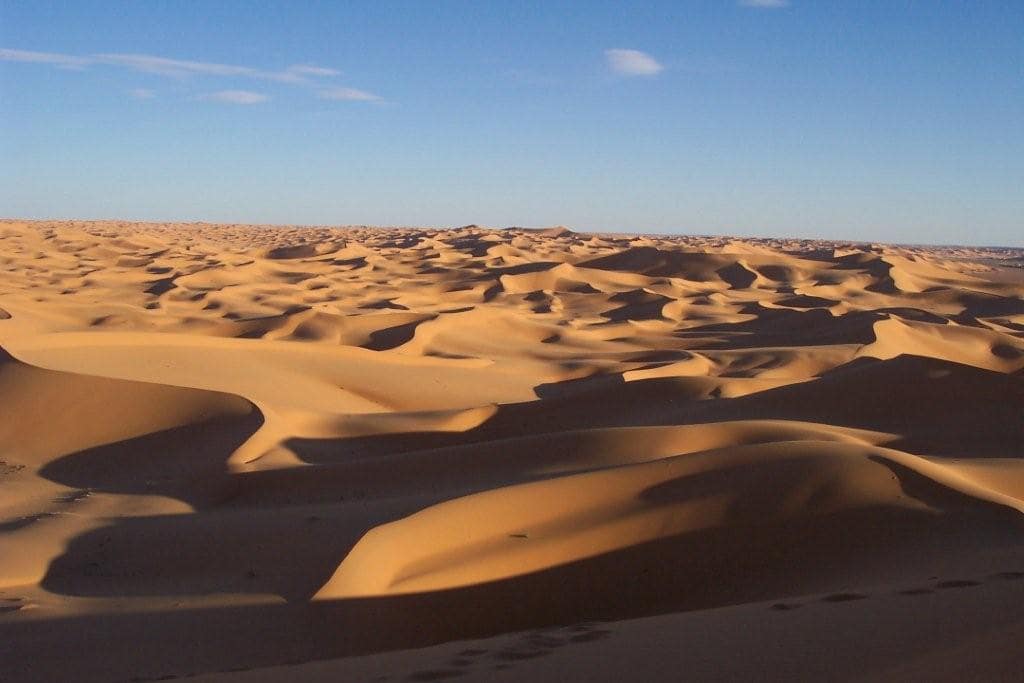
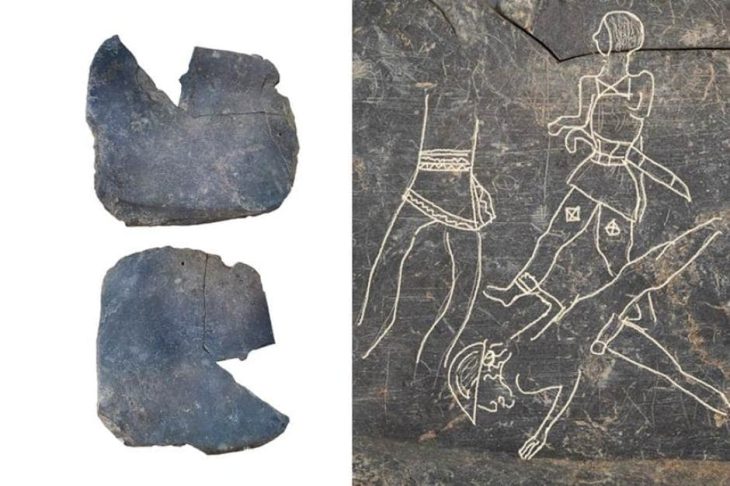
A team of researchers at Khalifa University in Abu Dhabi has developed a machine-learning algorithm to help them trawl vast tracts of the Rub al-Khali, or ‘Empty Quarter’— a desert spanning 250,000 square miles on the Arabian Peninsula.
Recently, artificial intelligence has emerged as a groundbreaking tool for uncovering hidden archeological treasures in the region, revolutionizing the field of desert archeology.
The desert is home to the site of Saruq Al-Hadid, which holds evidence of 5,000 years of human activity. The team used data from this site to train their algorithm to identify additional possible excavation sites in the vicinity.
Traditional ground surveys are challenging and expensive in the desert, and dune patterns and sandstorms have proven to be obstinate challenges for satellite imagery interpretation. The algorithm can analyze images obtained using synthetic aperture radar (SAR), a powerful radar system capable of penetrating sand and vegetation, allowing researchers to see hidden structures beneath the surface.
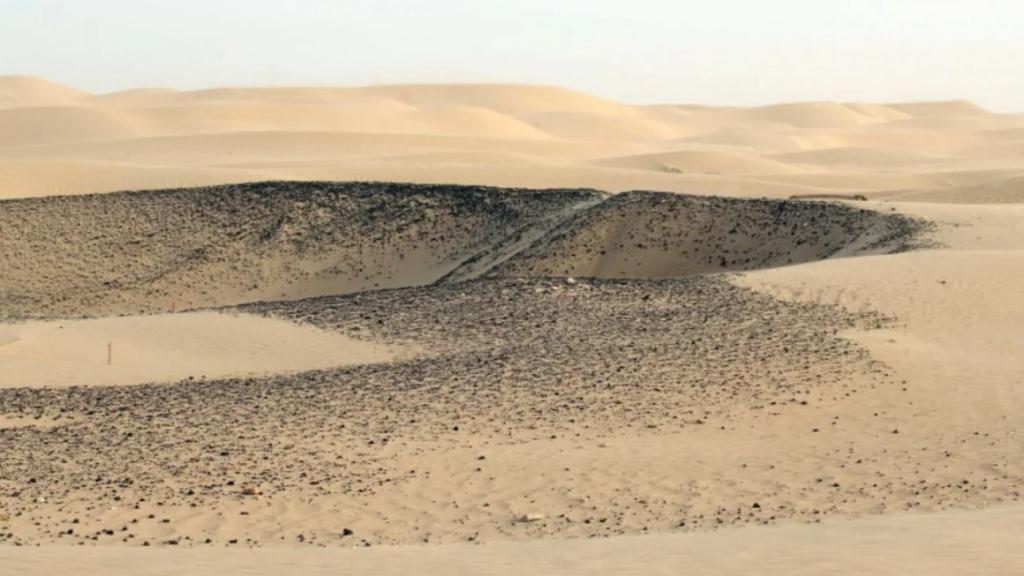

Satellite-borne SAR, which can cover a larger area than is feasible from the ground, was employed by the archaeologists. The team also used radar to perform a ground survey to replicate the satellite’s findings, thanks to funding from Dubai Culture, the government agency in charge of Saruq Al-Hadid. Both technologies are not new: machine learning has been gaining popularity in archaeology, and SAR imagery has been around since the 1980s.
But the use of the two together is a novel application, says Diana Francis, an atmospheric scientist and one of the lead researchers on the project., and to her knowledge, is a first in archaeology.
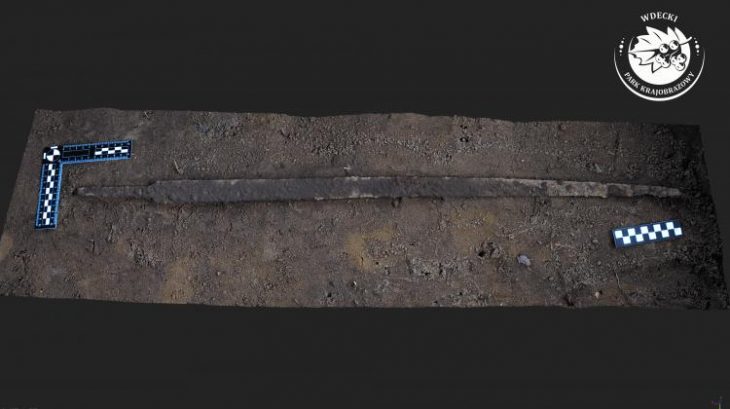
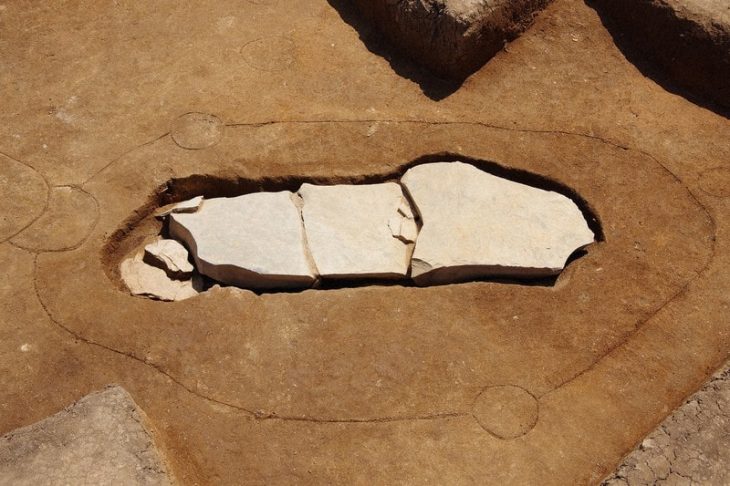
Through the use of machine learning and deep learning techniques, the team has developed an algorithm that can automatically detect features in the landscape with an accuracy of within 50 cm and generate 3D models of the expected structure.
Now, Dubai Culture plans to excavate the newly identified areas — and Francis hopes the technique can uncover more buried archaeological treasures in the future.
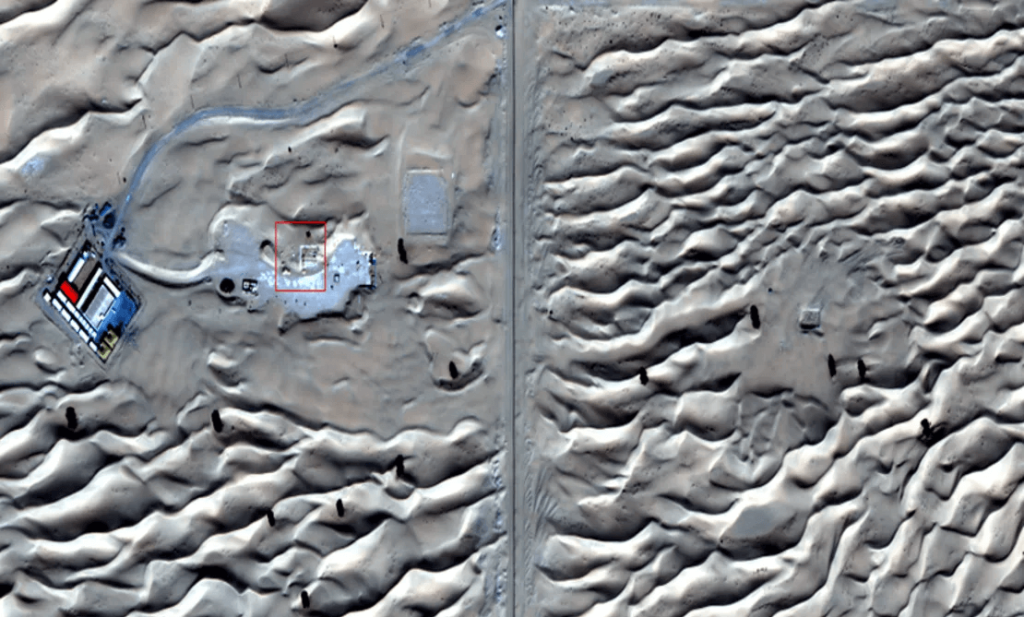

If the project is successful, it will expand the use of artificial intelligence in archaeology. The Arabian Peninsula is not the only place where artificial intelligence is being used in archaeology. For instance, A.I. demonstrated its worldwide potential in archaeological exploration when it helped uncover four new Nazca petroglyphs in Peru.
Some experts have urged caution against “over-reliance” on the technology, however. Hugh Thomas, an archaeology lecturer at the University of Sydney, told CNN that there remains nothing better than a “trained archaeological eye” to detect sites.
DOI:10.3390/geosciences13060179
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia Commons