their status and importance.
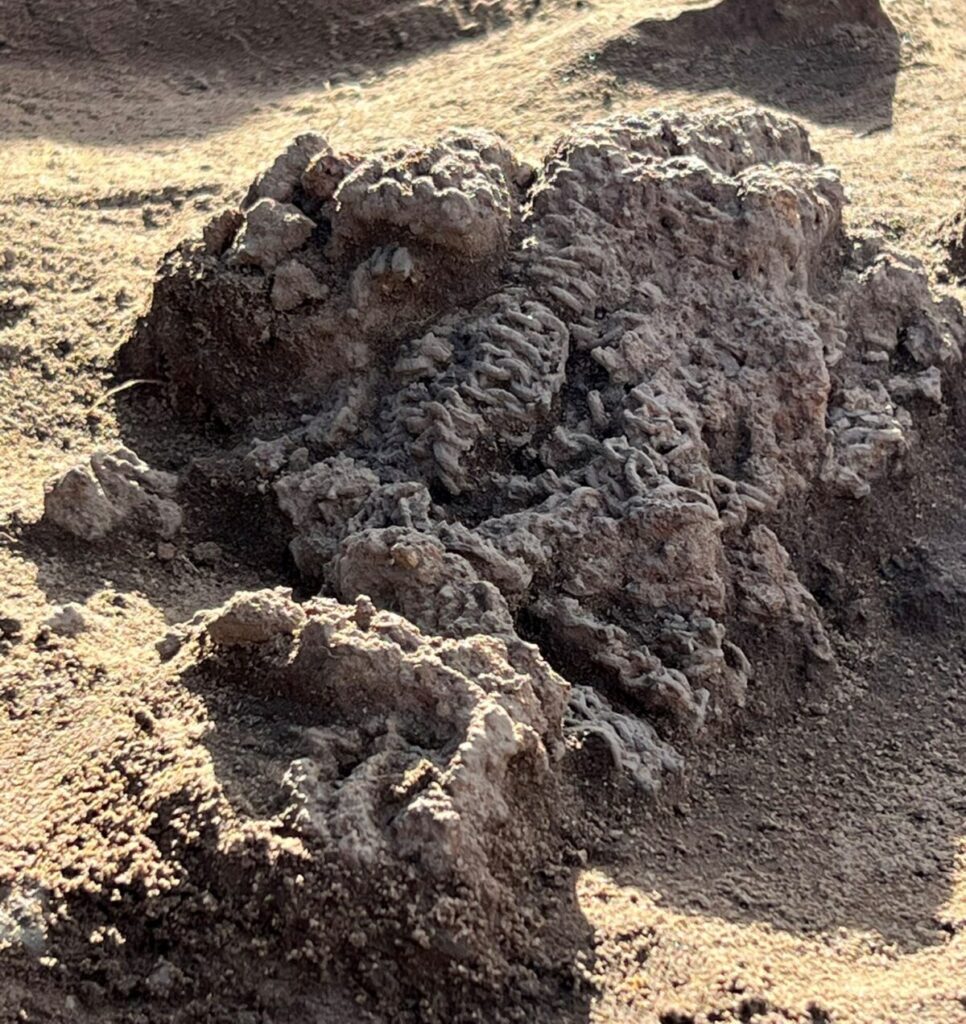

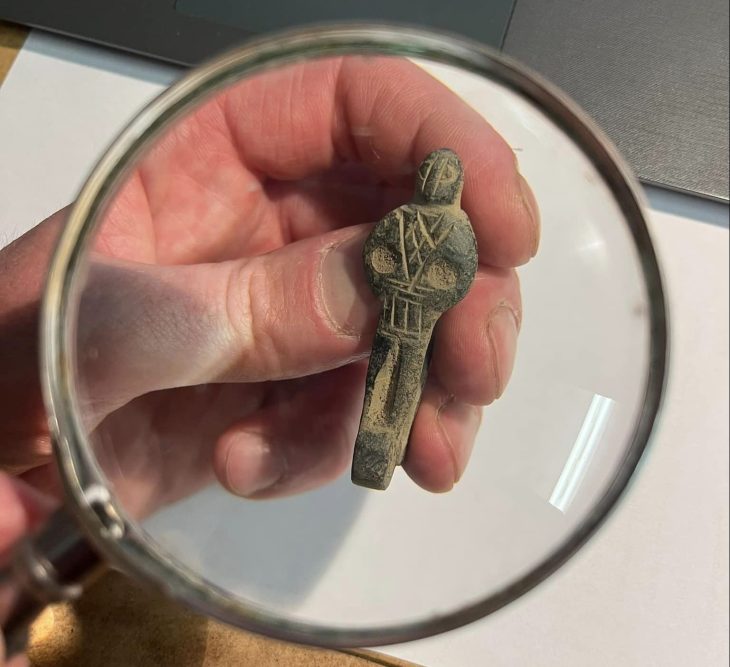
In addition to the extensive weapon sacrifice, archaeologists have uncovered fragments of two highly distinctive bronze neck rings at the Løsning Søndermark site. These rings exhibit striking similarities to imagery found on gold bracteates from the Vindelev Hoard, as well as other representations of Iron Age rulers.
The motif of a ring-bearer holding an oath ring in one hand, symbolizing power and influence, is a well-established theme in Nordic imitations of Roman gold medallions and gold bracteates. It is likely that the rings discovered at Løsning Søndermark served a similar function and may have been integral to the chieftain’s personal equipment, alongside the chainmail, sword, horse gear, and other military items that were part of the sacrificial offerings.
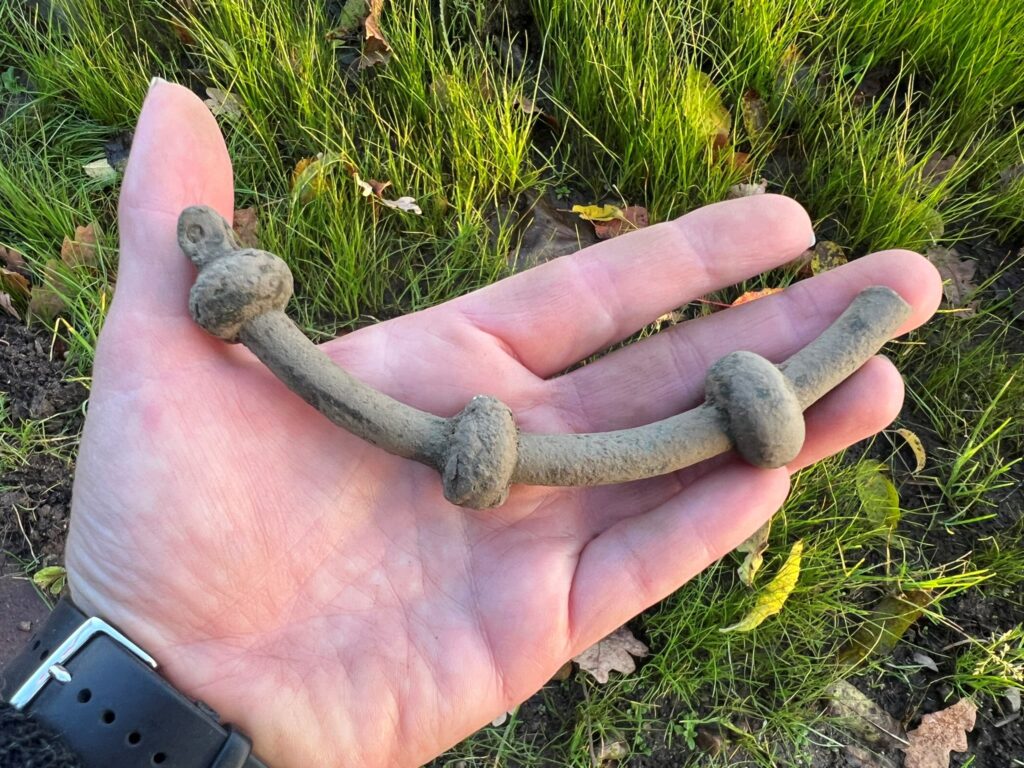

Notably, the ring-bearer depicted on the Vindelev bracteates is also adorned in a garment featuring an unusual pattern, which may represent chainmail akin to that found at Løsning Søndermark.
Starting Saturday, February 8, 2025, selected items from this remarkable find, including fragments of a Roman helmet, will be exhibited at the Cultural Museum in Vejle, providing the public with an opportunity to engage with Denmark’s rich archaeological heritage.
Cover Image Credit: Vejle Museums